Penurunan Persamaan Difraksi Cahaya pada Kristal (Hukum Bragg)
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the diffraction of light on crystals, starting with an introduction to crystal structures versus amorphous materials. It details the process of light diffraction, using mathematical equations to describe the angles and distances involved. The video also discusses practical applications, like analyzing crystal samples using X-ray diffraction. By understanding the interference patterns, researchers can determine the crystal structure of various materials. The explanation is supplemented with visual aids and step-by-step derivation of relevant equations.
Takeaways
- 📉 The video discusses the derivation of the Law of Diffraction related to the behavior of light on crystals.
- 💡 The Law of Motion governs the diffraction of light on crystals, which involves understanding atomic structures.
- 🔬 Crystals have a periodic atomic structure, unlike amorphous materials with irregular atomic arrangements.
- 💎 Common examples of crystals include diamonds, snowflakes, iron, and copper, while non-crystalline materials include plastics and glass.
- 🌈 The video explains how light, when shined on a crystal, gets diffracted, with the photons being reflected or scattered.
- 📐 The derivation involves calculating the wavelength differences between diffracted light paths and determining the diffraction angle.
- 🔍 The script demonstrates the use of trigonometric functions to analyze the diffraction patterns and calculate the wavelength components.
- 🧪 The general equation for light diffraction in crystals is introduced and explained step by step.
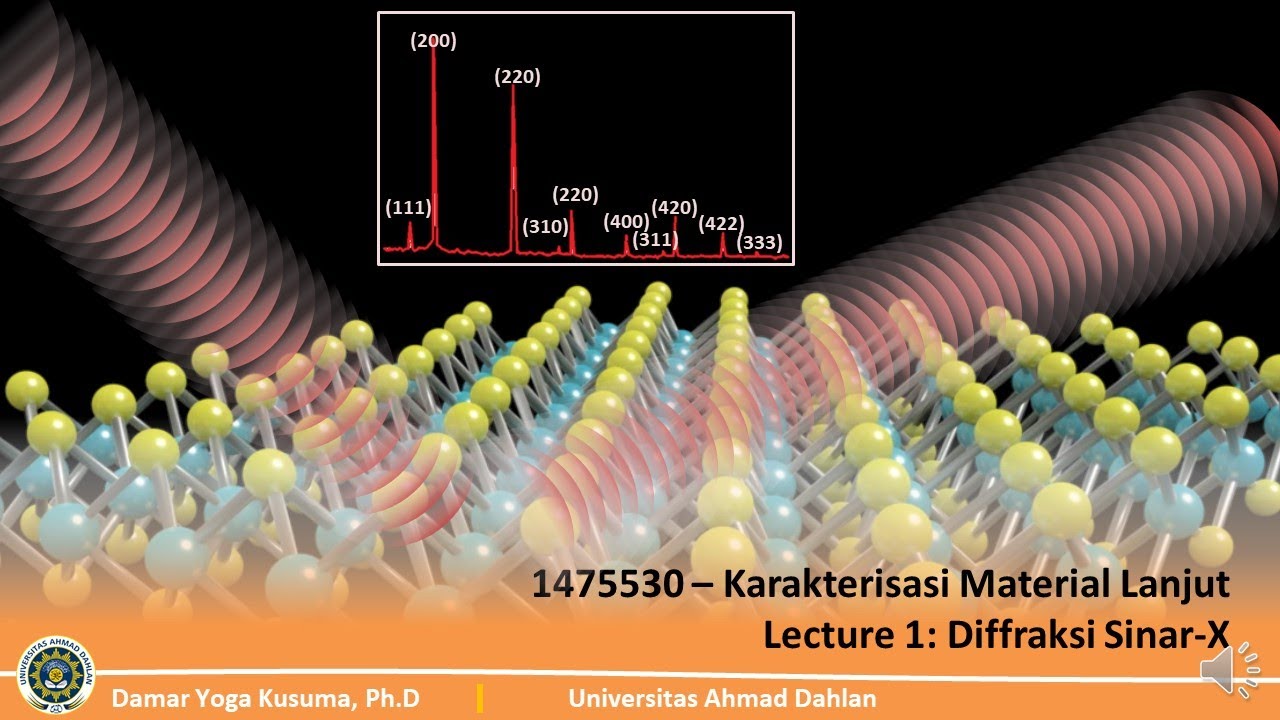
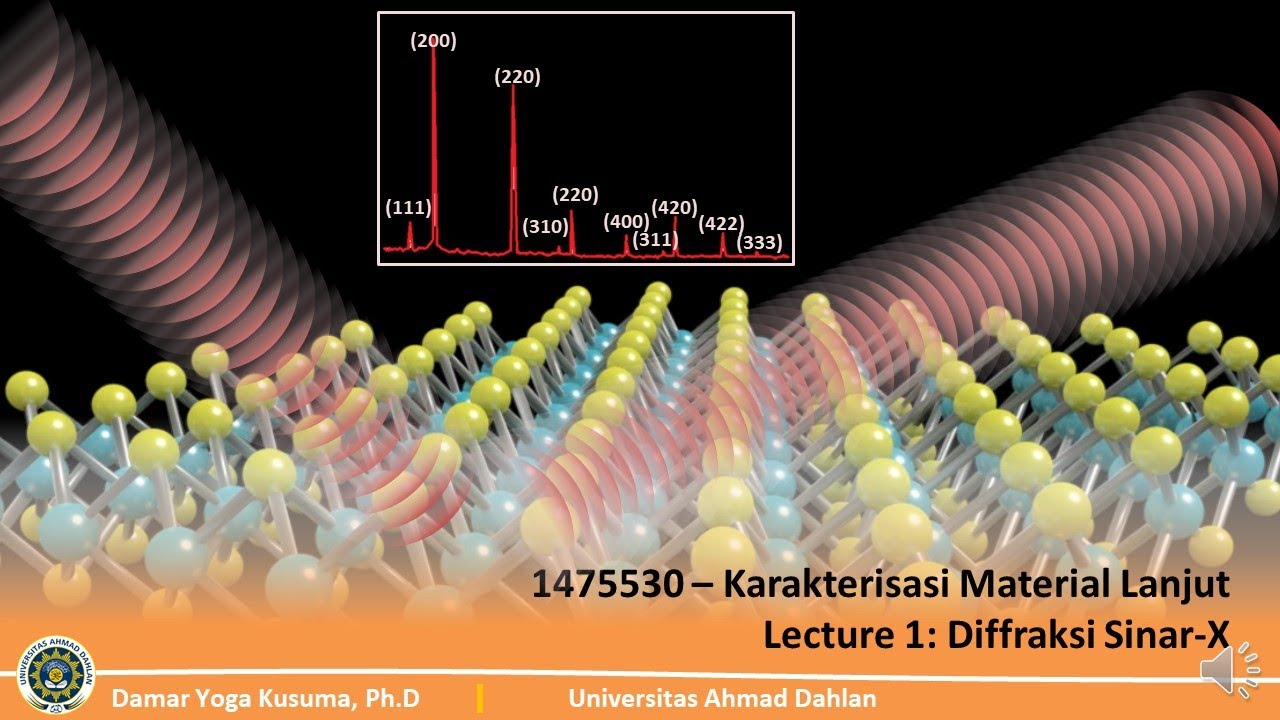
- ⚙️ The practical application of this law is seen in research, where X-ray diffraction patterns of sample powders help in identifying the structure of materials.
- 📊 The video concludes by discussing how the diffraction pattern intensity is plotted against the angle to analyze material properties.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the derivation of the diffraction equation related to the diffraction of light on a crystal.
What does the term 'crystal' refer to in the context of this video?
-In this video, a 'crystal' refers to a material that has a periodic and ordered atomic structure, in contrast to an amorphous structure, which lacks such order.
What examples of crystals are mentioned in the video?
-Examples of crystals mentioned in the video include diamonds, snowflakes, iron, copper, and salt.
What does the term 'diffraction of light' mean in the context of this video?
-In the context of the video, 'diffraction of light' refers to the bending and spreading of light waves when they encounter a crystal structure, resulting in a specific diffraction pattern.
How does the video explain the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection?
-The video explains that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, which is a principle used to understand the diffraction pattern when light interacts with a crystal.
What is the significance of the distance 'd' in the context of diffraction?
-The distance 'd' represents the spacing between atomic planes in a crystal, which is crucial in determining the diffraction pattern when light interacts with the crystal.
What is the role of the wavelength 'λ' in the diffraction equation?
-The wavelength 'λ' represents the wavelength of the light being diffracted, and it is a key component in the diffraction equation that describes the relationship between the diffraction angle, wavelength, and crystal spacing.
How is the diffraction equation derived in the video?
-The diffraction equation is derived by considering the path difference between light waves scattered by different atomic planes within the crystal and applying trigonometric relationships to these paths.
What practical application of the diffraction equation is mentioned in the video?
-The video mentions that the diffraction equation is used in scientific research, particularly in analyzing diffraction patterns obtained from X-ray diffraction experiments on crystalline samples.
How does the video describe the experimental setup for studying diffraction?
-The video describes an experimental setup where a sample of crystalline powder is exposed to X-rays, and the resulting diffraction pattern is measured by a detector, allowing for the determination of the crystal structure.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 1b)

Solids, Its Properties, and the Intermolecular Forces | Crystalline Solids and Amorphous Solids

10.3 Solids
UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 1c)

How do crystals work? - Graham Baird

Episode1 # Motif # Unit cell # Lattice # Law of Bravai's # Interfacial Angle
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
