Mr. Lahasky - APUSH Period 4 - Lecture #20 - Awakening and Reform
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the transformative social reform movements of the antebellum period, driven by the Second Great Awakening. It highlights the emergence of various reformers addressing education, alcoholism, mental health, gender equality, and slavery. Figures like Horace Mann, Dorothea Dix, and Elizabeth Cady Stanton are celebrated for their persistent efforts to instigate change despite societal opposition. The interplay of these movements underscores a collective quest for justice, illustrating how ordinary Americans can catalyze significant social progress. Ultimately, the legacy of these reformers laid foundational principles for future civil rights advancements in the United States.
Takeaways
- 😀 The antebellum period saw significant social reform movements influenced by the Second Great Awakening.
- 😀 Ordinary Americans played a crucial role in these movements, challenging the idea that only extraordinary individuals shape history.
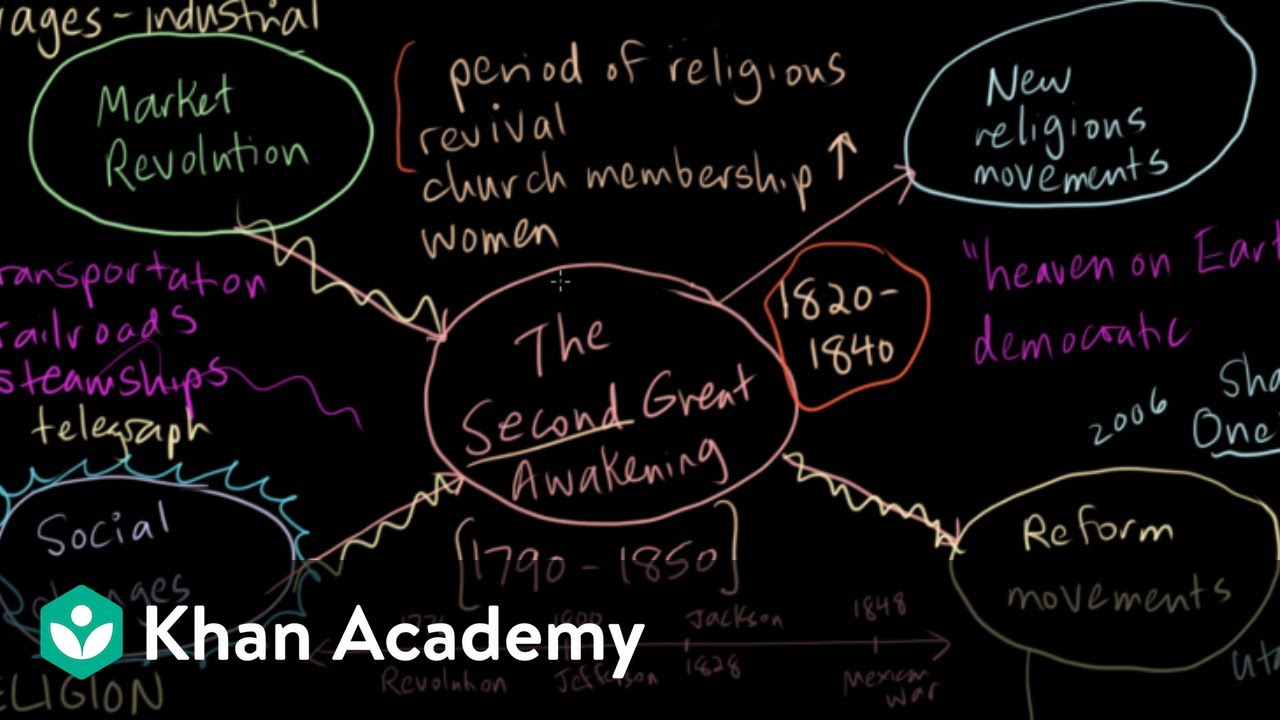
- 😀 The Second Great Awakening was a religious revival that inspired activism in various social issues, including education and abolition.
- 😀 Reformers like Dorothea Dix advocated for better treatment of the mentally ill and prison reforms, significantly impacting societal attitudes.
- 😀 Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Lucretia Mott were key figures in the women's rights movement, pushing for gender equality and suffrage.
- 😀 The temperance movement emerged as a response to alcohol abuse, highlighting its perceived negative impact on society.
- 😀 The abolitionist movement gained momentum from the Second Great Awakening, with leaders like Frederick Douglass and Sojourner Truth advocating for the end of slavery.
- 😀 Educational reforms were spearheaded by figures like Horace Mann, promoting public schooling and increasing literacy rates.
- 😀 The interconnectedness of various reform movements showcased a broader struggle for rights, as abolitionists often supported women's suffrage and vice versa.
- 😀 While progress was slow, the efforts of antebellum reformers laid essential groundwork for future advancements in American social justice.
Q & A
What was the main social context of the antebellum period in America?
-The antebellum period was characterized by significant social upheaval as America grappled with issues like education, mental health, gender equality, alcohol abuse, and slavery.
How did the Second Great Awakening influence social reform movements?
-The Second Great Awakening renewed interest in Protestant Christianity, leading to a wave of reform efforts addressing various societal issues and inspiring individuals to seek change.
In what ways did the Second Great Awakening differ from the First?
-Unlike the First Great Awakening, which unified various denominations, the Second Great Awakening was more diverse and contributed to increasing sectional divisions within the country.
Who were some key figures in the public education reform movement?
-Horace Mann was a prominent leader in the common schools movement, advocating for public education and emphasizing the moral education of students.
What role did women play in the antebellum reform movements?
-Women played crucial roles in various reform movements, including the temperance movement and prison reform, and were central to the early women's rights movement.
What was the significance of the Seneca Falls Convention in 1848?
-The Seneca Falls Convention marked a pivotal moment in the women's rights movement, where leaders like Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Lucretia Mott advocated for gender equality and women's suffrage.
How did abolitionists differ in their views on slavery during the antebellum period?
-While many northerners opposed slavery for political or economic reasons, abolitionists advocated for its moral abolition, leading movements that included prominent figures like Frederick Douglass and Sojourner Truth.
What were some experimental communities formed during the Second Great Awakening?
-Communities such as the Shakers, Oneida, and Mormons formed as experimental religious groups that sought to create utopian societies with unique practices.
What challenges did reformers face in their efforts?
-Reformers often encountered opposition, ridicule, and slow progress in their campaigns for change, but their persistence laid the groundwork for future advancements.
What lasting impact did the antebellum reform movements have on American society?
-The reform movements set the stage for significant social changes, leading to improvements in education, mental health care, women's rights, and ultimately contributing to the abolition of slavery.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)