FARMACOCINETICA E FARMACODINAMICA: DIFFERENZE - FARMACOLOGIA
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Maria Carnevale, a chemistry and pharmaceutical technologies expert, explains the essential concepts of pharmacology: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. She discusses how pharmacokinetics tracks a drug’s journey in the body—from absorption to elimination—while pharmacodynamics focuses on how drugs interact with their target receptors to produce effects. Maria breaks down these concepts in simple terms, making them accessible for students preparing for exams. She also invites viewers to explore her simplified video course for a deeper dive into pharmacology. Her approach is engaging, providing both theoretical and practical insights for optimal study results.
Takeaways
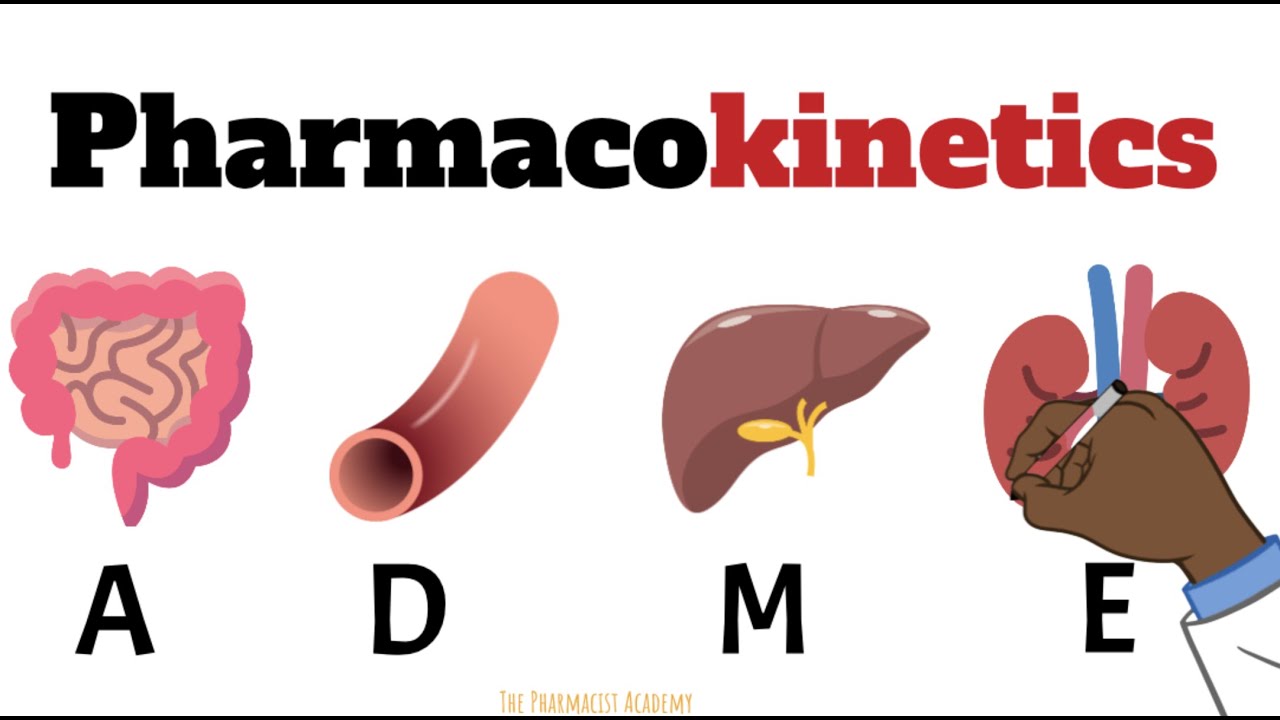
- 😀 Pharmacokinetics studies the effects a drug undergoes when it comes in contact with the body, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
- 😀 Pharmacodynamics focuses on the mechanism of action of the drug, explaining how it interacts with receptors to trigger a biological response.
- 😀 The pharmacokinetic process begins when the drug enters the body (e.g., oral administration) and continues as it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and finally excreted.
- 😀 The absorption of a drug into the bloodstream is critical for its distribution to various tissues and organs, including the targeted receptors for its effects.
- 😀 Pharmacokinetics includes the study of how drugs are metabolized, potentially becoming more active or inactive through chemical transformations.
- 😀 Excretion refers to the process of eliminating the drug from the body, which can happen through urine, feces, or other pathways like breast milk.
- 😀 Understanding pharmacokinetics helps in determining how long a drug remains in the body, how it acts, and how it should be dosed to achieve therapeutic effects.
- 😀 Pharmacodynamics explains how a drug binds to specific receptors and produces its intended therapeutic effect, such as pain relief from a painkiller.
- 😀 Pharmacokinetics ensures that the drug reaches the intended site of action by passing through the blood and reaching the target tissue or organ.
- 😀 It is essential to monitor how a drug is metabolized, as it can lead to either the formation of toxic metabolites or render the drug easier to eliminate from the body.
- 😀 Maria Carnevale invites students to explore her simplified pharmacology course for a more structured study approach, helping them better prepare for exams.
Q & A
What is pharmacokinetics?
-Pharmacokinetics is the branch of pharmacology that studies the effects a drug undergoes when it comes into contact with the body. It tracks the journey of the drug from administration, absorption, distribution, metabolism, to its elimination from the body.
What does pharmacodynamics study?
-Pharmacodynamics focuses on studying the mechanism of action of a drug. It explains how a drug interacts with receptors in the body and how it produces its therapeutic effect.
What is the main difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
-Pharmacokinetics deals with how the drug moves through the body (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination), whereas pharmacodynamics studies how the drug interacts with its target receptors and produces a biological response.
Why is absorption important in pharmacokinetics?
-Absorption is crucial because if a drug is not absorbed properly, it cannot enter the bloodstream, preventing it from reaching its target tissues and exerting its desired effect.
How does metabolism affect a drug?
-Metabolism involves chemical reactions that transform the drug within the body. These transformations can either activate or deactivate the drug, and they can also make the drug easier to eliminate. Some metabolites can be toxic, so monitoring these reactions is essential.
How does the body eliminate drugs?
-Drugs can be eliminated from the body through several routes, including urine, feces, and even breast milk. The process of elimination is important to clear the drug after it has exerted its effect.
What role do enzymes play in drug metabolism?
-Enzymes play a vital role in metabolizing drugs by modifying their chemical structure. This can make the drug more water-soluble, facilitating its excretion, or it can transform the drug into a metabolite with a different effect.
How does pharmacodynamics explain the action of a drug?
-Pharmacodynamics explains the drug's mechanism of action, focusing on how it binds to specific receptors in the body to trigger a biological response. For example, a painkiller like paracetamol works by binding to pain receptors to relieve pain.
What happens after a drug binds to its receptor in pharmacodynamics?
-Once the drug binds to its target receptor, it triggers a biological response that leads to the therapeutic effect, such as pain relief, reduction of inflammation, or other desired effects.
How does the interaction between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics influence a drug's effectiveness?
-The interplay between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics determines how effectively a drug works. If a drug is not absorbed or distributed correctly (pharmacokinetics), it cannot reach its target receptor, preventing the pharmacodynamic response. Conversely, pharmacodynamics explains how the drug produces its intended effect once it reaches the receptor.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)