Sistem Kendali 2.1. Dasar Transformasi Laplace
Summary
TLDRThis video script introduces key concepts in automatic control systems, with a focus on the Laplace transform. It reviews fundamental topics such as open-loop and closed-loop systems, explaining the significance of each and the role of components like controllers, actuators, and sensors. It also covers critical terms such as plants, processes, disturbances, and errors. The importance of mathematical modeling is discussed to predict system behavior and performance. Lastly, the Laplace transform is explained as a method to convert time-domain functions into the s-domain, helping to understand and analyze system dynamics more effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 Open-loop systems involve a direct input-output control, without feedback, whereas closed-loop systems include feedback where the output is compared to the desired input to minimize errors.
- 😀 A 'Plan' in an automatic control system refers to the physical object or system being controlled, such as machinery or electronic devices.
- 😀 The 'Process' is the operation or function being controlled in a system, which is influenced by the Plan.
- 😀 Disturbances are external or internal factors that negatively affect a system, like gravitational forces affecting the stability of a system.
- 😀 The 'Input' in a control system refers to the desired output or setpoint, which is what the system aims to achieve.
- 😀 Error is the difference between the desired input (setpoint) and the actual output of the system.
- 😀 A 'Control Signal' is generated by the controller to adjust the actuator in order to influence the system's behavior.
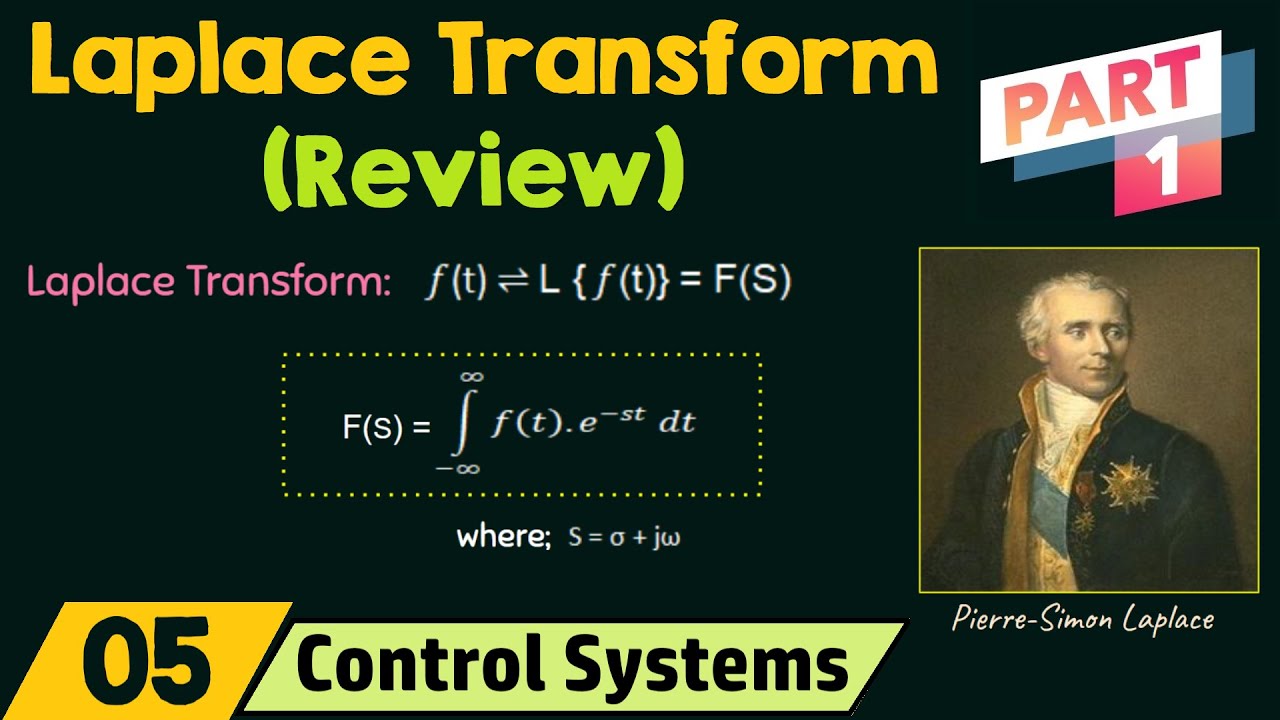
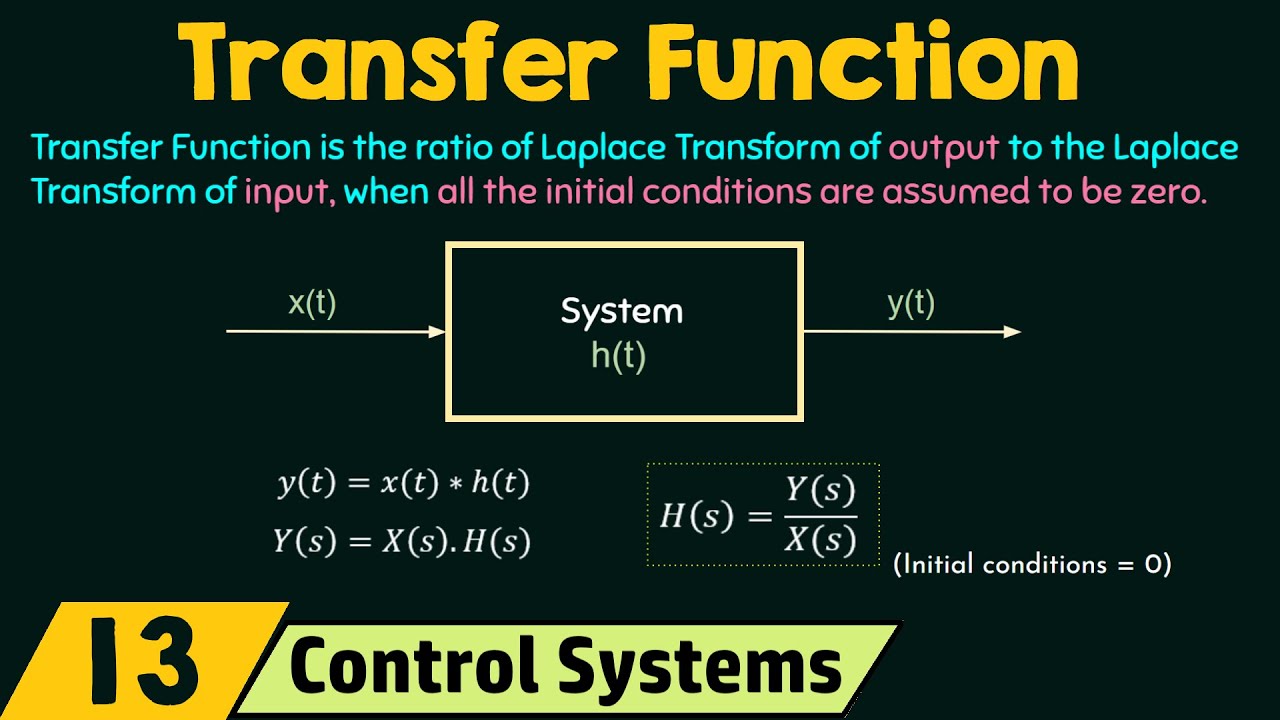
- 😀 The Laplace Transform is a mathematical tool used to model systems, predict outputs, and analyze the system's behavior.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform changes a function from the time domain (f(t)) to the Laplace domain (F(s)) using integration with an exponential factor.
- 😀 The purpose of the Laplace Transform is to better understand system behavior and predict outputs, especially in real-time systems.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform formula used in automatic control systems starts the integration from 0, as real-time systems do not operate starting from negative time.
Q & A
What is the purpose of reviewing material from previous lessons in the context of control systems?
-The review is essential to ensure a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts, especially since they form the basis for more advanced topics like Laplace transformation. For example, the differences between open-loop and closed-loop control systems are foundational concepts that directly influence the study of automatic control systems.
What are the key differences between open-loop and closed-loop control systems?
-In an open-loop system, the output is not fed back into the system for adjustments, and the control action is based solely on the input. In contrast, a closed-loop system includes feedback where the output is constantly monitored by a sensor and fed back into the controller to adjust the system's performance to meet the desired set point.
How is a 'plan' defined in the context of an automatic control system?
-A 'plan' refers to a physical object or process being controlled, such as a piece of equipment or machinery. The system works to influence the behavior of this plan to achieve a desired outcome.
What does the term 'disturbance' mean in an automatic control system?
-A disturbance refers to any external or internal signal or variable that negatively impacts the system's performance. For example, gravity can be considered a disturbance in a balancing system, where it affects the position of an object like a bicycle.
What is meant by the 'error' in a control system?
-Error is the difference between the desired input (set point) and the actual output of the system. This value is crucial for feedback in closed-loop systems to correct any discrepancies and adjust the system's behavior accordingly.
What role does the controller play in an automatic control system?
-The controller processes the input signal, computes the error, and generates a control signal that is sent to the actuator. The actuator then adjusts the physical system (the plan) to reduce the error and achieve the desired output.
Why is modeling a system mathematically important in control systems?
-Mathematical modeling allows engineers to understand the behavior and characteristics of a system. It helps predict system outputs under different conditions, making it easier to optimize and control the system effectively.
What is the purpose of using Laplace transformation in control systems?
-Laplace transformation is used to convert time-domain functions into the frequency domain (S-domain). This allows for easier analysis of system behavior, particularly in terms of stability, transient response, and system dynamics.
What is the basic formula for Laplace transformation?
-The basic formula for Laplace transformation is: F(s) = ∫[0,∞] f(t) * e^(-st) dt, where f(t) is the time-domain function, and F(s) is the resulting function in the Laplace domain. The integration is carried out from 0 to infinity, as real-time systems are typically considered from the start of the process (t = 0).
Why is the lower limit of the Laplace integral set to zero instead of negative infinity in control systems?
-In control systems, real-time processes cannot begin before time zero, which is why the lower limit of the Laplace integral is set to zero. This simplifies the modeling of systems that start at t = 0, rather than extending to negative infinity.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)