LAST LESSON OF UNIT 4
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging lecture, the instructor covers the Second Great Awakening and the Age of Reform, highlighting key movements such as religious revival, social reform, and moral responsibility. Topics like temperance, abolition, women’s rights, education, and prison reform are explored, showing how these movements were influenced by religious and democratic ideals. The lecture emphasizes the profound impact these movements had on shaping American society, promoting values of equality, individual responsibility, and social change. The instructor also provides students with guidelines for assignments and extra credit, encouraging them to actively engage in discussions and research.
Takeaways
- 😀 The teacher emphasizes the importance of completing all four weekly discussion questions by Friday at 11:59 PM for full credit.
- 😀 Missing assignments cannot be made up this quarter; if not turned in, they will result in a zero.
- 😀 Extra credit opportunities are available by contributing unfamiliar words and their definitions to the word wall or skolar wall for 10 points.
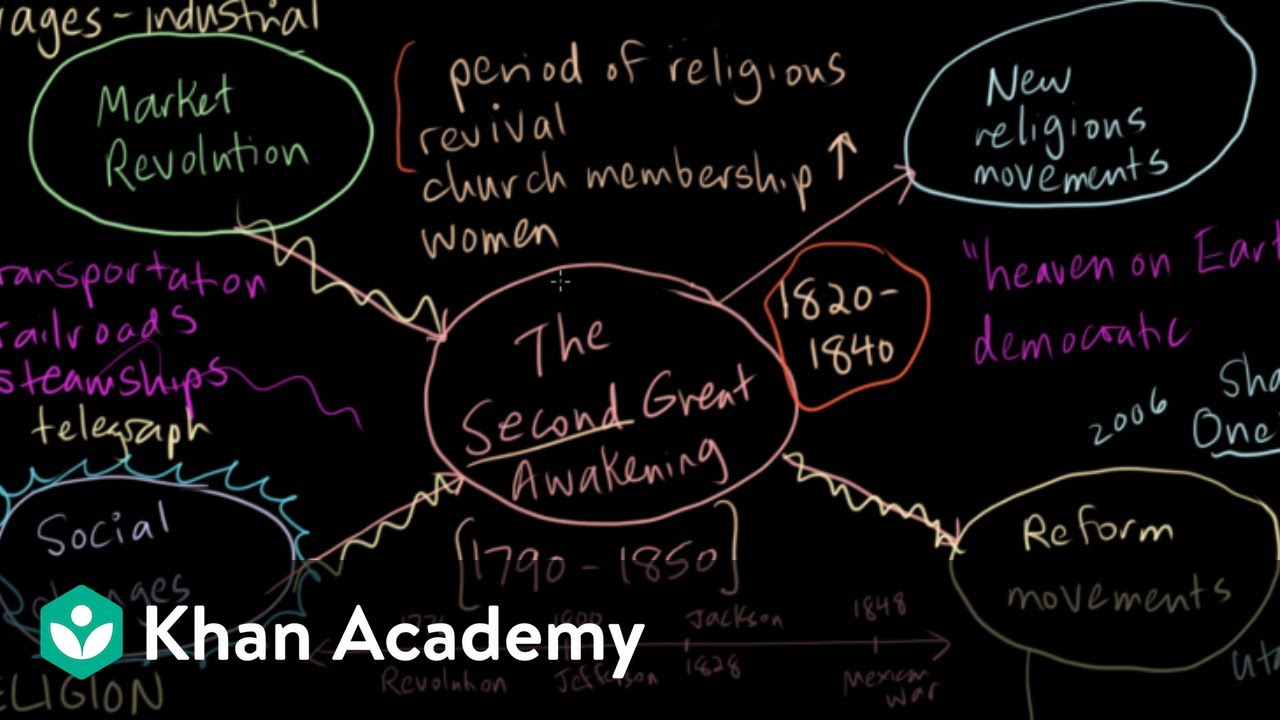
- 😀 The Second Great Awakening was a religious movement in the early 1800s that emphasized personal salvation, moral reform, and social responsibility.
- 😀 The Age of Reform, influenced by the Second Great Awakening, focused on issues like women's rights, prison reform, education, and temperance.
- 😀 Key figures of the Abolitionist Movement included William Lloyd Garrison and Frederick Douglass, who advocated for the end of slavery.
- 😀 The Women's Rights Movement, especially the Seneca Falls Convention of 1848, fought for gender equality and voting rights, paving the way for the 19th Amendment.
- 😀 Educational reform aimed at creating public schools accessible to all, with figures like Horace Mann advocating for tax-funded schools and teacher training.
- 😀 Prison and asylum reform sought better conditions for prisoners and the mentally ill, with leaders like Dorothea Dix advocating for humane treatment.
- 😀 All the reform movements, though varied in goals, were connected by the shared belief in individual responsibility and improving society, inspired by the Second Great Awakening.
Q & A
What is the focus of today's lesson?
-Today's lesson covers the Age of Reform and the Second Great Awakening, two interconnected movements that aimed to promote social reforms and personal religious responsibility in the early 19th century.
Why was the Second Great Awakening important?
-The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant Evangelical revival that emphasized personal salvation, moral reform, and social responsibility. It encouraged individuals to take an active role in their faith and in improving society.
What were the main social reforms inspired by the Second Great Awakening?
-The Second Great Awakening inspired a range of social reforms, including movements for women's rights, abolition of slavery, temperance (anti-alcohol), and prison and asylum reforms.
What was the Age of Reform?
-The Age of Reform, which took place from the 1820s to the 1850s, was a period of various social movements that sought to address issues such as slavery, women's rights, alcohol consumption, and public education. These movements were largely inspired by religious and democratic ideals from the Second Great Awakening.
How did the Age of Reform relate to the Second Great Awakening?
-The Age of Reform was directly inspired by the democratic and religious principles promoted during the Second Great Awakening, particularly the idea that individuals had a moral duty to reform society.
What was the temperance movement, and what did it aim to achieve?
-The temperance movement aimed to reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption, which was linked to social issues such as domestic violence and poverty. It gained traction in the 1820s with the formation of the American Temperance Society.
Who were some key figures in the abolitionist movement?
-Key figures in the abolitionist movement included William Lloyd Garrison and Frederick Douglass, who worked to expose the brutality of slavery and advocate for its abolition in the United States.
What was the role of the women's rights movement during this time?
-The women's rights movement fought for gender equality, particularly focusing on voting rights. It was highlighted by the 1848 Seneca Falls Convention, which produced the Declaration of Sentiments calling for women's equality.
What were some goals of the educational reform movement?
-The educational reform movement aimed to establish a public school system that was accessible to all children, emphasizing the importance of education for a functioning democratic society. Key figures like Horace Mann advocated for tax-funded public schools and better teacher training.
What was the prison and asylum reform about?
-Prison and asylum reform focused on improving conditions for prisoners and the mentally ill. Advocates like Dorothea Dix campaigned for humane treatment, separate facilities, and rehabilitation rather than punishment for the incarcerated and mentally ill.
How were all these reform movements connected?
-All these reform movements were united by the belief in personal responsibility and social reform, ideas that stemmed from the Second Great Awakening. Reformers sought to improve society by addressing moral injustices and advocating for a more equal and democratic society.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)