Types of stress in the crust
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the three main types of stress in the Earth's crust: compression, tension, and shear. Compression involves squeezing forces that fold rocks and create faults, commonly found at convergent plate boundaries. Tension, or extensional stress, pulls rocks apart, causing fractures and normal faults, typical at divergent boundaries. Shear stress occurs when forces push rocks in different directions, resulting in horizontal movement along strike-slip faults, usually at transform boundaries. The video illustrates how these stresses deform rock layers over time and links each stress type to specific tectonic settings, helping viewers understand the dynamic forces shaping the Earth's crust.
Takeaways
- 🟢 There are three basic types of stress in Earth's crust: compression, tension, and shear.
- 🟢 Compression is a squeezing force that pushes rocks toward each other.
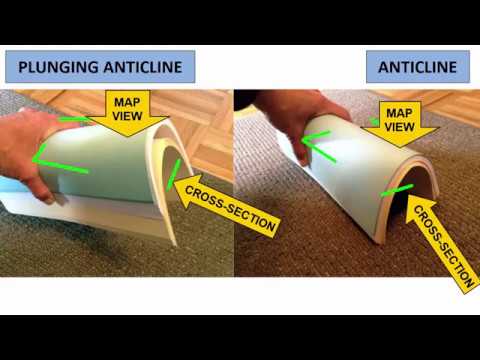
- 🟢 Compression can cause rocks to fold into anticlines (arch-like) and synclines (trough-like).
- 🟢 Compression can also create fractures and faults where rock blocks move relative to each other.
- 🟢 Tension is a pulling-apart force, also known as extensional stress.
- 🟢 Tension leads to fractures and downward movement of rock blocks along faults.
- 🟢 Shear stress occurs when forces push different parts of a rock in different directions.
- 🟢 Shear stress often results in strike-slip faults with horizontal movement of rocks.
- 🟢 Compression is typically found at convergent plate boundaries, where plates collide.
- 🟢 Tension is common at divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart.
- 🟢 Shear stress is characteristic of transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other.
- 🟢 Long-term stress in the crust results in various types of deformation including folding, faulting, and horizontal displacement.
Q & A
What are the three basic types of stress in Earth's crust?
-The three basic types of stress in Earth's crust are compression, tension, and shear.
How does compression affect rocks in the Earth's crust?
-Compression squeezes rocks, which can lead to folding into structures like anticlines and synclines, or fracturing that forms faults where rock blocks move relative to each other.
What type of stress is characterized by a pulling-apart force?
-Tension is characterized by a pulling-apart force, also known as extensional stress.
What is the typical result of tension on rock formations?
-Tension can cause fractures in rocks, allowing blocks to move downward along faults, forming normal faults.
Describe shear stress and its effects on rocks.
-Shear stress occurs when forces act in opposite horizontal directions on different parts of a rock region, causing horizontal shifting and resulting in strike-slip faults.
Where in tectonic settings would you expect to find rocks under compression?
-Rocks under compression are typically found at convergent plate boundaries, where tectonic plates collide.
Which type of plate boundary is associated with tension stress?
-Divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart, are associated with tension stress.
What type of fault is commonly formed due to shear stress?
-Strike-slip faults are commonly formed as a result of shear stress.
What is the difference in fault formation between compression and tension?
-Compression often leads to reverse or thrust faults where rocks are pushed together, while tension leads to normal faults where rocks move downward along fractures.
What are anticlines and synclines, and how do they form?
-Anticlines are arch-like folds, and synclines are trough-like folds in rock layers. They form when rocks in the crust are subjected to long-term compressional stress.
How does the duration of stress affect rock deformation?
-Stress acting over long periods of time can cause significant deformation in rocks, including folding, faulting, and horizontal displacement depending on the stress type.
Why do strike-slip faults occur at transform boundaries?
-Strike-slip faults occur at transform boundaries because the plates slide past each other, creating shear stress that shifts rocks horizontally.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)