What is an Analog Signal?
Summary
TLDRThis presentation explores the concepts of analog and digital signals, using clocks as an analogy to explain the differences. Analog signals can take any value within a range, like the continuous sweep of an analog clock's hands, whereas digital signals are discrete, similar to the fixed numbers displayed on a digital clock. The script further delves into the definition of discrete time signals, illustrating how they are a subset of analog signals, with values only known at specific time intervals, such as daily temperature readings at 11:00 AM. The presentation aims to clarify these fundamental electronic concepts for better understanding.
Takeaways
- 📈 The script discusses the concept of signals in electrical and electronics, emphasizing that a signal is essentially a change in current and voltage over time.
- 🕒 It uses the analogy of analog and digital clocks to differentiate between analog and digital signals, explaining that analog signals can take any value within a range, while digital signals are discrete and quantized.
- 🕰 The analog clock is described as having hands that can represent time in a continuous manner, allowing for any value between 0 and 24 hours.
- 📅 The digital clock is contrasted with the analog clock, showing that it represents time in discrete increments, lacking the ability to show fractions of a minute or second.
- 🌡️ An example of an analog signal is given with a temperature graph, illustrating how it can have any value between a minimum and maximum temperature.
- 🔋 The concept of an analog signal is further explained using the example of voltage, which can vary continuously between 0 and a maximum voltage (Vmax).
- ⏱️ The script introduces the term 'discrete time signal,' defined as a signal that is defined at discrete intervals of time, unlike continuous signals.
- 📊 A graph is used to demonstrate the concept of a discrete time signal, showing how it only has defined values at specific times, with unknown values in between.
- 📉 The importance of understanding discrete time signals is highlighted as a precursor to understanding digital signals.
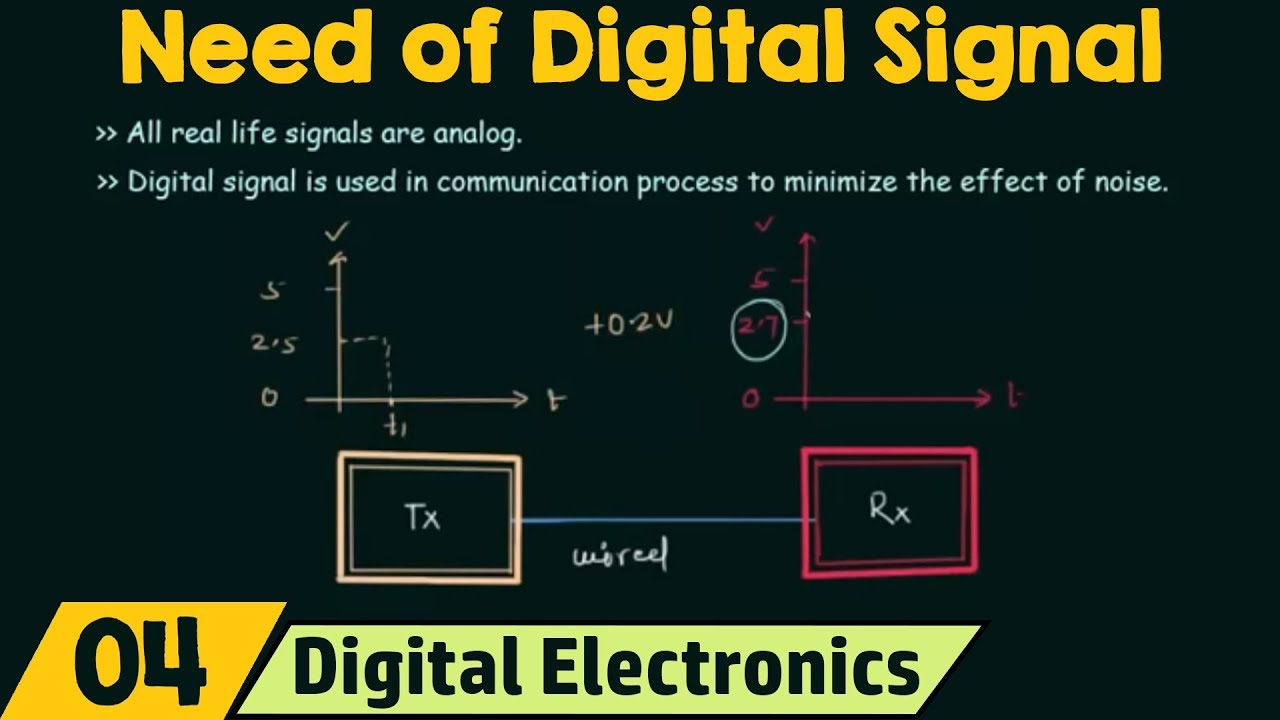
- 🔍 The script clarifies that all real-life signals are analog by nature, but we may only monitor or have access to them at discrete points in time, resulting in a discrete time signal.
- 📝 The takeaways from the script are the understanding of analog signals, which can take any value within a limit, and discrete time signals, which are subsets of analog signals and only have defined values at certain time intervals.
Q & A
What is the main difference between an analog clock and a digital clock as explained in the script?
-The main difference is that an analog clock has hands that can represent any time value within 24 hours continuously, while a digital clock represents time in discrete levels, such as hours and minutes, without showing seconds, and cannot display intermediate values like 11 minutes and 30 seconds.
What does the script imply when it says a signal in electrical and electronics is a change in current and voltage with time?
-The script implies that a signal is essentially the variation of electrical properties, such as current and voltage, over time, which can be used to transmit information.
What is an analog signal according to the script?
-An analog signal is one that can take any value within a given limit, representing a continuous range of values, similar to how an analog clock can show any time within 24 hours.
Can you explain the concept of a discrete time signal using the script's temperature example?
-A discrete time signal is defined for discrete intervals of time. In the script's example, the temperature is measured at specific times (e.g., 11:00 AM daily), and the values between these measurements are not known or recorded, creating a series of discrete data points over time.
How does the script differentiate between analog and digital signals in the context of electronics?
-The script differentiates them by stating that an analog signal can take on any value within a given range, like voltage levels from 0 to Vmax volts. In contrast, digital signals are not explicitly discussed, but by analogy to the digital clock, they would have discrete levels and not allow for intermediate values.
What does the script suggest about the relationship between discrete time signals and analog signals?
-The script suggests that discrete time signals are a subset of analog signals. This means that while all real-life signals are analog and can have continuous changes, discrete time signals only capture the values at specific, discrete time intervals.
Why does the script use temperature as an example to explain analog signals?
-The script uses temperature as an example because it can vary continuously and take on any value within a range (e.g., from 0°C to Tmax), illustrating the concept of an analog signal that can have a continuous spectrum of values.
How does the script's explanation of a digital clock help in understanding digital signals?
-The script's explanation of a digital clock helps in understanding digital signals by showing that digital representations only allow for certain discrete values, such as whole minutes and hours, without any intermediate or fractional values in between.
What is the significance of the Tmax and Vmax in the script's explanation of analog signals?
-Tmax and Vmax represent the maximum possible values for temperature and voltage, respectively. They are used to illustrate the concept that an analog signal can take any value within a defined range, from a minimum to a maximum.
How does the script define the term 'discretized' in the context of signals?
-In the context of signals, 'discretized' refers to the process of dividing a continuous signal into discrete intervals or points in time, as demonstrated by the temperature measurements at specific times of the day.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)