Lec 11: Data Types in C++ - part 2 | float Data Type | C++ Tutorials for Beginners
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to understanding floating-point data types in C++, focusing on `float`, `double`, and `long double`. It covers their precision, range, and how to properly declare and print them using the `setprecision` function. Viewers are encouraged to practice their understanding through coding challenges, which help solidify knowledge and improve programming skills. The video also touches on advanced topics like floating-point representation and offers coding contest opportunities for further learning and practice.
Takeaways
- 😀 The `float`, `double`, and `long double` are the main floating-point data types in C++.
- 😀 `float` uses 4 bytes of memory and has up to 7 significant digits of precision.
- 😀 `double` uses 8 bytes of memory and provides up to 15 significant digits of precision.
- 😀 `long double` offers even greater precision (up to 18 significant digits) and uses 12 bytes of memory.
- 😀 To print floating-point numbers with more precision, use the `setprecision()` function from the `<iomanip>` library.
- 😀 The `f` suffix is used for `float` numbers, while `long double` is a standalone type that doesn’t require a suffix.
- 😀 Precision settings can be adjusted in C++ using the `fixed` and `setprecision()` functions for formatting output.
- 😀 The range of values for each type: `float` (−3.4e38 to 3.4e38), `double` (−1.7e308 to 1.7e308), and `long double` varies based on the compiler.
- 😀 Scientific notation is commonly used for very large or very small numbers (e.g., 1.2e+4 for 12000).
- 😀 Geeks4Gigs is hosting a summer challenge focused on Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA), with weekly contests and prizes like smartwatches and tablets.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The video discusses floating-point data types in C++, specifically the `float`, `double`, and `long double` types, their precision, range, and practical use cases.
What is a floating-point number, and how is it used in C++?
-A floating-point number is a number that can represent both integer and fractional values. In C++, floating-point numbers are used to store decimal values and are represented by the `float`, `double`, and `long double` data types.
What is the precision of a `float` data type in C++?
-The `float` data type in C++ has a precision of 7 digits. This means it can represent numbers with up to 7 significant digits accurately.
How does the precision of a `double` differ from a `float`?
-A `double` data type has a higher precision than a `float`. While `float` can handle 7 digits of precision, `double` can represent numbers with up to 15 digits of precision.
What is the range of values that a `float` data type can hold?
-The `float` data type can represent values ranging from approximately `-3.4e+38` to `+3.4e+38`.
What does the `long double` data type offer compared to `float` and `double`?
-The `long double` data type provides the highest precision and range. It can hold values with up to 18 digits of precision, making it suitable for calculations that require very high accuracy.
What is the role of `setprecision()` in C++ when working with floating-point numbers?
-`setprecision()` is used in C++ to control the number of digits displayed after the decimal point when printing floating-point numbers. It allows you to adjust the output precision for different data types.
Why is it important to choose the correct floating-point data type for a task?
-Choosing the correct floating-point data type ensures that the calculations are accurate and efficient. For tasks requiring high precision, `double` or `long double` should be used, while `float` is appropriate for less demanding tasks with lower precision requirements.
What does adding an `f` after a number mean in C++?
-In C++, adding an `f` after a number signifies that the value should be treated as a `float` type. For example, `3.14f` indicates that the value is a `float` rather than a `double`.
How does the output precision of floating-point numbers differ from their actual precision in memory?
-The output precision of floating-point numbers, controlled by `setprecision()`, may differ from their internal precision in memory. For example, a `double` has 15 digits of precision internally, but the output can be limited to fewer digits based on the precision setting.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

03 - Programação em Linguagem C - Tipos Básicos (int, float, char, etc.)
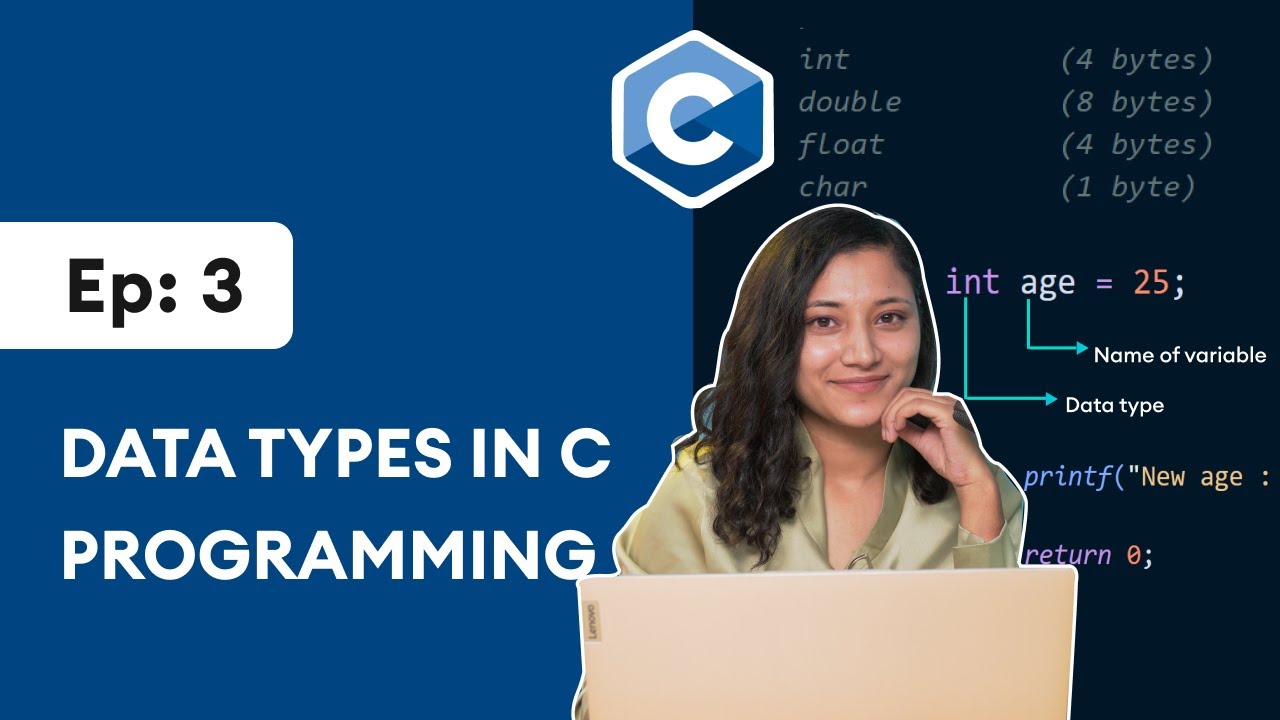
#3: Data Types in C Programming | C Programming for Beginners
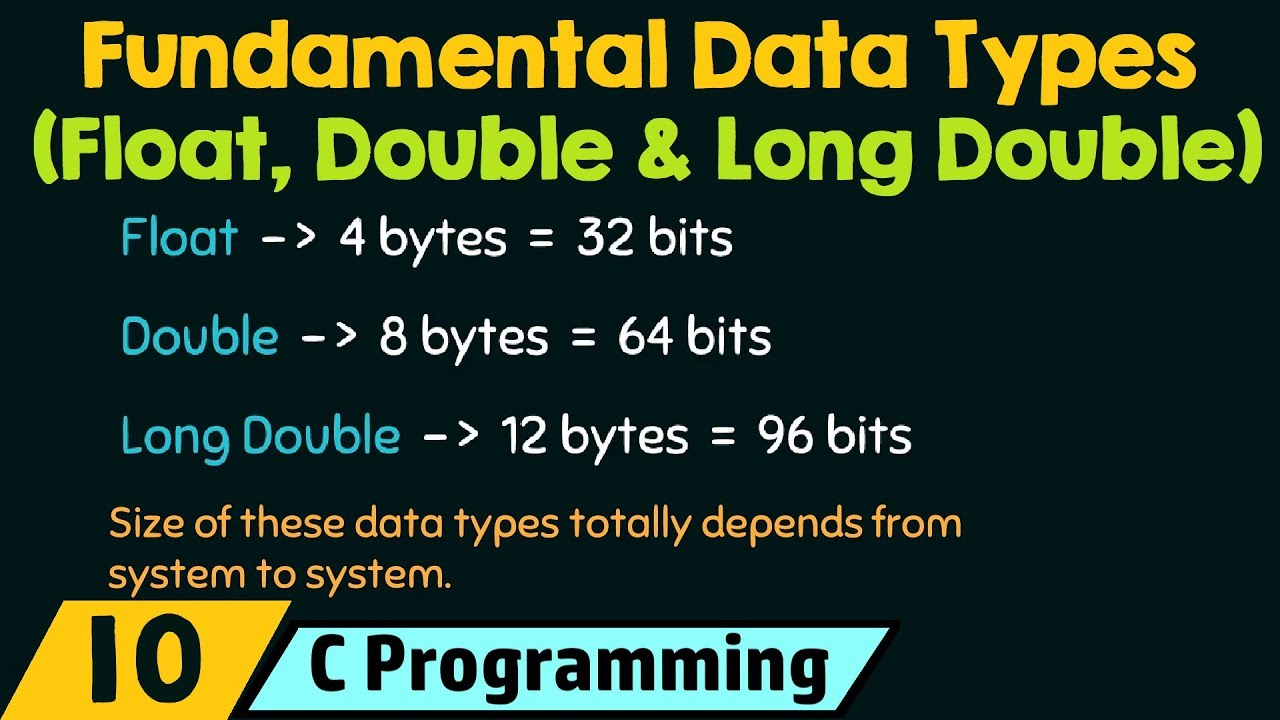
Fundamental Data Types − Float, Double & Long Double

#6 Data types in Java

C++ 03 | Tipe Data pada Pemrograman C++ | Tutorial Dev C++ Indonesia

Primitives Data Types In Java - All the Primitives And What They Do
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
