Aneuploidi (Mutasi Kromosom akibat perubahan jumlah kromosom)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains chromosomal mutations, focusing on aneuploidy, where chromosome numbers are abnormal due to errors in cell division. It covers various conditions caused by aneuploidy, including Turner Syndrome (monosomy), Down Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Jacob Syndrome, and Triple X Syndrome (trisomy). The video highlights their genetic causes, symptoms, and impacts on physical and mental development. It also discusses diagnostic methods like karyotyping and provides insights from a Down Syndrome infographic. The content is aimed at helping viewers understand the causes, symptoms, and risks associated with chromosomal disorders.
Takeaways
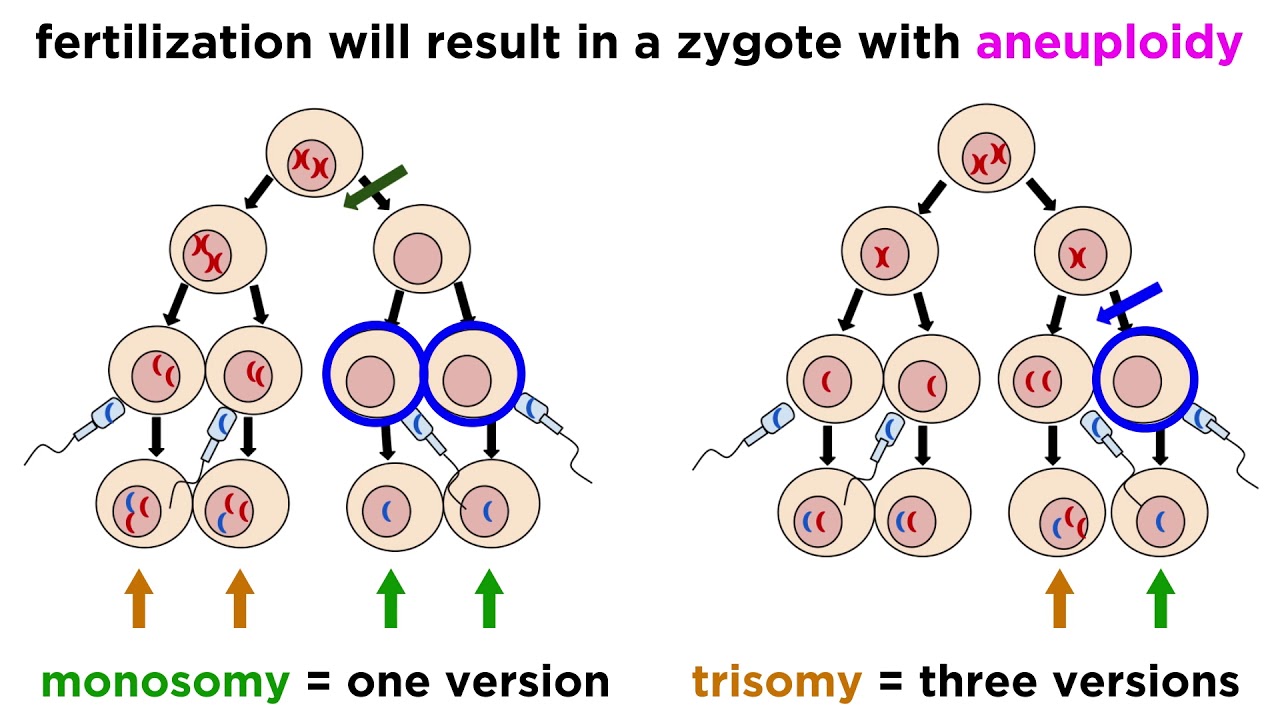
- 😀 Aneuploidy refers to variations in chromosome number, caused by the addition or loss of one or a few chromosomes.
- 😀 Aneuploidy is caused by a process called nondisjunction, where chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division.
- 😀 There are several types of aneuploidy: monosomy (loss of one chromosome), trisomy (gain of one chromosome), and tetrasomy (gain of two chromosomes).
- 😀 Monosomy (2N-1) involves losing one chromosome, such as in **Turner syndrome**, where a female has only one X chromosome (X0).
- 😀 Trisomy (2N+1) involves the addition of one chromosome, as seen in **Down syndrome**, where there is an extra chromosome 21 (47 chromosomes in total).
- 😀 **Down syndrome** (Trisomy 21) is characterized by physical features such as a flat face, short stature, heart defects, and intellectual disabilities.
- 😀 **Klinefelter syndrome** (47, XXY) occurs when a male has an extra X chromosome. Individuals may have small testicles, breast development, and are often infertile.
- 😀 **Jacob syndrome** (47, XYY) is caused by an extra Y chromosome. It leads to taller stature, longer fingers, and potential developmental issues with the spine.
- 😀 **Female Super Syndrome** (47, XXX) occurs when a female has three X chromosomes. Affected individuals are often taller, with weak muscles and larger gaps between their eyes.
- 😀 An infographic discussed in the video explains Down syndrome, correcting common misconceptions such as the percentage of cases caused by different forms of trisomy.
- 😀 A key takeaway from the Down syndrome infographic is that the risk of having a child with Down syndrome increases slightly with maternal age, but the actual risk is less than often believed (1 in 1000 at age 30).
Q & A
What is aneuploidy?
-Aneuploidy is a variation in the number of chromosomes due to the loss or gain of one or more chromosomes, but it does not affect the entire genome.
How does aneuploidy occur?
-Aneuploidy occurs as a result of nondisjunction, which is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division.
What is disomy?
-Disomy refers to the normal pairing of chromosomes, where an individual has two copies of each chromosome (2N).
What are some examples of aneuploidy conditions in humans?
-Examples of aneuploidy conditions in humans include Turner syndrome (monosomy 2N -1), Down syndrome (trisomy 2N + 1), Klinefelter syndrome (trisomy 2N + 1), Jacob syndrome (trisomy 2N + 1), and female supernumerary syndrome (trisomy with 3 X chromosomes).
What is Turner syndrome?
-Turner syndrome is a condition caused by monosomy 2N -1, where there is a missing X chromosome. People with Turner syndrome have immature sexual organs, short stature, and normal intelligence, but they are sterile.
What is Down syndrome and what are its characteristics?
-Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 2N + 1, where there is an extra chromosome 21, leading to a total of 47 chromosomes. Characteristics include distinctive facial features, short stature, heart defects, susceptibility to infections, weak respiratory function, and mental retardation.
What is Klinefelter syndrome?
-Klinefelter syndrome is a condition caused by trisomy 2N + 1, where males have an extra X chromosome. It leads to small testes, sterility, enlarged breasts, and normal intelligence but with feminine secondary sexual characteristics.
What is Jacob syndrome?
-Jacob syndrome is caused by an extra Y chromosome (trisomy 2N + 1), leading to physical characteristics such as tall stature, a broad head, widely spaced eyes, curved fingers, scoliosis, and intellectual disabilities.
What is female supernumerary syndrome?
-Female supernumerary syndrome occurs when there are three X chromosomes in a person (trisomy 2N + 1 with 3 X chromosomes). It is characterized by taller than average height, long limbs, muscle weakness, and sometimes ovarian abnormalities, but most affected individuals have normal sexual development and fertility.
What are the main causes of Down syndrome?
-The main causes of Down syndrome are trisomy 21 (94%), mosaicism (2%), and translocation (4%), as explained in the infographics shared in the lecture.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)