O Discreto Charme das Partículas Elementares parte III - Aula de física - Ensino médio
Summary
TLDRThis script explores fundamental concepts in particle physics, focusing on the Standard Model of particles, including leptons, quarks, and bosons, as well as the forces that govern the universe. The conversation delves into historical discoveries, like the Higgs boson and atomic models, explaining the crucial role of particles like the photon and gluon in interactions. Additionally, the script discusses the relationship between mass, energy, and the universe's formation. Throughout, the importance of understanding the smallest particles to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos is emphasized, with insights into both theoretical physics and astronomical observations.
Takeaways
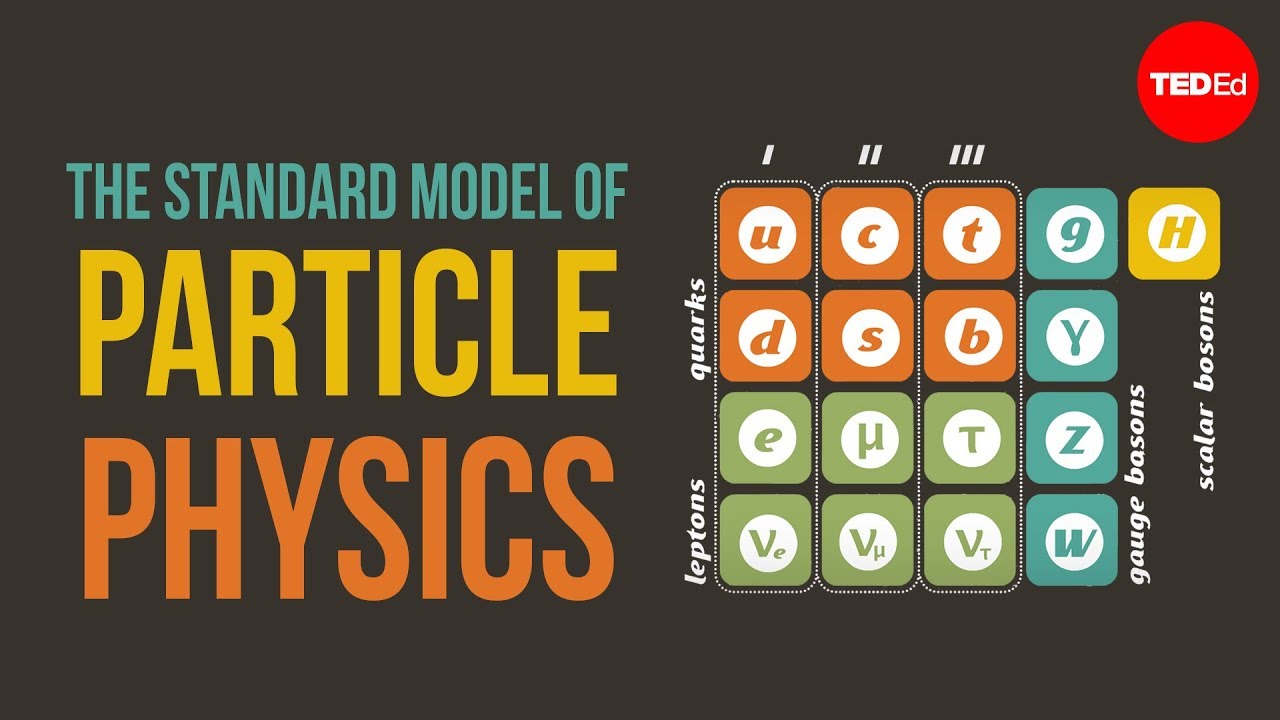
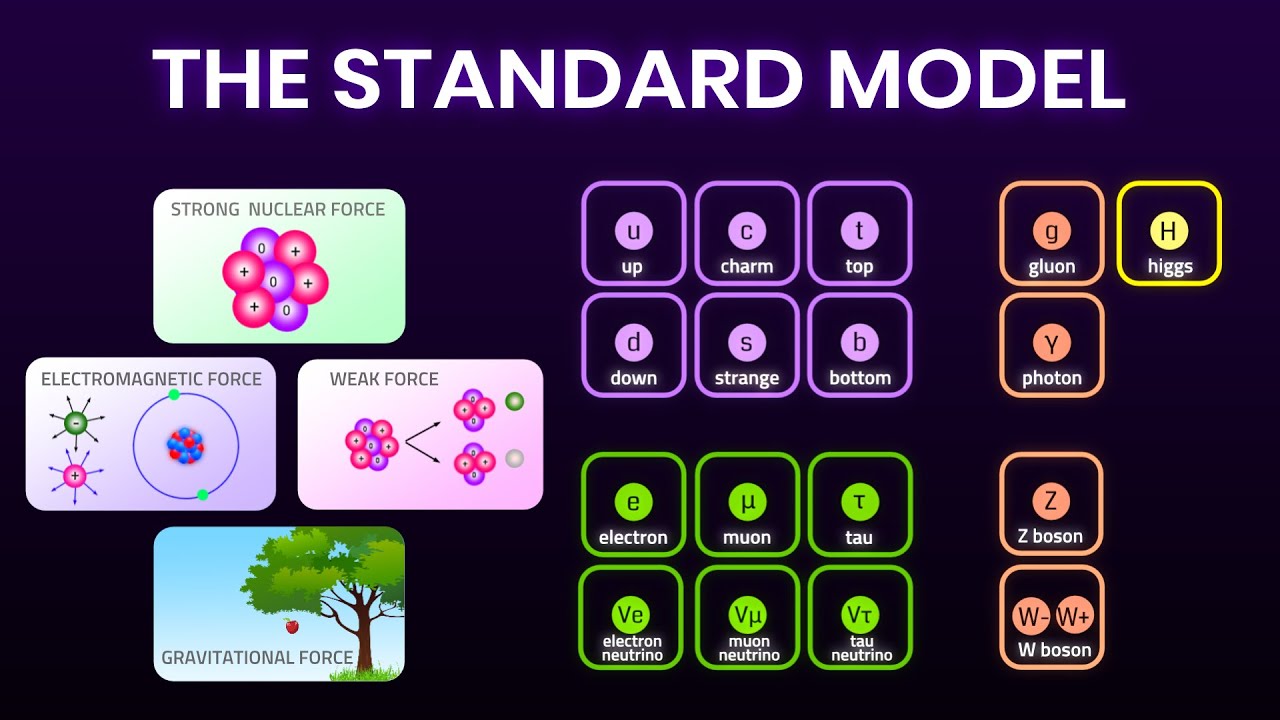
- 😀 The Standard Model of particle physics includes fundamental particles like leptons, quarks, and mediators.
- 😀 Leptons include electrons, neutrinos, muons, and tau particles.
- 😀 Quarks are categorized into three families: up, strange, and top quarks.
- 😀 Neutrons and protons are not considered fundamental particles as they are made up of quarks.
- 😀 The Higgs boson is a crucial particle that gives mass to other particles, confirmed by the discovery in 2012.
- 😀 The strong force is mediated by gluons, which are responsible for holding quarks together inside particles.
- 😀 The electromagnetic force is mediated by photons, affecting charged particles like electrons and protons.
- 😀 The weak force, responsible for radioactive decay, is mediated by W and Z bosons.
- 😀 The gravitational force, though one of the fundamental forces, is not yet fully explained in particle physics.
- 😀 The study of atomic structure, such as the Bohr model, helps understand the behavior of particles in atoms, including electron energy levels and light emission.
Q & A
What are the eight leptons in the Standard Model of particle physics?
-The eight leptons in the Standard Model include the electron, electron neutrino, muon, muon neutrino, tau, tau neutrino, and their corresponding antiparticles.
What are the three families of quarks in the Standard Model?
-The three families of quarks are: the first family with the up and down quarks, the second family with the strange and charm quarks, and the third family with the top and bottom quarks.
Where do neutrons and protons belong in the Standard Model?
-Neutrons and protons are not elementary particles, so they do not appear in the Standard Model. They are composed of quarks and are part of the hadrons family.
What role do bosons play in particle interactions?
-Bosons act as mediators of the fundamental forces in the universe. For example, the photon mediates the electromagnetic force, the gluon mediates the strong force, and the W and Z bosons mediate the weak force.
What is the Higgs boson, and why is it significant?
-The Higgs boson is a particle that was proposed to explain how particles acquire mass. It was a crucial part of the Standard Model, and its discovery in 2012 confirmed the existence of the Higgs field, which gives particles their mass.
What is the role of the Higgs field in particle physics?
-The Higgs field gives particles mass. When particles interact with this field, they acquire mass, which is a key component in the Standard Model of particle physics.
How does the discovery of the Higgs boson relate to the early universe?
-The discovery of the Higgs boson helped scientists understand the conditions of the early universe. It provided insights into how particles gained mass after the Big Bang, which was essential for the formation of matter as we know it.
What are antiparticles, and how do they relate to normal particles?
-Antiparticles are counterparts to normal particles, having the opposite charge. For example, the antiparticle of the electron (negatively charged) is the positron (positively charged).
What is the relationship between the four fundamental forces?
-The four fundamental forces are the strong force, weak force, electromagnetic force, and gravitational force. Each governs different interactions: the strong force binds atomic nuclei, the weak force governs radioactive decay, the electromagnetic force acts between charged particles, and the gravitational force is the attraction between masses.
How do scientists use light from stars to understand the universe?
-Scientists study the light emitted by stars to determine the elements present in them. By analyzing the spectrum of light, they can identify which elements are in the stars, thus helping us understand both the stars' composition and the broader universe.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
What’s the smallest thing in the universe? - Jonathan Butterworth
All Fundamental Forces and Particles Explained Simply | Elementary particles

Programa "O Discreto Charme das Partículas Elementares" Parte 1

All of PARTICLES & QUANTUM in 15 mins - AS & A-level Physics

O Discreto Charme das Partículas Elementares Parte II - Aula de física - Ensino médio

Fermions and Bosons
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
