Anticholinergic Bronchodilators (OVERVIEW) | Parasympatholytic Agents
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a concise overview of anticholinergic bronchodilators, a key class of medications used to treat obstructive respiratory conditions like asthma and COPD. It explains how these drugs work by blocking acetylcholine to relax airway muscles, highlighting three types: short-acting for acute attacks, long-acting for maintenance, and ultra-long-acting for prolonged control. The video also covers examples of each type and discusses common side effects, such as tachycardia and dry mouth. A reminder emphasizes the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for medical advice.
Takeaways
- 😀 Anticholinergic bronchodilators are used to treat obstructive respiratory conditions like asthma, chronic bronchitis, and COPD.
- 🩺 These medications act on the parasympathetic nervous system by blocking acetylcholine, promoting relaxation of smooth muscles in the airways.
- 🚑 There are three primary types of anticholinergic bronchodilators: short-acting, long-acting, and ultra-long-acting.
- ⚡ Short-acting agents are rescue drugs for acute bronchospasm, such as during an asthma attack.
- 📅 Long-acting agents are maintenance medications for chronic conditions like stable asthma or COPD.
- ⏳ Ultra-long-acting agents have a similar function to long-acting agents and help maintain control over chronic bronchospasm.
- 💊 Examples of short-acting agents include ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) and oxytropium bromide (OxyVent).
- 🛡️ Aclidinium bromide (Tudorsa) is an example of a long-acting anticholinergic agent.
- 🌟 Tiotropium bromide (Spiriva) and umeclidinium (Anoro) are examples of ultra-long-acting agents.
- ⚠️ Common side effects of anticholinergic bronchodilators include tachycardia, dry mouth, and increased body temperature.
Q & A
What are anticholinergic bronchodilators used for?
-Anticholinergic bronchodilators are used to treat obstructive respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
How do anticholinergic bronchodilators work?
-These medications act on the parasympathetic nervous system by blocking acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that causes the constriction of smooth muscles in the airways, thus promoting relaxation and alleviating bronchospasm.
What are the three primary types of anticholinergic bronchodilators?
-The three primary types are short-acting, long-acting, and ultra-long-acting anticholinergic agents.
What is the role of short-acting anticholinergic agents?
-Short-acting anticholinergic agents, also known as rescue drugs, are used for the immediate treatment of acute bronchospasm, such as during an asthma attack.
Can you provide an example of a long-acting anticholinergic agent?
-An example of a long-acting anticholinergic agent is aclidinium bromide, marketed as Tudorza.
What is the difference between long-acting and ultra-long-acting anticholinergic agents?
-Long-acting agents are used for maintaining control of chronic bronchospasm, while ultra-long-acting agents have a similar mechanism but provide an extended duration of action for even longer control.
What are some common examples of ultra-long-acting anticholinergic agents?
-Examples of ultra-long-acting anticholinergic agents include tiotropium bromide (Spiriva) and umeclidinium (Anoro).
What are some common side effects of anticholinergic bronchodilators?
-Common side effects include tachycardia, dry mouth, increased body temperature, cessation of sweating, dilated pupils, fluid retention, and in some cases, anxiety.
Why is it important for healthcare professionals to be familiar with anticholinergic medications?
-Understanding anticholinergic medications is crucial for healthcare professionals, especially respiratory therapists, as they are commonly used in managing patients with respiratory conditions.
What should patients do if they need medical advice regarding their treatment with anticholinergic bronchodilators?
-Patients should speak with their doctor for personalized medical advice and treatment regarding their use of anticholinergic bronchodilators.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines, Symptoms, Medicine Lecture USMLE

COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) Nursing Interventions Management Treatment NCLEX Part 2
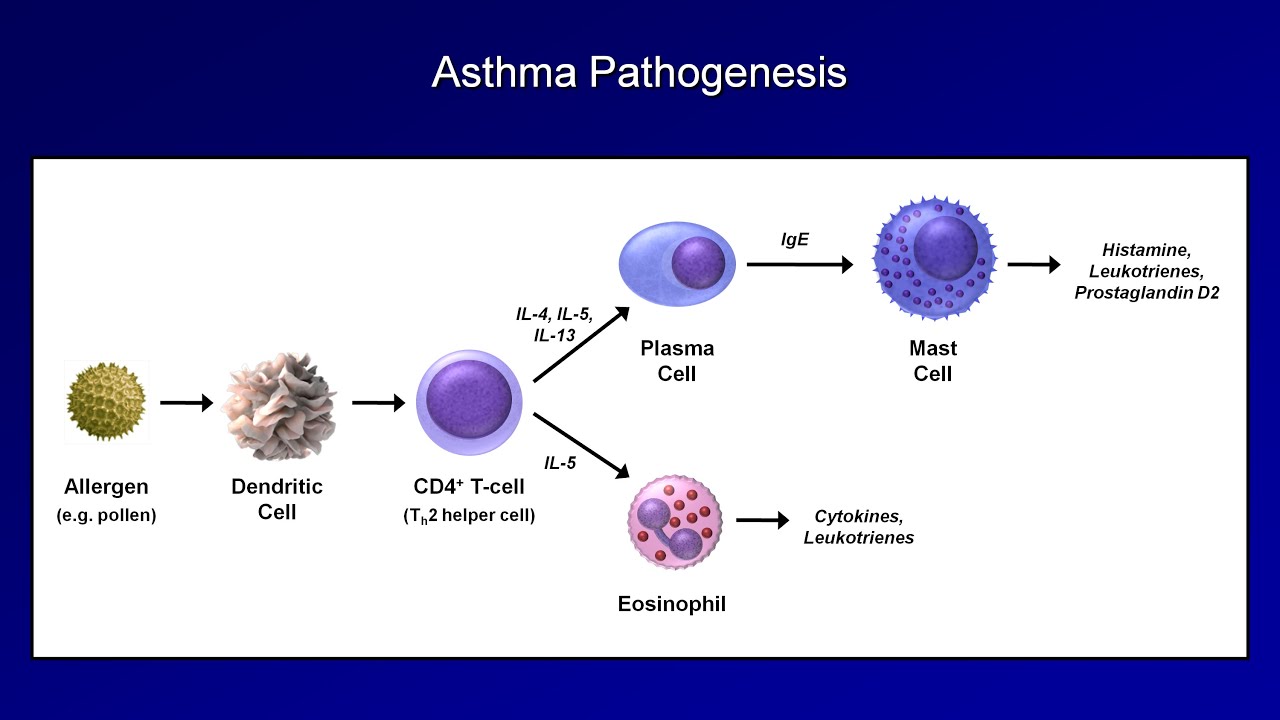
Asthma and COPD - Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology

Pharmacology: Drugs for Asthma and COPD, Animation
Spirometry, Lung Volumes & Capacities, Restrictive & Obstructive Diseases, Animation.

Hypertension/Angina Medications - Pharmacology - Cardiovascular | @LevelUpRN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
