Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Summary
TLDRThis educational video offers an in-depth overview of pharmacology, focusing on the distinction between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. It explains key concepts such as bioavailability, first-pass effect, drug metabolism, volume of distribution, half-life, and elimination. The script simplifies complex pharmacokinetic principles, providing mnemonics and examples to aid understanding, and emphasizes the importance of these concepts in clinical practice.
Takeaways
- 📚 Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are two fundamental concepts in pharmacology. Pharmacokinetics deals with how drug concentration changes over time, while pharmacodynamics is about the relationship between drug concentration and its effects.
- 🔑 A helpful mnemonic for remembering the difference is 'pharmacokinetics' sounds like 'kinetics tick', associating the concept with time, as a clock ticks.
- 💊 Bioavailability refers to the fraction of a drug that reaches systemic circulation in an unchanged form. IV formulations have 100% bioavailability, whereas oral formulations have less due to the first-pass effect.
- 🚫 The first-pass effect is the pre-systemic metabolism or elimination of a drug, primarily occurring in the liver and intestines, which reduces the overall bioavailability of orally administered drugs.
- 🌡 Metabolism involves the conversion of drugs into metabolites and is categorized into phase 1 (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) and phase 2 (conjugation like sulfation, methylation, acetylation, and glucuronidation).
- 👴 Geriatric patients tend to favor phase 2 metabolism, which can lead to adverse effects if they are slow metabolizers due to the potential buildup of drugs in their system.
- 📦 Volume of distribution is a theoretical measure of the space within the body that a drug occupies relative to its plasma concentration, indicating where the drug accumulates in the body.
- ⏳ Half-life is the time it takes for the concentration of a drug in the body to be reduced by half, and it's crucial for understanding how long it takes to reach steady-state concentrations.
- 📉 Zero-order elimination has a constant rate of elimination, while first-order elimination's rate is proportional to the drug concentration, with most drugs following first-order kinetics.
- 🚰 Elimination is the process by which a drug is cleared from the body, and it can be affected by diseases that impair cardiac, hepatic, or renal function.
- 🔄 Steady state is reached when the drug concentration in the body remains constant over time, determined by half-life, while the magnitude of the steady-state concentration is influenced by the drug's clearance and dosage.
Q & A
What is the main difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
-Pharmacokinetics describes the relationship between drug concentration and time, focusing on how drug concentration changes over time. Pharmacodynamics, on the other hand, is a more general term that describes the relationship between drug concentration and the effect of the drug.
What does the term 'bioavailability' refer to in pharmacology?
-Bioavailability refers to the fraction of a drug that is available to the systemic circulation in an unchanged form after it has undergone various processes that may change its availability.
Why do oral formulations of drugs generally have less than 100% bioavailability?
-Oral formulations have less than 100% bioavailability due to the first-pass effect, which involves pre-systemic metabolism or elimination of a drug in the intestinal epithelium and liver, reducing its overall bioavailability.
What is the first-pass effect and how does it impact drug bioavailability?
-The first-pass effect refers to the process where a drug taken orally undergoes metabolism or elimination in the liver and intestinal epithelium before entering systemic circulation, thus reducing the amount of unchanged drug available to the body.
Can you explain the difference between phase 1 and phase 2 metabolism in drug processing?
-Phase 1 metabolism involves oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis reactions, often associated with the p450 enzyme system. Phase 2 metabolism is conjugation, including processes like sulfation, methylation, acetylation, and glucuronidation.
Why is the volume of distribution an important concept in pharmacokinetics?
-The volume of distribution is important because it is a theoretical volume that indicates where in the body a drug is accumulating. It helps to understand whether a drug is highly bound to plasma proteins or widely distributed into tissue compartments.
What is the relationship between half-life and the time it takes to reach steady state for a drug?
-The time to reach steady state is related to the drug's half-life. It generally takes about four to five half-lives to reach steady state, where the drug concentration in the body remains constant over time.
What is the difference between zero-order and first-order elimination in terms of drug processing in the body?
-Zero-order elimination has a constant rate of elimination regardless of drug concentration, while first-order elimination has a rate of elimination that is directly proportional to the drug concentration.
Why is it important to understand the initial drop in drug concentration after administration?
-The initial drop in drug concentration is important to understand because it is primarily due to distribution into tissues rather than elimination. This concept helps in appreciating how drugs are processed and can impact clinical decisions.
How does the clearance of a drug affect the steady-state concentration?
-Clearance, along with the dose of the drug, determines the magnitude of the steady-state concentration. However, it does not affect the fact that the drug has reached a steady state, which is determined solely by the drug's half-life.
What are some examples of drugs that undergo zero-order elimination?
-Some common examples of drugs that undergo zero-order elimination are aspirin, ethanol, and phenytoin. These are exceptions to the more common first-order elimination process.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
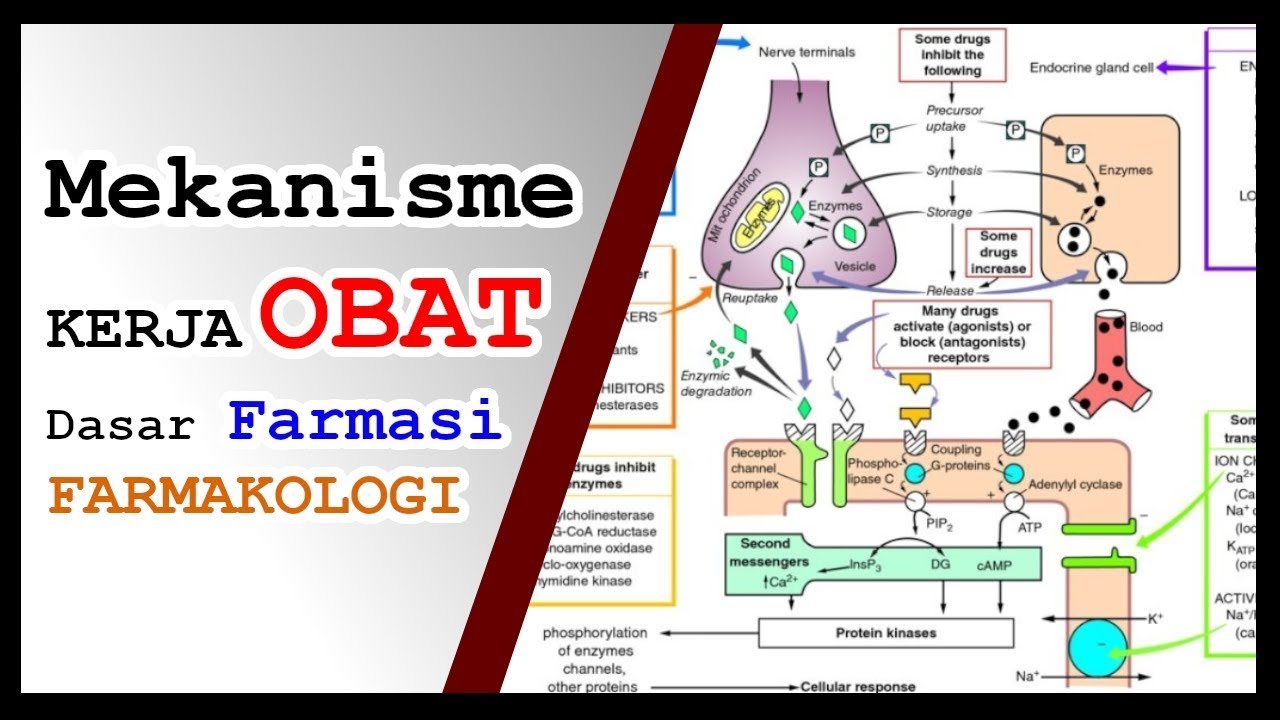
Farmakologi Medis - Mekanisme Kerja Obat Dasar Farmasi (1/5)

Pharmacology MADE EASY (Drugs and Receptors) - Perfect for beginners

Konsep Dasar Farmakologi

Pharmacodynamics - What the med does to your body - Quick Review - Pharmacology Lectures

FARMACOCINETICA E FARMACODINAMICA: DIFFERENZE - FARMACOLOGIA
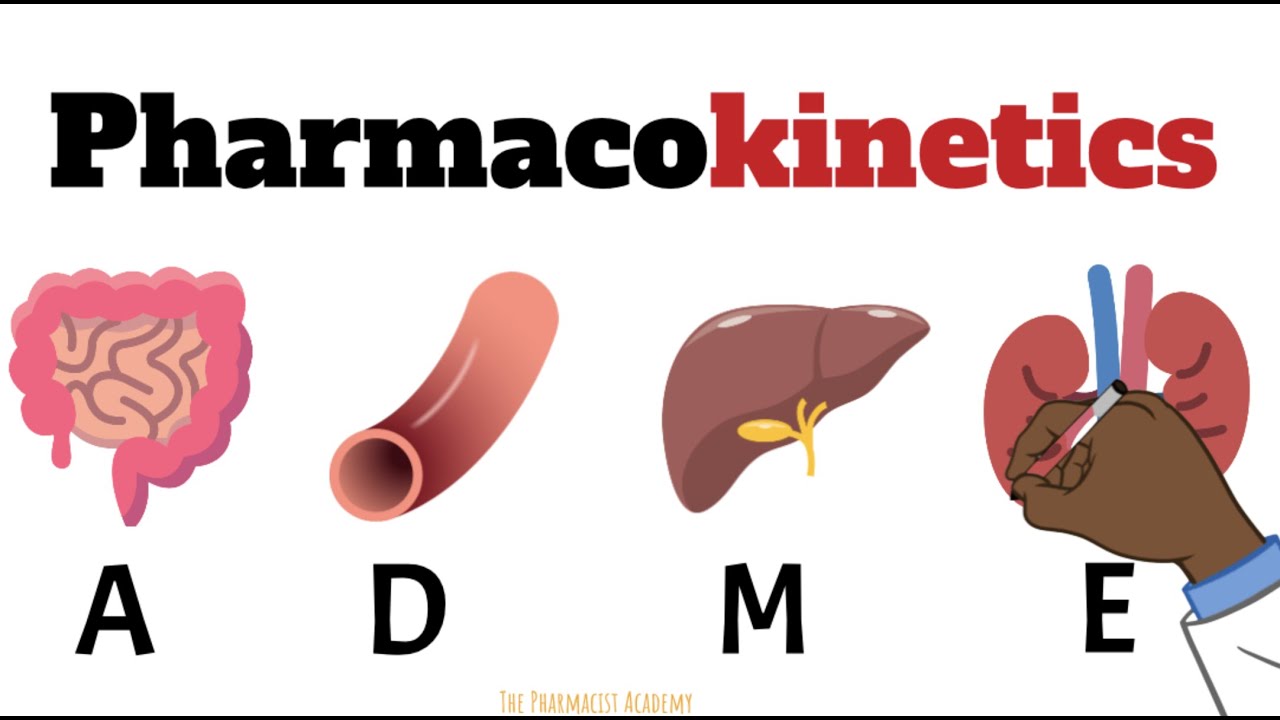
Pharmacokinetics MADE EASY FOR BEGINNERS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
