Kelenjar Hipofisis ( Pituitari )
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on the pituitary gland and its crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through the hormones it produces. The video covers the different lobes of the pituitary, including the anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes. It explains key hormones such as Growth Hormone (GH), Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), Prolactin, Gonadotropins (FSH and LH), Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH), Oxytocin, and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH). The video also highlights the effects of hormone deficiencies and excesses, offering viewers an in-depth understanding of the pituitary gland's functions in the human body.
Takeaways
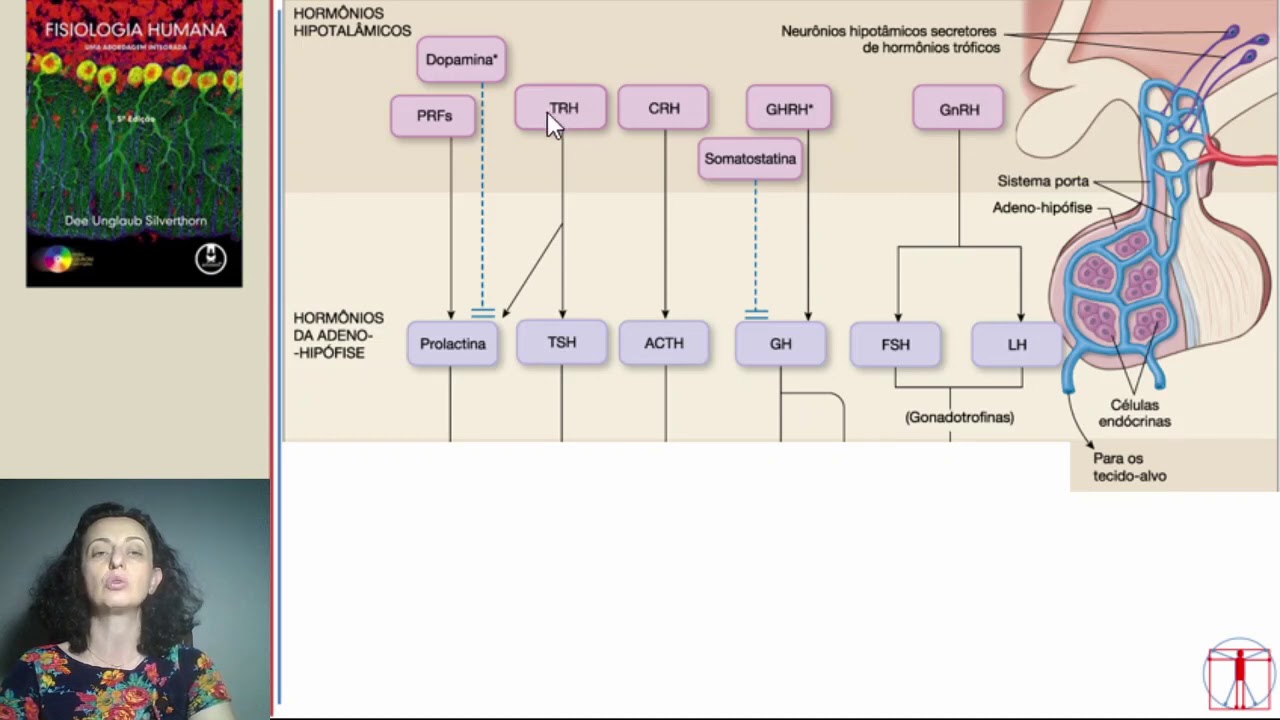
- 😀 The pituitary gland, located below the hypothalamus, plays a central role in regulating various hormones.
- 😀 The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland produces key hormones like Growth Hormone (GH), Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), and Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH).
- 😀 Growth Hormone (GH) regulates cell division and regeneration, with imbalances leading to dwarfism (deficiency) or gigantism/acromegaly (excess).
- 😀 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) controls the production of thyroid hormones and imbalances can lead to conditions like goiter.
- 😀 ACTH regulates cortisol production in the adrenal cortex, with deficiencies leading to Addison's disease and excess causing Cushing's syndrome.
- 😀 Prolactin (PRL) stimulates milk production during late pregnancy, with an excess causing overproduction of milk and a deficiency reducing milk supply.
- 😀 Gonadotropin hormones, including Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH), regulate the reproductive organs and gamete production.
- 😀 FSH in females stimulates follicle development and estrogen production, while in males it regulates spermatogenesis.
- 😀 LH in females triggers ovulation and progesterone production, while in males it stimulates testosterone production in the testes.
- 😀 The intermediate lobe of the pituitary produces Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH), which affects pigmentation and can lead to conditions like albinism or melanism.
- 😀 The posterior lobe of the pituitary releases Oxytocin, which aids in uterine contractions during childbirth, and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), which regulates water retention and urine output.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the pituitary gland?
-The primary function of the pituitary gland is to regulate various physiological processes through the production of hormones that control the functions of other glands in the endocrine system, earning it the nickname 'master gland'.
How is the pituitary gland divided and what are its parts?
-The pituitary gland is divided into three parts: the anterior lobe (front), intermediate lobe (middle), and posterior lobe (back). Each part produces specific hormones that serve different functions in the body.
What is the role of growth hormone (GH)?
-Growth hormone (GH) regulates cell division, growth, and regeneration. A deficiency can result in dwarfism, while an excess leads to gigantism or acromegaly, characterized by abnormal growth.
What does thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) do in the body?
-Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. A deficiency causes goiter, while excess TSH can result in hyperthyroidism, an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
What are the consequences of an imbalance in adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
-ACTH regulates the adrenal cortex to produce corticosteroids. A deficiency leads to Addison's disease, causing fatigue and skin pigmentation changes, while an excess causes Cushing's syndrome, characterized by excessive cortisol production.
What is the function of prolactin (PRL) in the body?
-Prolactin stimulates the production of milk in lactating women. A deficiency can result in insufficient milk production, while excess prolactin can lead to overproduction of milk.
How does follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) function differently in men and women?
-In women, FSH regulates the development of ovarian follicles and estrogen production. In men, FSH controls spermatogenesis in the testes. Deficiencies in either sex can lead to infertility.
What is the role of luteinizing hormone (LH) in reproduction?
-In women, LH triggers ovulation and promotes progesterone production, while in men, LH stimulates testosterone production in the testes. Imbalances in LH can cause issues such as irregular menstruation or lack of secondary sexual characteristics.
What does the intermediate lobe of the pituitary produce, and what is its effect?
-The intermediate lobe of the pituitary produces melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), which influences skin pigmentation by increasing melanin production. A deficiency causes albinism, while an excess leads to melanism (excess melanin).
How do oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) function in the body?
-Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions during labor and milk ejection, while ADH regulates water reabsorption in the kidneys. A deficiency of ADH leads to diabetes insipidus, while excess ADH causes water retention and reduced urine output.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

KELENJAR HIPOFISIS - MODUL ADRENAL DAN HIPOFISIS - dr Reza Rinadhi Bramantya, SpPD-KEMD

Sistem Hormon_(Sistem Koordinasi Bagian 2 )_Biologi SMA XI

Hypothalamus-Hypophysen-Achsen - Zentrale Regulation des endokrinen Systems - AMBOSS Auditor

Understanding the Hypothalamus and Pituitary

Sistema Endócrino: Introdução | Anatomia e etc
Endocrinologia 2 - Eixo hipotálamo-hipófise
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
