Asam Karboksilat dan Ester | KIMIA KELAS 12
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Pakjo explains the structure and nomenclature of carboxylic acids and esters, focusing on their functional groups and differences. He demonstrates how to name compounds based on their structure, including examples like butanoic acid and isopropyl propanoate. The video also covers esterification, where carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form esters, and the reverse process, hydrolysis, which breaks esters into carboxylic acids and alcohols. Everyday examples like acetic acid (vinegar) and ethyl butyrate (pineapple essence) are also discussed, offering practical insights into these organic compounds.
Takeaways
- 😀 Alkanes derivatives discussed in the video include carboxylic acids and esters.
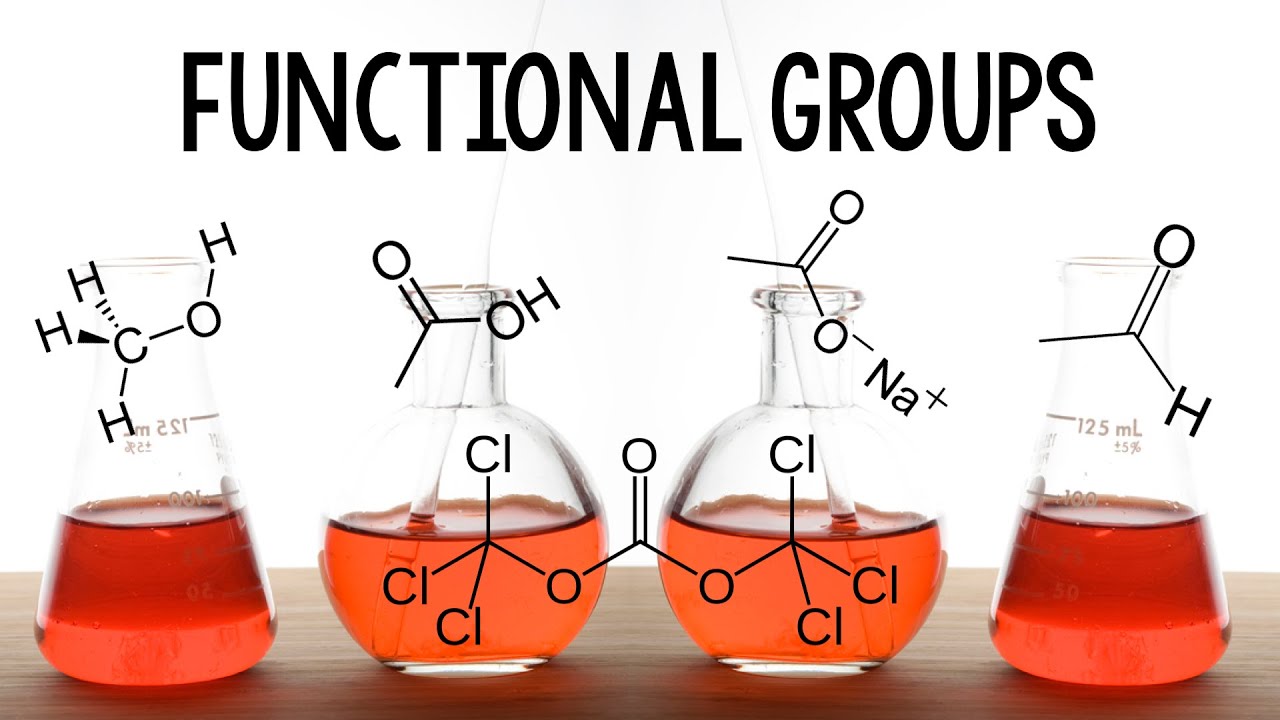
- 😀 Both carboxylic acids and esters have the same chemical formula (C_nH_2nO_2) but differ in their functional groups.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids have a -COOH group, while esters have a -COOR group, where 'R' represents an alkyl group.
- 😀 The functional group of a carboxylic acid consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to a hydroxyl group (OH).
- 😀 Esters have a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to an oxygen atom that connects to an alkyl group.
- 😀 In carboxylic acids, the hydrogen (H) is directly attached to the hydroxyl group (OH), whereas in esters, the oxygen connects to another alkyl group.
- 😀 The nomenclature of carboxylic acids follows a system where the 'acid' part is mentioned first, followed by the alkyl or branch group.
- 😀 Esters are named by first stating the alkyl group attached to the ester and then the alkanoate part (the acid portion).
- 😀 Common examples include acetic acid (also known as vinegar) and ethyl butyrate (which gives pineapple scent).
- 😀 Esterification is a reaction where a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester and water.
- 😀 Hydrolysis of esters (reverse esterification) produces a carboxylic acid and alcohol when the ester is reacted with water.
Q & A
What are carboxylic acids and esters, and how are they related?
-Carboxylic acids and esters are organic compounds that have the same molecular formula (CnH2nO2) but differ in their functional groups. Carboxylic acids have a carboxyl group (COOH), while esters have an ester group (COO). The difference lies in the position of the hydrogen atom, which is replaced by an alkyl group in esters.
How do you name a carboxylic acid?
-To name a carboxylic acid, first identify the longest carbon chain that includes the carboxyl group (COOH) and number it so that the carboxyl group is at position 1. The name ends with '-anoic acid'. If there are alkyl groups attached to the chain, their position and names are indicated before the main name.
How do you name an ester?
-To name an ester, identify the alkyl group attached to the oxygen atom, which comes first in the name, followed by the alkanoate part. The alkanoate is named based on the carboxyl group from which it is derived, with the '-ate' suffix replacing '-ic acid' from the parent carboxylic acid.
What is the difference between the functional groups of carboxylic acids and esters?
-Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group (COOH), which has both a carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl (OH) group. Esters contain an ester group (COO), where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkyl group, linking the carbonyl to the oxygen atom of the ester.
What is esterification, and what is an example reaction?
-Esterification is the process of forming an ester by reacting a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. An example reaction is when propanoic acid reacts with 2-propanol to form isopropyl propanoate and water.
How does esterification work at a molecular level?
-In esterification, the hydroxyl group (OH) from the carboxylic acid combines with a hydrogen atom from the alcohol, forming water. The alkyl group from the alcohol then bonds with the carbonyl group of the carboxylic acid, forming an ester.
What is hydrolysis of an ester, and how does it occur?
-Hydrolysis of an ester is the reverse reaction of esterification, where an ester reacts with water (and often an acid catalyst) to break down into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. For example, ethyl acetate can be hydrolyzed into acetic acid and ethanol.
What are some common examples of carboxylic acids and esters in daily life?
-A common example of a carboxylic acid is acetic acid, which is found in vinegar. An example of an ester is ethyl butyrate, which gives off a pineapple-like aroma and is used as a flavoring essence.
What is the significance of naming conventions for carboxylic acids and esters?
-Naming conventions for carboxylic acids and esters help chemists clearly communicate the structure and functional groups of these compounds. Proper naming is essential for identification, synthesis, and understanding of their chemical properties and reactivity.
Why is the position of the carboxyl group important when naming carboxylic acids?
-The position of the carboxyl group is important because it defines the starting point of the carbon chain in carboxylic acids. It ensures consistency and clarity in naming, with the carboxyl group always being at position 1 in the longest chain.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)