Organic Biochemistry ScreenCast Session 6 Nucleic Acids.mp4
Summary
TLDRIn this informative screencast on the chemistry of nucleic acids, Mr. Gailes explains the essential role of nucleic acids as genetic molecules in eukaryotic cells. He outlines the structure of nucleotides, the building blocks of nucleic acids, detailing their components: a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The lecture covers the distinctions between DNA and RNA, emphasizing their respective roles in storing and transmitting genetic information. Mr. Gailes also introduces key concepts such as phosphodiester linkages and complementary base pairing, providing a comprehensive overview of the molecular basis of heredity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Digital technology has revolutionized communication, making it faster and more accessible than ever.
- 🌍 The rise of social media has transformed how people interact and share information globally.
- 📱 Mobile devices have become essential tools for communication, allowing users to connect anytime and anywhere.
- 🧑🤝🧑 Online platforms facilitate diverse social interactions, impacting relationships and community building.
- 📉 Traditional media consumption has declined as audiences shift towards digital content, altering the media landscape.
- 🔍 Big data analytics enables businesses to understand consumer behavior and tailor communication strategies.
- 🛡️ Digital technology raises concerns regarding privacy and data security, prompting discussions about ethical standards.
- 🗣️ The use of digital communication tools enhances collaboration in professional environments, improving efficiency.
- 🎨 Digital art forms, including video art, have gained prominence, reflecting cultural and political narratives.
- 👩🏫 Digital education tools have transformed learning experiences, providing students with more interactive and personalized opportunities.
Q & A
What are nucleic acids and why are they important?
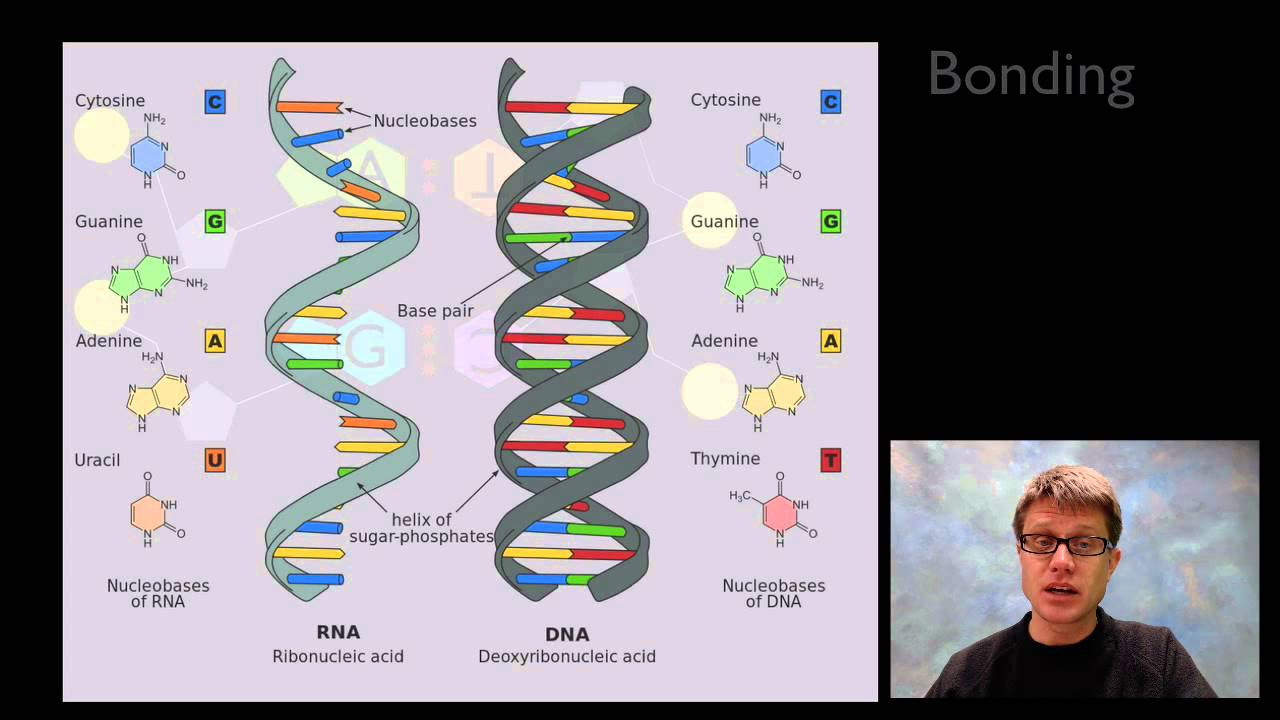
-Nucleic acids are organic acids that contain phosphate groups and are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Their primary function is to store and transmit genetic information across generations.
What components make up a nucleotide?
-A nucleotide consists of three basic parts: a five-carbon sugar (pentose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the significance of the sugar phosphate backbone in nucleic acids?
-The sugar phosphate backbone is formed by phosphodiester linkages between nucleotides, providing structural integrity and directionality to the nucleic acid strand.
How do nucleotides bond to form nucleic acids?
-Nucleotides bond together through dehydration synthesis, which removes water to form a strong covalent bond called a phosphodiester linkage.
What are the two classes of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids?
-The two classes of nitrogenous bases are purines, which include adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines, which include thymine, cytosine, and uracil.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
-RNA (ribonucleic acid) is single-stranded and contains ribose sugar, while DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is double-stranded and contains deoxyribose sugar. Additionally, RNA uses uracil instead of thymine.
What is complementary base pairing?
-Complementary base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids, where adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and guanine pairs with cytosine.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in nucleic acids?
-Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases stabilize the double helix structure of DNA, with guanine and cytosine forming three hydrogen bonds and adenine and thymine forming two.
What is the primary function of DNA?
-The primary function of DNA is to store genetic information that determines traits, which is essential for inheritance and the functioning of living organisms.
What is the process of transcription in relation to RNA?
-Transcription is the process by which the genetic code in DNA is copied into RNA, which then carries this information to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)