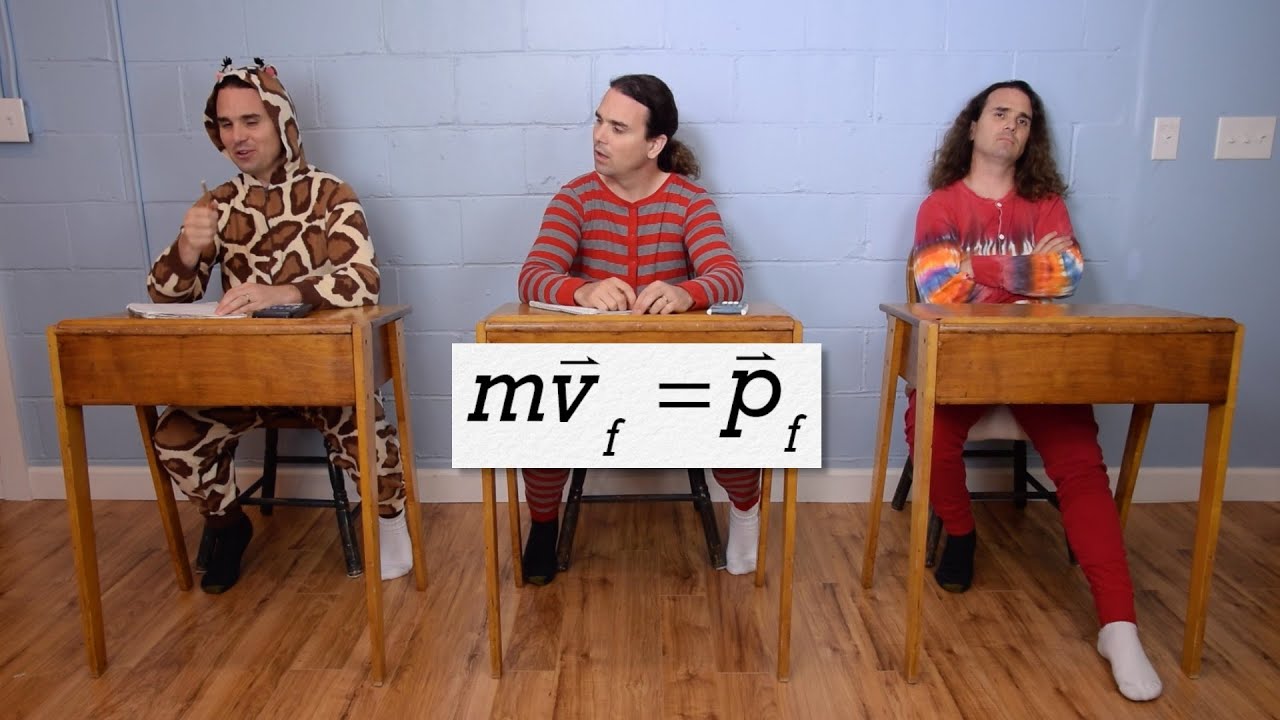Newton's second law of motion |⚡3d animation | Class 9, Physics |
Summary
TLDRThis educational script explores Newton's second law of motion through relatable examples like soldiers using momentum to break down gates and stunts in movies. It illustrates how momentum changes with acceleration and is directly proportional to the force applied. The script uses a billiard table scenario to demonstrate the law, showing how increased force results in greater momentum and distance traveled by the ball, highlighting the foundational principle that underpins many of our daily actions.
Takeaways
- 📚 Newton's Second Law of Motion is the focus of the module, illustrating the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
- 🏰 The historical example of using logs to break down fort gates demonstrates how momentum, a product of mass and velocity, can be increased by acceleration.
- 🏃♂️ The army's increasing velocity while running towards the gate shows how momentum changes even when mass remains constant.
- 🎥 Movie stunts, like breaking down doors, highlight the increase in an object's momentum due to acceleration.
- 💥 The rate of change of momentum is directly related to the object's acceleration, a key concept in Newton's Second Law.
- 🎱 A billiard table example shows how the application of force changes the velocity and, consequently, the momentum of the balls.
- 🟡 The yellow ball's motion after being hit by the cue ball illustrates a direct change in velocity and momentum.
- 🔄 The direction of the yellow ball's motion mirrors the cue ball's direction, indicating the conservation of momentum in the collision.
- 🚀 Applying more force with the cue results in the yellow ball traveling a greater distance, demonstrating the proportionality between force and momentum change.
- 🤔 Many everyday actions and phenomena can be explained by Newton's Second Law of Motion, emphasizing its practical applications.
- 🌐 The script effectively uses relatable examples to explain a fundamental principle of physics, making complex concepts more accessible.
Q & A
What is Newton's second law of motion?
-Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of an object's momentum is proportional to the applied force and occurs in the same direction as the applied force.
Why do armies in period films run back before ramming a log into a gate?
-They run back to gain velocity, which when combined with the mass of the log, generates enough momentum to break down the gate.
How does the momentum of the army holding the log change during their run-up to the gate?
-The momentum changes as their velocity increases during the run-up, even though the mass of the log remains constant.
What is an example of Newton's second law in action from the script?
-The example of the cue ball hitting the yellow ball on a billiard table illustrates the law, as the change in momentum of both balls is proportional to the force applied.
How does the momentum of an object relate to its acceleration?
-The momentum of an object increases when it accelerates, as the rate of change of momentum depends on the object's acceleration.
What happens when the cue ball hits the yellow ball with more force?
-The yellow ball moves a longer distance before coming to rest, indicating that the applied force has increased its momentum.
In the script, what is the relationship between the direction of the applied force and the change in momentum?
-The change in momentum takes place in the same direction as the applied force, as per Newton's second law.
Why does the cue ball move with less velocity after hitting the yellow ball?
-The cue ball transfers some of its momentum to the yellow ball, causing it to move with less velocity while the yellow ball gains momentum and moves faster.
What does the script suggest about the connection between everyday actions and Newton's second law?
-The script suggests that many of our actions, such as playing billiards, are based on the principles of Newton's second law of motion.
How can the concept of momentum be observed in a movie stunt where an actor breaks down a door?
-The momentum of the actor increases as they accelerate towards the door, allowing them to break it down with the force of their body.
What is the importance of understanding Newton's second law in analyzing physical scenarios?
-Understanding Newton's second law helps to predict and analyze the motion of objects under the influence of forces, which is crucial in various physical scenarios including sports, engineering, and everyday life.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)