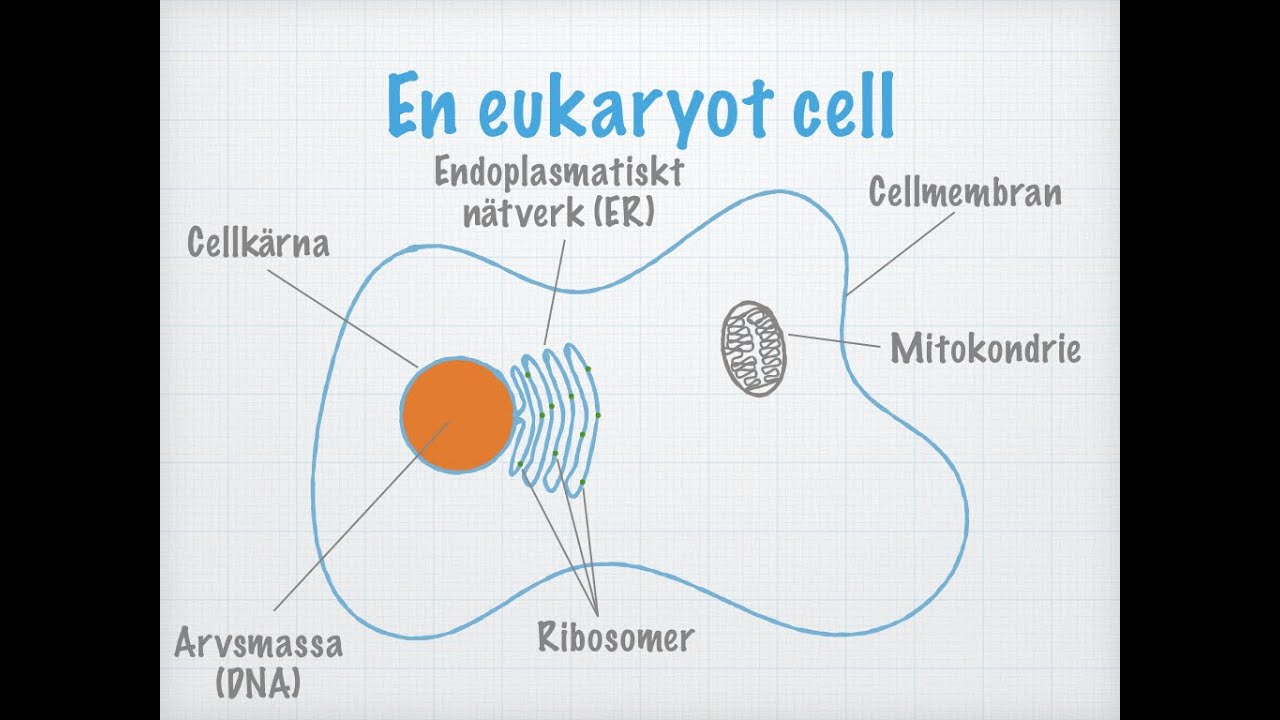
Biochemistry and Clinical pathology Chapter 1 | Cell and it's biochemical organization #biochemistry
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the role of key biomolecules in living organisms, focusing on proteins, DNA, RNA, carbohydrates, lipids, and micromolecules. It details how DNA carries genetic material and RNA facilitates protein synthesis. The video also covers the energy storage and release functions of carbohydrates (glycogen) and lipids, emphasizing their roles in short-term and long-term energy needs. The explanation of micromolecules like amino acids and monosaccharides is also highlighted. The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to subscribe, like, and join a Telegram group for further learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 Proteins are made up of amino acids and play essential roles in forming structures and performing various biological functions.
- 😀 DNA is a complex molecule made of nucleotides and carries genetic material, ensuring inheritance from parents to offspring.
- 😀 RNA, made from ribonucleotides, helps in protein synthesis by carrying information from DNA to make proteins.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are made of monosaccharides and are an important energy source, stored as glycogen and converted to glucose when needed.
- 😀 Lipids are complex biomolecules made of fatty acids and serve as a long-term energy source for the body.
- 😀 Proteins are crucial for various functions in the body, including enzyme activity, structural support, and signaling.
- 😀 The process of inheritance involves the transfer of genetic material from parents to children, as carried by DNA.
- 😀 Carbohydrates fulfill short-term energy needs, while lipids are essential for long-term energy storage.
- 😀 Lipids start breaking down into energy once carbohydrate stores are depleted, providing energy during prolonged fasting or lack of food.
- 😀 Micromolecules like amino acids and monosaccharides are smaller and simpler, while macromolecules like proteins and carbohydrates are more complex and perform critical biological functions.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to engage with educational content by liking, subscribing, and joining a community for further learning and resources.
Q & A
What are proteins made of, and what role do they play in the body?
-Proteins are made up of amino acids. They play a crucial role in forming structures within the body and performing various functions, such as enzyme catalysis, transport, and immune defense.
How does DNA contribute to inheritance?
-DNA carries genetic material that is passed from parents to their offspring. This inheritance process determines traits and genetic characteristics, such as physical features and other inherited qualities.
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
-RNA plays a major role in protein synthesis by carrying genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are made. It acts as a messenger and directs the assembly of amino acids into proteins.
How are carbohydrates stored and utilized for energy?
-Carbohydrates are stored in the body as glycogen, primarily in the liver and muscles. When needed for energy, glycogen is converted to glucose, which is then used by the body to produce immediate energy.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term energy sources?
-Carbohydrates are the primary short-term energy source, providing immediate energy needs. Lipids, on the other hand, serve as a long-term energy reserve, being stored as fat and converted to energy when carbohydrates are depleted.
How do lipids contribute to energy storage and utilization?
-Lipids are stored in the body as fat and act as the second major source of energy. When carbohydrates are exhausted, lipids are broken down to release fatty acids, which are used for long-term energy needs.
What are micromolecules, and how do they differ from macromolecules?
-Micromolecules are smaller molecules, such as amino acids and monosaccharides, while macromolecules are larger, more complex molecules, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
What is the building block of DNA, and how does it relate to its function?
-The building block of DNA is the nucleotide. Nucleotides link together to form the DNA structure, which carries genetic information essential for heredity and cellular functions.
Why is glycogen important for short-term energy?
-Glycogen is important for short-term energy because it serves as the body's reserve of glucose. When quick energy is needed, glycogen is converted into glucose and released into the bloodstream for immediate use.
How do proteins function beyond structure in the body?
-Proteins also act as enzymes, catalysts for biochemical reactions, hormones that regulate various body processes, and antibodies that help protect the body from infections and diseases.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)