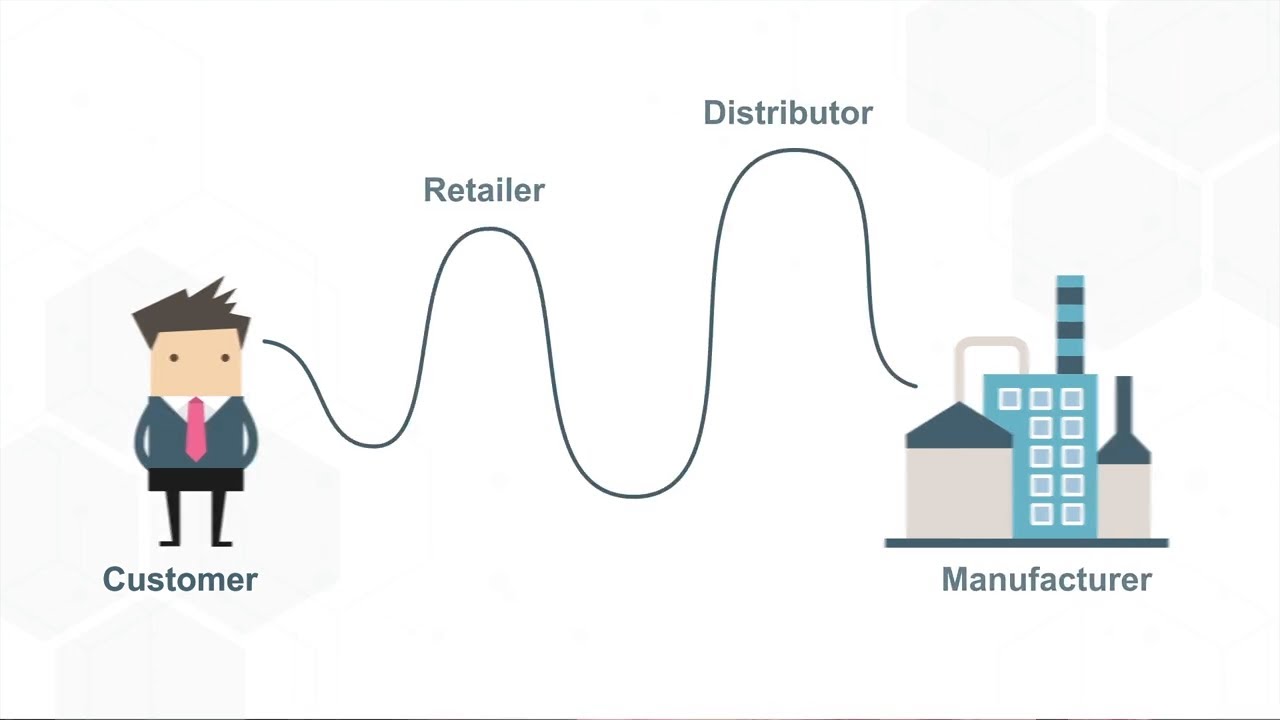
The Bullwhip Effect 101
Summary
TLDRThe Bullwhip Effect occurs when small variations in consumer demand lead to amplified fluctuations in orders upstream, disrupting supply chains. Using the example of Pampers, the script highlights how promotional sales trigger a cascade of exaggerated orders from retailers to manufacturers, causing stockouts, overproduction, and increased costs. Key causes include price fluctuations, order batching, shortage gaming, and inaccurate demand forecasting. The solution lies in improved communication, more frequent ordering, better demand visibility, and reducing lead times to prevent further disruptions and optimize the supply chain.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Bullwhip Effect refers to the distortion of the supply chain caused by small changes in consumer demand, magnifying through the levels of the supply chain.
- 😀 The term 'Bullwhip Effect' is used because the oscillating demand in the supply chain resembles the cracking of a whip.
- 😀 The Bullwhip Effect can lead to significant problems like inventory disruptions, quality control issues, decreased customer service, and increased costs.
- 😀 A sales promotion or price discount can cause retailers to place bulk orders, which may disrupt the entire supply chain and create demand uncertainty.
- 😀 Retailers may place large orders in response to a sale, which leads to a ripple effect of excessive orders to distributors and manufacturers, ultimately causing supply shortages and inefficiencies.
- 😀 The Bullwhip Effect can lead to factories overproducing and then facing excess stock, which may result in inventory cuts and wasted resources.
- 😀 Incorrect demand forecasting and order batching contribute to the Bullwhip Effect, as large, infrequent orders may not reflect actual consumption patterns.
- 😀 Price fluctuations and sales promotions often lead to large bulk orders, which do not represent the true market demand and cause misalignment in supply and demand.
- 😀 Shortage gaming occurs when customers exaggerate their orders during shortages, exacerbating the supply chain disruption when actual demand is revealed.
- 😀 Effective communication across the supply chain is critical in preventing the Bullwhip Effect, ensuring real-time visibility of demand, inventory, and orders to reduce inefficiencies.
Q & A
What is the Bullwhip Effect in supply chains?
-The Bullwhip Effect refers to the distortion of demand within a supply chain, where small variations in customer demand cause larger oscillations in orders as they move upstream from retailers to distributors and suppliers.
Why is it called the Bullwhip Effect?
-It is called the Bullwhip Effect because, as demand fluctuations magnify through the supply chain, it resembles the action of a cracking whip.
What are the main consequences of the Bullwhip Effect?
-The Bullwhip Effect can lead to inventory disruptions, quality control problems, reduced customer service, and increased costs for materials and manpower.
Can you explain the example of the Bullwhip Effect in Procter & Gamble's diaper supply chain?
-In the example, a sale at Walmart causes a spike in demand for Pampers, leading to larger orders from the retailer. This escalates through the supply chain, with distributors and manufacturers struggling to meet the demand. This results in overstocking, delays, and stockouts, negatively impacting both the supply chain and customers.
What is meant by 'order batching' in the context of the Bullwhip Effect?
-Order batching refers to companies placing larger orders in batches to avoid frequent order processing or high transportation costs. This creates irregular demand patterns and contributes to the Bullwhip Effect.
How do price fluctuations and sales promotions contribute to the Bullwhip Effect?
-Sales promotions and price discounts lead customers to buy in bulk, skewing actual consumption patterns. This creates an artificial spike in demand, which gets amplified as orders are placed up the supply chain.
What is shortage gaming, and how does it contribute to the Bullwhip Effect?
-Shortage gaming occurs when customers exaggerate their orders to secure more product during times of supply shortages. This results in distorted orders and overcompensation, exacerbating demand fluctuations.
How does demand forecasting inaccuracy contribute to the Bullwhip Effect?
-Inaccurate demand forecasting leads to incorrect stock levels, which causes overordering or stockouts. Companies often add safety stock with long lead times, amplifying fluctuations in demand as they try to compensate.
What countermeasures can be used to address fluctuating prices?
-Fluctuating prices can be replaced with everyday low prices to stabilize demand and reduce the volatility caused by promotions and discounts.
What role does communication play in preventing the Bullwhip Effect?
-Effective communication across the entire supply chain is crucial. Sharing data, visibility into point-of-sale data, and better coordination help reduce misunderstandings and prevent demand from being distorted as it moves through the chain.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)