Alteration of Chromosome Number and Structure
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating world of chromosomal alterations, focusing on changes in chromosome number and structure. It explains the processes of mitosis and meiosis, highlighting how errors like nondisjunction can lead to aneuploidy and conditions like Down syndrome. The video also covers polyploidy, particularly in plants, and structural chromosome changes such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. These changes can have significant effects, leading to genetic disorders or even miscarriage. The video provides a deeper understanding of these complex genetic phenomena and their impact on organisms.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chromosomes are essential in understanding genetics and heredity, with their number and structure influencing organism development.
- 😀 Mitosis ensures that cells retain the same genetic material, while meiosis contributes to genetic diversity by producing gametes.
- 😀 Errors in chromosome number during meiosis can result in aneuploidy, where a zygote has either too many or too few chromosomes.
- 😀 Nondisjunction in meiosis can lead to gametes with abnormal chromosome counts, leading to conditions like Down syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome.
- 😀 Aneuploidy results in monosomy (one chromosome) or trisomy (three chromosomes) of a particular chromosome.
- 😀 Polyploidy refers to organisms having more than two sets of chromosomes, such as triploidy (3n) or tetraploidy (4n), which are common in plants like bananas and wheat.
- 😀 Polyploid animals are rare, but polyploid plants are common and vital in agriculture.
- 😀 Chromosome structure can change through various mechanisms like deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation, often due to radiation or other damaging agents.
- 😀 Deletion and duplication are common during meiosis, where unequal DNA exchange leads to missing or extra information on chromosomes.
- 😀 Chromosomal alterations can lead to miscarriages, genetic disorders, or early childhood death, depending on the nature and severity of the changes.
Q & A
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis is the process where a cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells, maintaining the same chromosome number. Meiosis, on the other hand, is the process that produces gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the chromosome number, promoting genetic diversity through the combination of genetic material from both parents.
What is nondisjunction in meiosis?
-Nondisjunction is the failure of chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis, resulting in gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes. This can lead to conditions like trisomy or monosomy when fertilization occurs with a normal gamete.
What is aneuploidy, and how does it arise?
-Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell. It arises when nondisjunction occurs during meiosis, leading to gametes with too many or too few chromosomes. Fertilization of these abnormal gametes can result in conditions like Down syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome.
What is the difference between monosomy and trisomy?
-Monosomy occurs when a cell has only one copy of a chromosome instead of two, while trisomy occurs when there are three copies of a chromosome instead of two. Both are types of aneuploidy, resulting in genetic disorders like Turner syndrome (monosomy X) and Down syndrome (trisomy 21).
What is polyploidy, and how does it differ from aneuploidy?
-Polyploidy is the condition where an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes, such as triploidy (3n) or tetraploidy (4n). Unlike aneuploidy, which involves an abnormal number of a specific chromosome, polyploidy involves changes to the entire chromosome set.
Why are polyploid plants common but polyploid animals rare?
-Polyploidy is common in plants because it can lead to greater size, improved disease resistance, and faster growth, making it advantageous. However, polyploidy in animals is rare due to the complications it causes in development and reproduction.
What are some examples of polyploid plants?
-Examples of polyploid plants include bananas (triploid, 3n), wheat (hexaploid, 6n), and strawberries (octoploid, 8n), all of which have multiple sets of chromosomes in each cell.
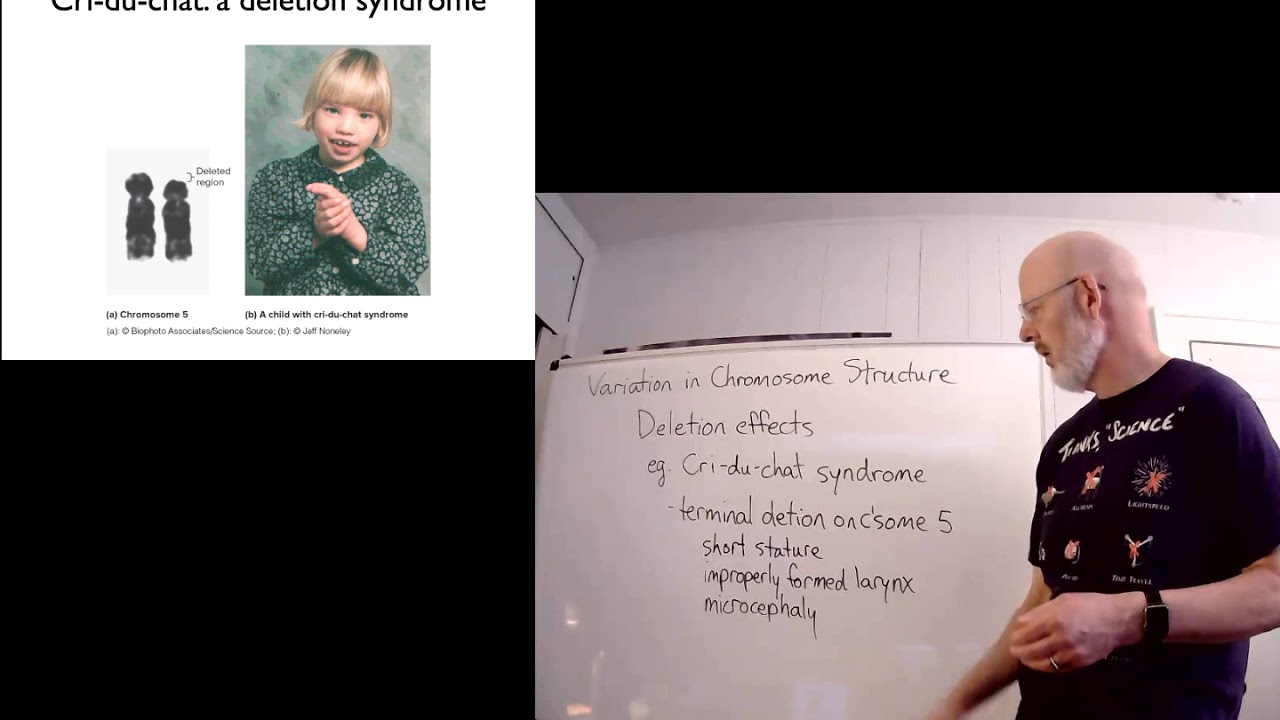
What is a chromosomal deletion, and how does it occur?
-A chromosomal deletion occurs when a fragment of a chromosome is lost, which can result in the loss of important genes. It may be caused by radiation or other damaging agents, and it can be detected when chromosomes break apart.
What are the consequences of chromosomal duplication?
-Chromosomal duplication occurs when a section of a chromosome is repeated. This can lead to an imbalance in gene dosage, which may disrupt normal development and function, and can result in genetic disorders or developmental issues.
How can chromosomal translocations affect an organism?
-Chromosomal translocations occur when a segment of one chromosome attaches to a different, nonhomologous chromosome. This can disrupt normal gene function and lead to genetic disorders, depending on which genes are involved in the translocation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)