2021 04 05 IPP 3 2 Sensor Transmitter
Summary
TLDRThis lecture focuses on the fundamentals of sensors and transmitters, explaining their roles in measuring process variables like temperature, pressure, and flow. It delves into the different types of output signals (pneumatic, electrical, and digital) and the importance of key parameters such as range, span, and zero. The relationship between the transmitter output and the process variable is often linear, though it can be nonlinear in some cases. The lecture also explores signal conversion (analog to digital and vice versa) and introduces the mathematical models used to describe these components in a process control system.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sensors produce a mechanical or electrical phenomenon to measure variables like temperature, pressure, and flow.
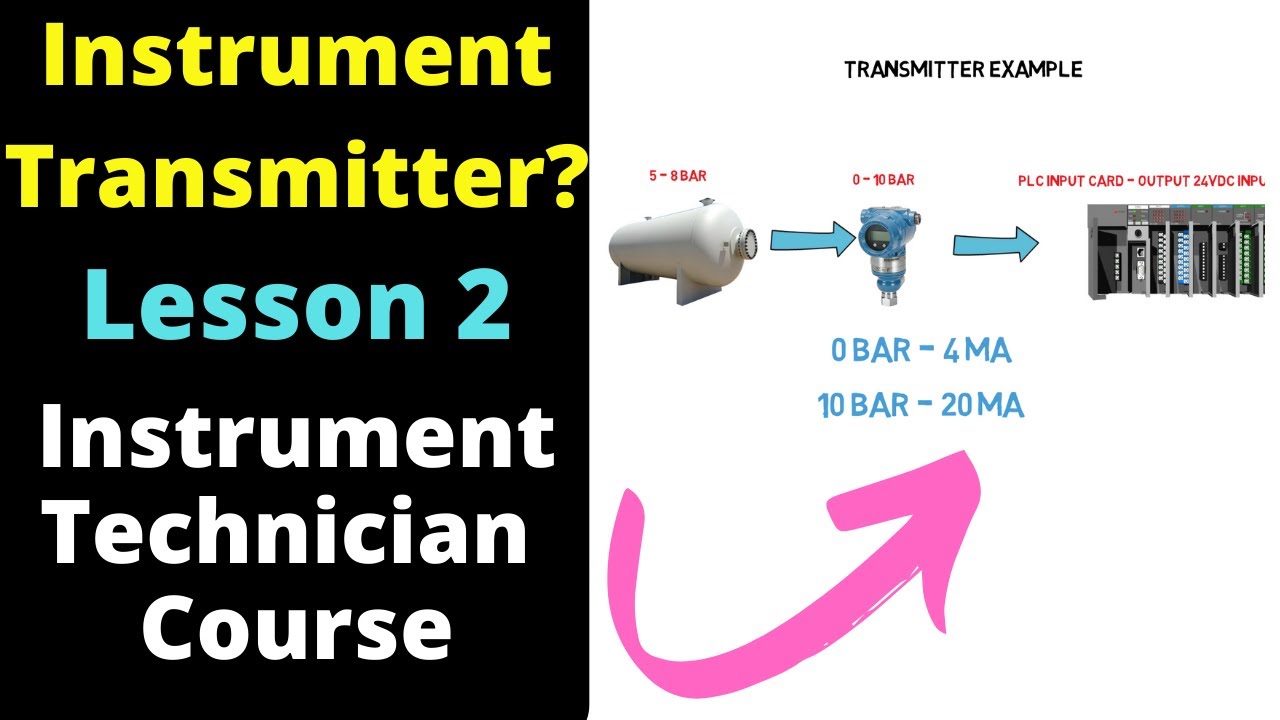
- 😀 Transmitters convert the sensor's measured phenomenon into a transmitted signal, which is sent to a controller.
- 😀 The ideal relationship between a transmitter output and the process variable is linear, where the transmitter output is proportional to the process variable.
- 😀 Three important terms in transmitter-sensor combinations are range (low to high value), span (difference between low and high values), and zero (the lowest value in the range).
- 😀 There are different signal types for sensors and transmitters, including pneumatic, electric (e.g., milliampere and voltage), and digital signals.
- 😀 Pneumatic signals are typically in the 3-15 psig range, while electric signals can be 4-20 mA, 1-5 V, and 0-10 V.
- 😀 Digital signals only have two values, 0 and 1, and are used for discrete data transmission.
- 😀 Transducers change the signal form (e.g., pneumatic to electric, or analog to digital) based on the required output type.
- 😀 Transmitter gain is the ratio of the change in output to the change in input. It helps determine how much the output changes relative to the input measurement.
- 😀 Some transmitter outputs may be non-linear, as seen in applications like differential pressure sensors used to measure volumetric flow rate.
- 😀 For simplification, the transfer function for sensor-transmitter models is often represented as a first-order model (K / (s + 1)), where 'K' represents the gain.
Q & A
What is the role of a transmitter in a sensor system?
-The transmitter's role is to convert the mechanical, electrical, or other types of signals from the sensor into a format that can be transmitted to the controller for processing.
What are the different types of output signals mentioned for transmitters?
-The three main types of output signals mentioned are mechanical, electrical (such as current or voltage), and digital (discrete signals with values 0 and 1).
How is the transmitter output signal ideally related to the process variable?
-Ideally, the transmitter output signal is linear and proportional to the process variable being measured, such as pressure or temperature.
What are the three important factors related to the combination of transmitter and sensor?
-The three important factors are range (the low and high values of the measured process variable), span (the difference between the high and low values), and zero (the lowest value of the range).
What is the difference between linear and nonlinear transmitter outputs?
-In linear systems, the transmitter output changes proportionally to the process variable, while in nonlinear systems, such as those using differential pressure sensors, the relationship between the output and the process variable is more complex and not directly proportional.
What is the significance of transmitter gain?
-Transmitter gain is the ratio of the change in output signal to the change in the input (process variable). It determines how sensitive the transmitter is to variations in the measured variable.
Can you explain the relationship between differential pressure sensors and volumetric flow rate?
-For differential pressure sensors, the relationship to volumetric flow rate is nonlinear, where the output signal is proportional to the square of the flow rate, requiring a more complex mathematical model to describe the behavior.
What is a transfer function, and how is it used in sensor-transmitter systems?
-A transfer function is a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the input (measured process variable) and the output (transmitter signal). It helps in predicting how the system behaves and is used for system design and control purposes.
What is the mathematical model for a first-order sensor-transmitter system?
-The mathematical model for a first-order sensor-transmitter system typically includes a time constant and a gain factor. It can be represented by a transfer function that models the system's dynamic response.
How do the different types of signals (analog, digital) impact the sensor-transmitter system?
-Analog signals, such as current and voltage, provide continuous data that is proportional to the measured variable, while digital signals provide discrete values (0 or 1) and are typically used for binary systems. The choice of signal type influences the complexity and precision of the measurement system.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Transmitter Explained | Types of Transmitters

What is a Sensor? Different Types of Sensors, Applications

1. Introduction - Process Control Instrumentation -
What is a Transmitter -Instrumentation Technician Course - Lesson 2

Pressure Sensor, Transducer, and Transmitter Explained | Application of Each

What Is Industrial Instrumentation? Start Here! 💡 Ep1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
