priv
Summary
TLDRIn this educational script, a class discussion on Newton's method for solving nonlinear equations unfolds, with a student, Ben Campbell, intriguingly suggesting that Joseph Raphson, not Newton, was the true inventor. The narrative pivots to a game show scenario, where Ben applies statistical reasoning to increase his chances of winning a car by switching doors, highlighting the importance of variable change in decision-making. The script concludes with a lesson on overcoming emotional biases and trusting in math, as Ben secures the car over a goat.
Takeaways
- 📚 Newton's method is a technique used to solve nonlinear equations by iteratively approximating the root of a function.
- 🕵️♂️ Joseph Raphson, not Isaac Newton, is credited by some as the original author of the method, but Newton's name is more widely recognized due to better publicity.
- 📉 Newton's method can fail if the initial guess is too far from the actual root, highlighting the importance of choosing a good starting point.
- 🎓 The script humorously suggests that after 1700, little is known about Raphson, except for his discovery of the cabala, which is a playful jab at historical obscurity.
- 🚗 The 'game show host problem' is a classic probability puzzle that illustrates the concept of conditional probability and the value of changing one's initial choice based on new information.
- 🧠 Ben Campbell, a student in the script, correctly applies statistical reasoning to the game show problem, demonstrating the power of logic over intuition.
- 🔄 The concept of 'variable change' is introduced as a key factor in decision-making, emphasizing the need to reassess situations when new information becomes available.
- 📈 After the game show host opens a door, the probability of winning the car changes from 33.3% to 66.7% if one decides to switch doors, showcasing the impact of conditional probability.
- 🏆 Ben's decision to switch doors is rewarded with a new car, symbolizing the triumph of rational analysis over emotional decision-making.
- 📚 The script ends with a reminder to students to pick up their graded papers, tying back to the educational setting of the conversation.
Q & A
What is Newton's method and how is it used?
-Newton's method is a numerical technique used to find the roots of a real-valued function. It is particularly useful for solving nonlinear equations.
Who is credited with discovering Newton's method?
-Isaac Newton is commonly credited with the method, but Joseph Raphson also published the same method 50 years earlier.
Why didn't Joseph Raphson get credit for Newton's method?
-Raphson did not get as much credit as Newton possibly due to Newton having a better publicist and because after 1700, very little is known about Raphson's life and work.
What is a drawback of Newton's method?
-If the starting value is too far from the true zero, Newton's method can fail to converge to the correct solution.
What is the 'game show host problem' mentioned in the script?
-The 'game show host problem' is a hypothetical scenario where a contestant on a game show must choose between three doors, with one hiding a car and the others goats. The host, knowing what's behind the doors, opens one with a goat and offers the contestant a chance to switch their choice.
Why should Ben switch his choice of doors in the 'game show host problem'?
-Ben should switch his choice because after the host opens a door with a goat, the probability of the car being behind one of the remaining doors changes. If Ben initially chose a door with a 33.3% chance of having the car, switching would give him a 66.7% chance of winning the car.
What is the significance of the Monty Hall problem in the script?
-The Monty Hall problem illustrates the importance of understanding probability and variable change. It demonstrates that making decisions based on statistical reasoning can lead to better outcomes than relying on intuition or fear.
What does the script suggest about the role of emotions in decision-making?
-The script suggests that emotions like paranoia and fear can cloud judgment and lead to suboptimal decisions. It encourages using logic and mathematical reasoning to make better choices.
How does the script use humor to discuss serious mathematical concepts?
-The script uses humor by comparing the historical credit for Newton's method to modern public relations and by joking about Raphson's discovery of the Kabbalah before Madonna.
What lesson does the script offer about the importance of considering variable change?
-The script emphasizes that accounting for changes in variables, as in the Monty Hall problem, can significantly impact the outcome of a decision and lead to more favorable results.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Game Theory Scene | 21(2008) | Now Playing

METODE NUMERIK P7 PART 1/2 | METODE NEWTON-RAPHSON UNTUK MENYELESAIKAN PERSAMAAN NON LINIER
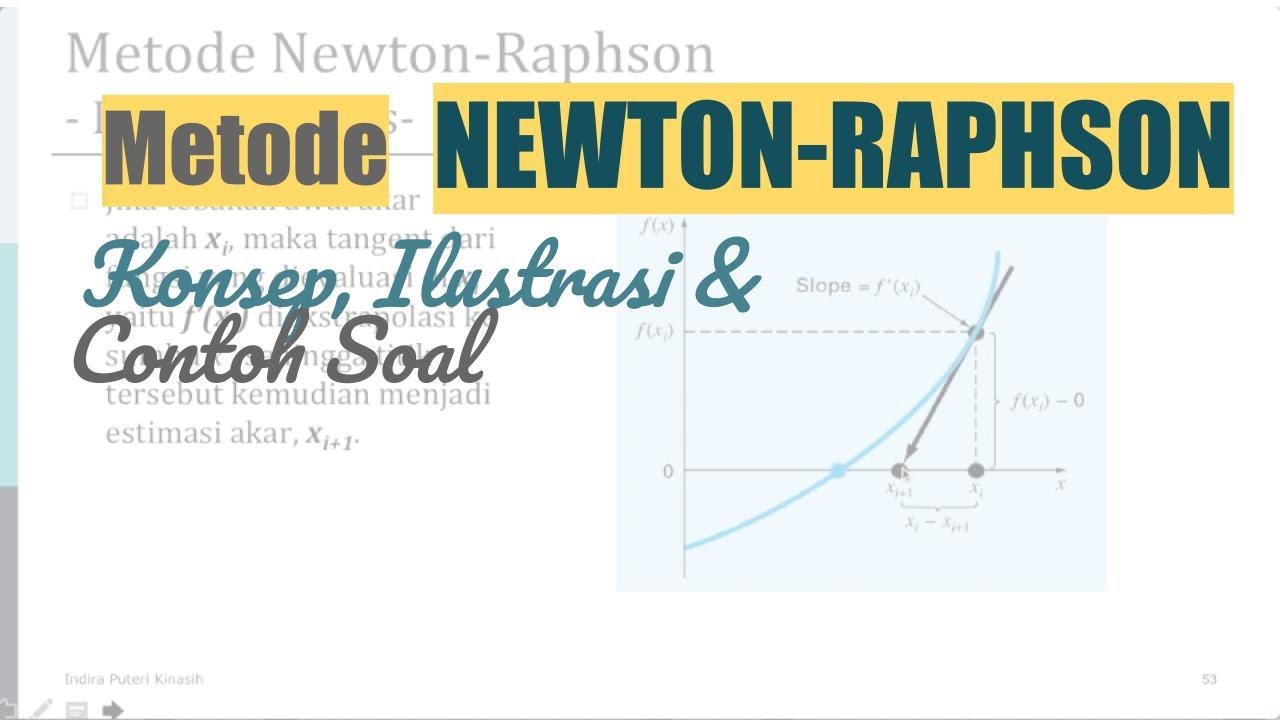
Metode Newton Raphson (Konsep & Contoh) [Metode Numerik]

Newton Raphson Load Flow Solution - 3 Bus - Part 1 of 3

8. METODE LELARAN TITIK TETAP - FIX POINT ITERATION - METODE NUMERIK

Optimisasi Statistika - Kuliah 6 part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
