Proteins and Nucleic Acids
Summary
TLDRIn this educational screencast, we explore proteins and nucleic acids, crucial biomolecules that play essential roles in genetic information transfer and bodily functions. Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are responsible for transmitting genetic traits through specific base pair combinations. DNA's unique double-helix structure and its role in coding for proteins highlight its importance. Meanwhile, proteins are formed from 20 different amino acids linked by peptide bonds, creating polypeptides that must be properly folded to function. The video emphasizes the intricate processes behind these biomolecules, showcasing their significance in biology.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Nucleic acids, primarily DNA and RNA, are essential for transferring genetic information from one generation to the next.
- 🔍 DNA is located in the nucleus of the cell and has a characteristic double-helix shape.
- 📚 DNA consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (ribose), and four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- 🔗 The specific pairing of bases (A with T and C with G) determines the genetic makeup of an organism.
- 🧬 Genes are segments of DNA that dictate specific traits, such as hair color, through combinations of base pairs.
- ⚠️ Mutations in DNA can occur due to errors in replication, leading to variations in traits inherited from parents.
- 💪 Proteins serve a variety of functions in the body, including enzymatic, structural, storage, and hormonal roles.
- 🍃 Proteins are constructed from 20 different amino acids, which are linked through peptide bonds.
- 💧 Dehydration synthesis is the process that connects amino acids, producing water molecules with each bond formed.
- 📦 A polypeptide chain must be folded into a specific shape in the Golgi apparatus to function properly as a protein.
Q & A
What are the main functions of nucleic acids?
-Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, primarily function to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next.
What is the structure of DNA?
-DNA has a double-helix shape, resembling a twisted ladder, made up of a sugar-phosphate backbone and four types of nitrogenous bases.
What components make up the DNA molecule?
-DNA is composed of sugars, phosphates, and four different nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.
How do DNA and RNA differ in structure?
-DNA is double-stranded and has a double-helix structure, while RNA is single-stranded.
What is a gene?
-A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the base pair combination responsible for a specific trait.
How do mutations in DNA occur?
-Mutations in DNA can occur due to errors in replication, leading to differences in the genetic code compared to the parents.
What roles do proteins play in the body?
-Proteins serve various functions including enzymes, structural components, storage, and hormones for signaling.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
-Proteins are made from 20 different amino acids that combine in various sequences to form polypeptides.
What is dehydration synthesis in protein formation?
-Dehydration synthesis is the process by which amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide, resulting in the release of water molecules.
What happens to a polypeptide before it becomes a functional protein?
-A polypeptide must be folded and packaged in the Golgi apparatus to achieve its specific shape before it can function as a protein.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud

4 Biological Molecules: Structure and Their Function || A quick guide to Understanding biomolecules

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)
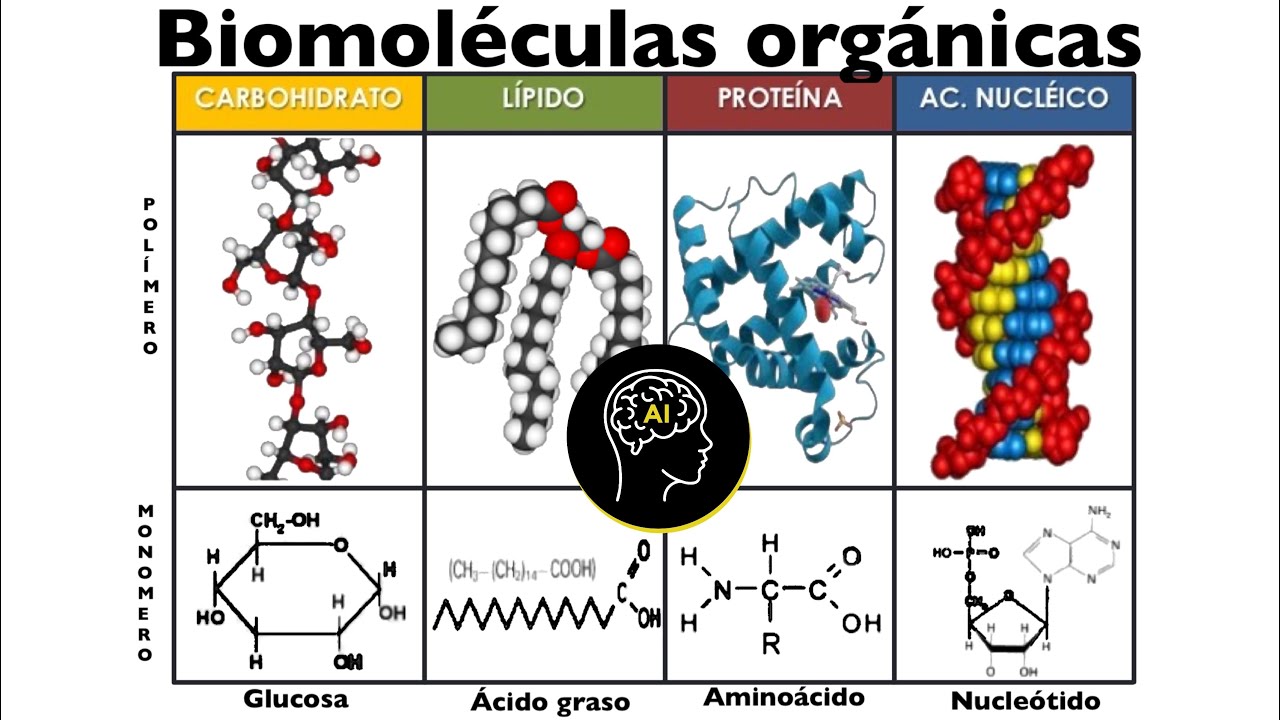
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

Biomolecules (Updated 2023)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)