Resumão: SISTEMA ENDÓCRINO
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Natália Reinect provides a comprehensive overview of the endocrine system, explaining its importance in regulating various bodily functions through hormone secretion. She discusses the roles of key endocrine glands, including the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, and gonads, highlighting their specific hormones and functions. The video also touches on how hormones communicate with target cells and organs to maintain balance within the body. Natália offers a valuable review for students preparing for exams and invites viewers to engage with additional resources, courses, and social media platforms for further learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 The endocrine system is crucial for regulating various bodily functions through hormone production and secretion.
- 😀 Hormones are chemical messengers that affect target cells, which have specific receptors to respond to those hormones.
- 😀 Hormones can act locally (autocrine or paracrine communication) or travel through the bloodstream (endocrine communication).
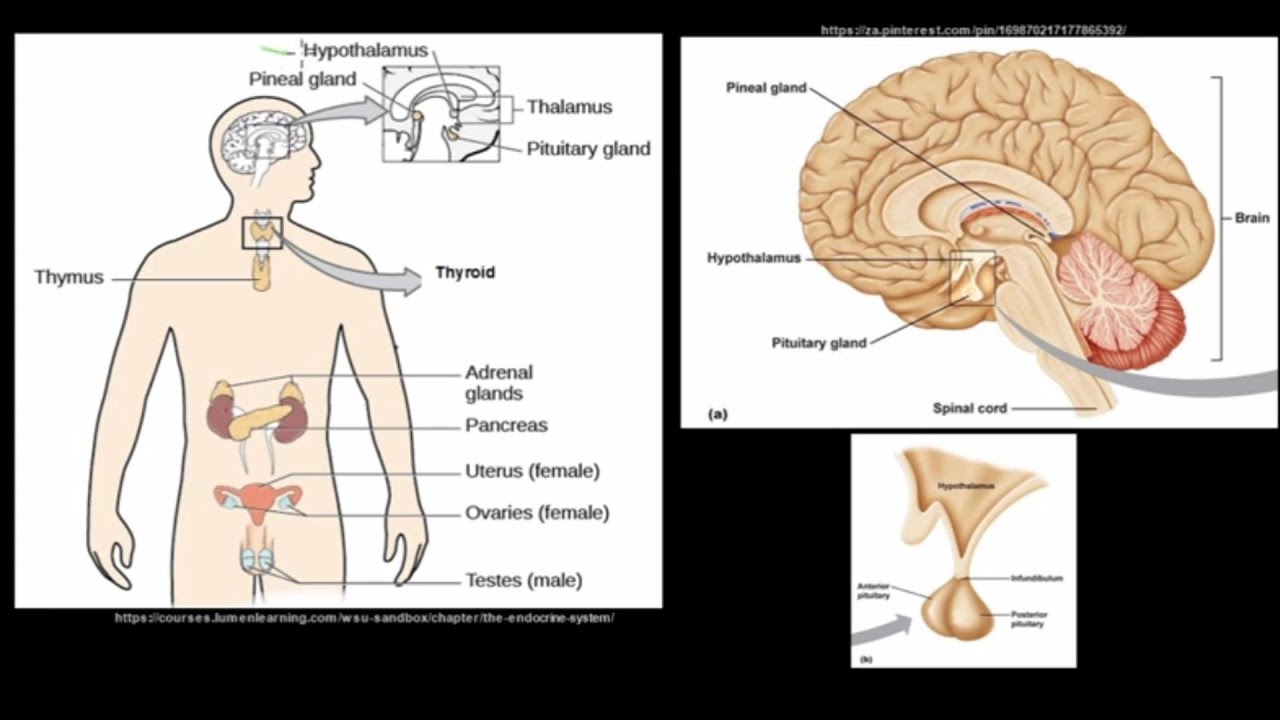
- 😀 The hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary and produces several hormones that regulate pituitary function.
- 😀 The pituitary gland is referred to as the 'master gland' because it controls the activity of other endocrine glands.
- 😀 The thyroid produces thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate metabolism, and calcitonin, which regulates calcium levels.
- 😀 Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which increases blood calcium levels.
- 😀 The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, which help regulate blood glucose levels.
- 😀 The adrenal glands consist of the cortex (producing cortisol and aldosterone) and the medulla (producing adrenaline and noradrenaline).
- 😀 The gonads (testes and ovaries) produce hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone, which are essential for sexual development and reproduction.
- 😀 Other organs like the kidneys, heart, liver, and placenta also contribute to endocrine functions in the body.
Q & A
What is the role of the endocrine system in the body?
-The endocrine system regulates and controls various bodily functions through the production and secretion of hormones, which act as chemical messengers to influence cells, tissues, and organs.
What are hormones and how do they function?
-Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system. They can alter the functioning of a target cell, which is a cell that has specific receptors for that hormone.
What is the difference between autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine communication?
-Autocrine communication occurs when hormones act on the same cell that produced them. Paracrine communication happens when hormones act on neighboring cells, while endocrine communication involves hormones being released into the bloodstream to act on distant target cells.
What is the function of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system?
-The hypothalamus produces hormones that regulate the anterior part of the pituitary gland, influencing the secretion of various hormones that control other endocrine glands.
What is the role of the pituitary gland, and why is it called the 'master gland'?
-The pituitary gland, often called the 'master gland,' controls the function of other endocrine glands. It produces hormones like growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and others that regulate key body functions.
What hormones are produced by the thyroid gland and what do they regulate?
-The thyroid gland produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which regulate the body's metabolic rate. It also produces calcitonin, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
What is the function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
-Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is produced by the parathyroid glands and increases the calcium levels in the blood by stimulating the release of calcium from bones.
How do the adrenal glands function in the endocrine system?
-The adrenal glands have two parts: the cortex and the medulla. The cortex produces hormones like cortisol (which regulates inflammation and metabolism) and aldosterone (which controls sodium reabsorption in the kidneys), while the medulla produces adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are involved in the fight-or-flight response.
What role do the gonads (testes and ovaries) play in the endocrine system?
-The gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females) produce sex hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone, which regulate the development of sexual characteristics and reproductive processes.
What are some non-endocrine tissues that have endocrine functions?
-Certain tissues, such as the nervous tissue, liver, kidneys, heart, stomach, intestines, adipose tissue, and placenta, also have endocrine functions, despite not being classified as traditional endocrine glands.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

tugas Ilmu Biomedik Dasar, tentang sistem endokrim. Kelompok 2
Grade 12 Life Sciences Responding to the Environment The Endocrine System

KELENJAR HIPOFISIS - MODUL ADRENAL DAN HIPOFISIS - dr Reza Rinadhi Bramantya, SpPD-KEMD

Resumão: SISTEMA REPRODUTOR MASCULINO

[#1] INTRODUÇÃO SISTEMA ENDÓCRINO: O que são HORMÔNIOS? Como são classificados? Quais os tipos?

GCSE Biology - Endocrine System & Hormones #59
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)