Plasmid DNA vector in gene cloning | plasmid vector | pbr322 vector | puc 19 vector
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the world of plasmid vectors, a crucial component in recombinant DNA technology. It explains plasmids as self-replicating, circular DNA molecules used for gene delivery and amplification, particularly in E. coli bacteria. The script highlights two common plasmid vectors, pBR322 and pUC19, discussing their naming, components, and functions. It further clarifies the distinction between cloning and expression vectors, the importance of insert size, and the features essential for a DNA molecule to serve as a vector. The advantages of plasmid vectors, such as ease of handling and high copy numbers, are contrasted with their limitations, mainly the maximum insert size they can accommodate.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Plasmid vectors are essential tools in recombinant DNA technology for gene delivery and amplification.
- 🔄 Plasmids are self-replicating, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules that can be used for cloning and expression purposes.
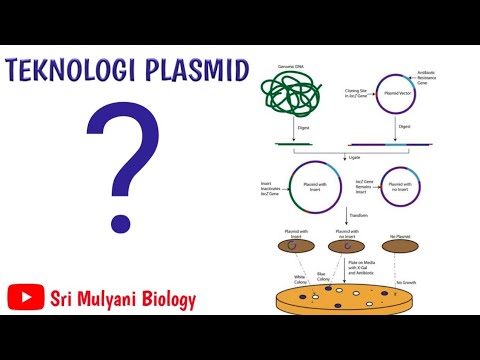
- 🔍 Plasmid vectors must have an origin of replication (ori), a multiple cloning site (MCS), and a selectable marker for successful cloning.
- 📏 Plasmid vectors typically have an insert size limitation, ranging from 5 to 25 kilobases (kb), depending on the vector type.
- 🚀 Two common plasmid vectors mentioned are pBR322 and pUC19, each with specific features and uses.
- 📦 Plasmids are advantageous due to their small size, ease of handling, and large copy numbers within host cells.
- 🔬 Plasmids are ideal for cloning small DNA fragments and can also be used for gene expression if equipped with a promoter region.
- 🛑 The main disadvantage of plasmid vectors is their limited insert capacity, which restricts the size of the target gene that can be cloned.
- 🔬 The script discusses the components of plasmid vectors, including origin of replication, selectable markers (often antibiotic resistance genes), and multiple cloning sites.
- 🔑 Selectable markers are crucial for distinguishing between recombinant and non-recombinant plasmids, aiding in the selection process.
- 🔬 The script also mentions the importance of the copy number of plasmids within a host cell, which can vary and affect the efficiency of cloning.
Q & A
What is a plasmid vector in the context of recombinant DNA technology?
-A plasmid vector is a self-replicating, circular double-stranded DNA molecule used as a vehicle to deliver and amplify a target gene within a host cell, commonly used in molecular cloning and gene expression.
What are the two main types of vectors mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of vectors mentioned are cloning vectors, which deliver the target gene into the host cell for amplification, and expression vectors, which allow the target gene to be transcribed and translated into a protein.
Why are plasmid vectors named with specific codes like pBR322 or pUC19?
-The names pBR322 and pUC19 are specific identifiers for particular plasmid vectors, which may reflect certain characteristics or features of the plasmid, such as its size, origin, or resistance markers.
What is the significance of the copy number in plasmid vectors?
-The copy number refers to the number of plasmid copies that can be present within a single host cell. It is significant because it affects the efficiency of gene amplification, with higher copy numbers generally leading to more efficient amplification.
What are the essential components of a plasmid vector?
-Essential components of a plasmid vector include an origin of replication (ori), a selectable marker (often an antibiotic resistance gene), multiple cloning sites (also known as polylinker or MCS), and a promoter region if used as an expression vector.
What is the insert size limitation for plasmid vectors?
-The insert size for plasmid vectors generally ranges from 5 to 25 kilobases (kb), with specific vectors like pUC19 having a maximum insert size of 15 kb.
What is the purpose of the selectable marker in a plasmid vector?
-The selectable marker, often an antibiotic resistance gene, is used to distinguish between recombinant plasmids containing the target DNA and non-recombinant plasmids, allowing for the selection of successfully modified plasmids.
What are the advantages of using plasmid vectors for molecular cloning?
-Plasmid vectors are advantageous due to their small size, ease of handling and purification, efficient selection and screening processes, and their natural self-replication within bacterial hosts, making them ideal for cloning small DNA fragments.
What is the main disadvantage of using plasmid vectors for cloning larger DNA sequences?
-The main disadvantage is the limited insert size that plasmid vectors can accommodate. Attempting to clone larger sequences can lead to issues with recombinant plasmid formation, maintenance within the host cell, and reduced transformation efficiency.
Can you provide an example of a plasmid vector mentioned in the script?
-An example of a plasmid vector mentioned in the script is pUC19, which has specific features such as an origin of replication, a promoter, and antibiotic resistance sites, making it suitable for both cloning and expression purposes.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)