VLAN trunking
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial guides users through configuring VLANs on network switches and setting up trunking with the 802.1Q protocol. It covers how to assign different VLANs to devices, set up trunk ports for multiple VLAN traffic, and troubleshoot network connectivity using ping tests. The video explains the process of VLAN tagging and frame forwarding, demonstrating how switches handle VLANs and ensuring communication between devices within the same VLAN. The tutorial also introduces the concept of Inter-VLAN Routing, which will be covered in the next video.
Takeaways
- 😀 VLANs are configured to segment different departments: Sales (VLAN 10), Administration (VLAN 20), and Technicians (VLAN 99).
- 😀 Each department's PCs are assigned IP addresses within their respective subnets (e.g., 192.168.10.x for Sales, 192.168.20.x for Admin).
- 😀 Switches need to be configured with VLANs and assigned specific ports to each VLAN for proper communication.
- 😀 Trunking between switches allows the transmission of multiple VLANs over a single link, avoiding the need for multiple cables.
- 😀 802.1Q is the protocol used for VLAN tagging, where a tag is added to the Ethernet frame to indicate which VLAN the frame belongs to.
- 😀 In trunk mode, switches send frames with VLAN tags to indicate the source VLAN. The receiving switch processes the tag to forward the frame to the correct port.
- 😀 VLAN tagging ensures that multiple VLANs can be transmitted over a single trunk link, like an 'autostrada' (highway) for frames.
- 😀 A switch adds a VLAN tag (802.1Q) to frames before sending them across a trunk link, and removes the tag when forwarding frames to the destination device.
- 😀 A ping test between PCs in the same VLAN should succeed, while communication between PCs in different VLANs will fail without Inter-VLAN Routing.
- 😀 Broadcast frames are forwarded by the switch to all ports in the same VLAN, except the one from which the frame originated.
- 😀 The next step after configuring VLANs and trunking would be to implement Inter-VLAN Routing to enable communication across VLANs.
Q & A
What are the three VLANs defined in the network setup?
-The three VLANs defined are Sales (green), Administration (orange), and Technicians (blue).
How are the VLANs assigned to specific subnets?
-Each VLAN is assigned a distinct subnet: Sales VLAN is 192.168.10.0/24, Administration is 192.168.20.0/24, and Technicians is 192.168.99.0/24.
Why are the PCs named with the 'PC10', 'PC20', and 'PC99' prefixes?
-The PCs are named with prefixes corresponding to their respective VLANs: 'PC10' for Sales VLAN, 'PC20' for Administration, and 'PC99' for Technicians, followed by a unique number for each device.
What is the significance of configuring the switch ports as 'Trunk' ports?
-Configuring the switch ports as 'Trunk' allows them to carry traffic for multiple VLANs over a single physical link, using VLAN tagging to distinguish between the VLANs.
What protocol is used for VLAN tagging between switches?
-The protocol used for VLAN tagging between switches is 802.1q, which inserts a VLAN tag into Ethernet frames to indicate which VLAN they belong to.
How does VLAN tagging work in practice when frames are sent between switches?
-When a frame is sent, the switch adds a VLAN tag (802.1q header) to the frame. The second switch reads the tag and forwards the frame to the correct port based on the VLAN ID. If necessary, the second switch removes the tag before forwarding the frame to the destination port.
What is the purpose of using a crossover cable between the two switches?
-A crossover cable is used to connect the two switches directly. It facilitates communication between switches by transmitting frames from one switch to the other, while the trunk ports manage the VLAN tagging.
Why is it necessary to configure the trunk ports to allow specific VLANs?
-It is necessary to configure trunk ports to allow specific VLANs so that only the relevant VLAN traffic is transmitted over the trunk link. This provides control over which VLANs can be communicated between switches.
How does a switch handle broadcast frames within a VLAN?
-When a broadcast frame is sent, the switch forwards the frame to all ports within the same VLAN, except the port from which it was received. The broadcast is limited to the devices within the same VLAN.
What is the expected behavior when a ping is sent between devices on the same VLAN versus different VLANs?
-When a ping is sent between devices on the same VLAN, the frame is forwarded without VLAN tagging. For devices on different VLANs, the frame is tagged with the appropriate VLAN ID and needs inter-VLAN routing to be communicated across VLANs.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
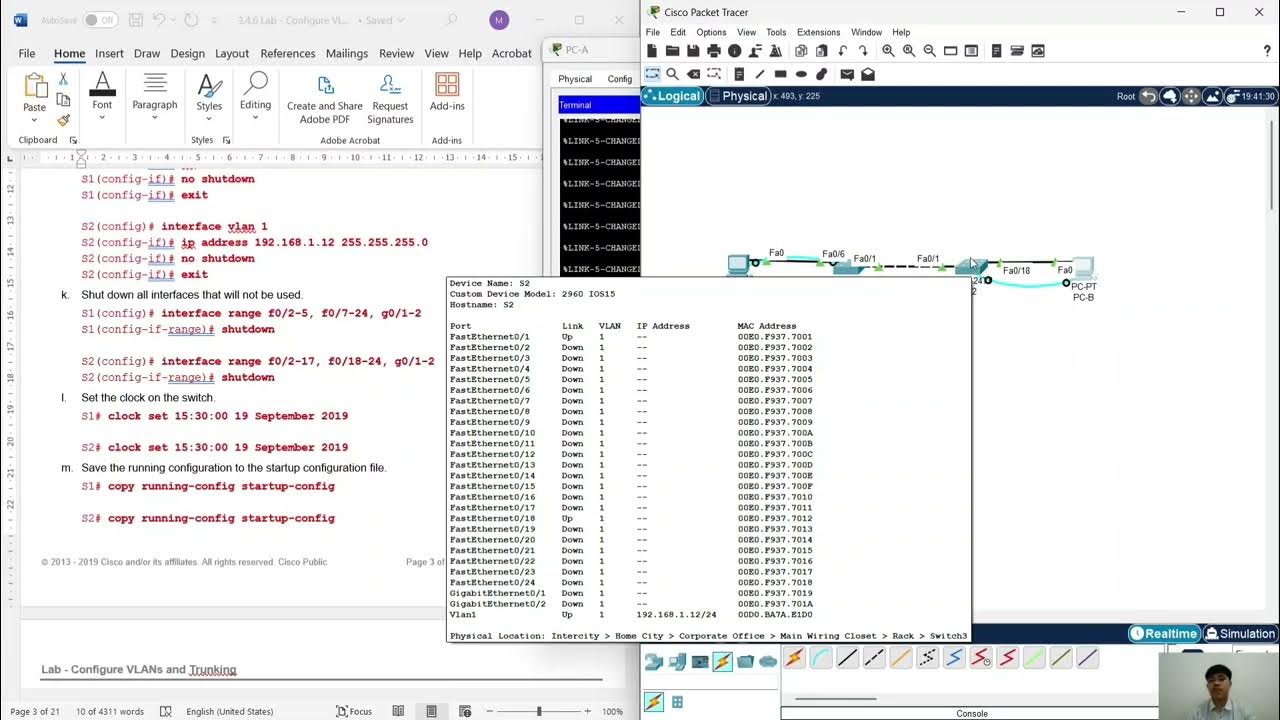
Configure VLANs and Trunking.
Rancang Bangun Vlan di Aplikasi Cisco Paket Tracer
VLAN dan Trunk - Penjelasan dan Latihan - 3.6.1 Implement VLANs & Trunking
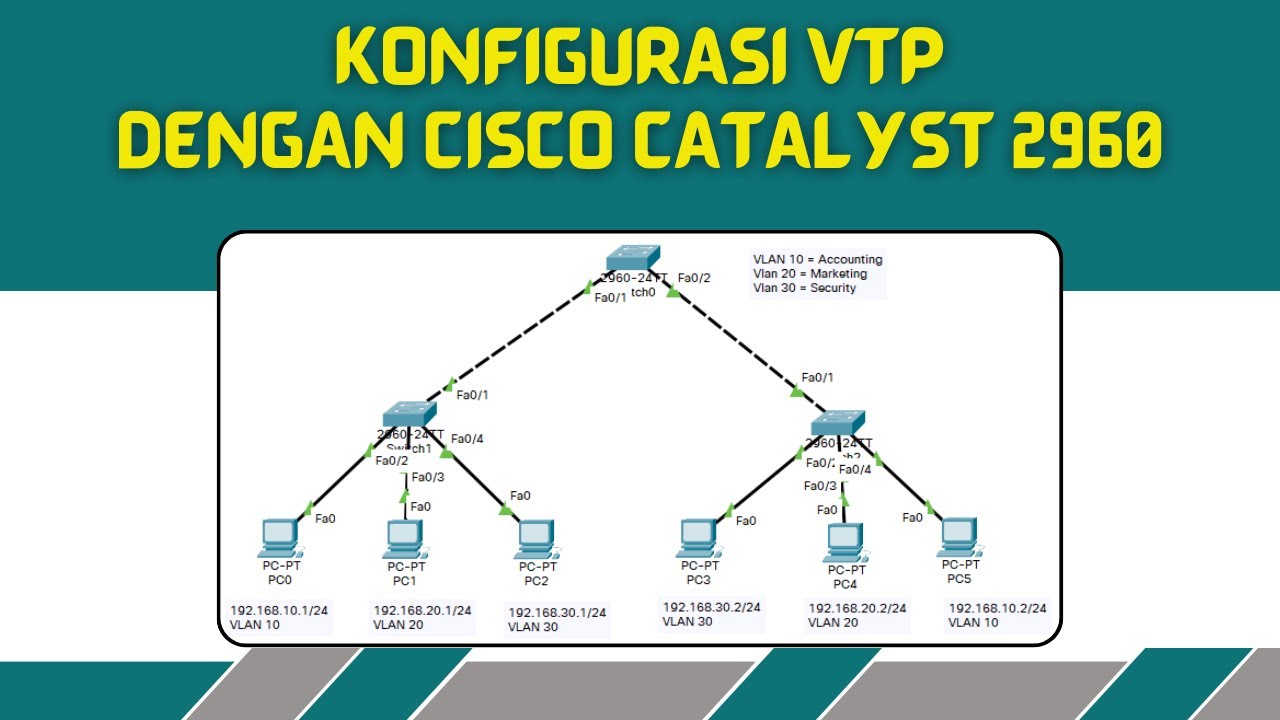
KONFIGURASI VLAN TRUNKING PROTOKOL DENGAN CISCO CATALYST 2960
Router on a Stick Inter-VLAN Routing | CISCO Certification

Aula 04 - Curso de Redes de Computadores Básico Mão na Massa - Gateway e Interface Vlan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
