Folds and Faults
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explores the causes and consequences of stress applied to rocks, focusing on the three main types of stress: compression, tension, and shear. It delves into how these stresses lead to different types of deformation, such as brittle, ductile, and elastic deformation, and their impact on rock structures. The tutorial also covers faults and folds, explaining how different stresses create various fault types (e.g., strike-slip, dip-slip, normal, reverse) and how folds are classified based on their shape. The importance of understanding these processes is emphasized for applications in geosciences, resource exploration, and construction.
Takeaways
- 😀 Compression stress occurs at convergent plate boundaries, causing rocks to be squeezed and leading to thicker crust.
- 😀 Tension stress happens at divergent plate boundaries, pulling rocks apart and thinning the crust.
- 😀 Shear stress occurs at transform plate boundaries, where rocks slide past each other, similar to pushing on a deck of cards.
- 😀 Rocks experience deformation through elastic, ductile (plastic), or brittle deformation, depending on the stress applied.
- 😀 Elastic deformation occurs when stress is low, and rocks return to their original shape after pressure is released.
- 😀 Ductile (plastic) deformation happens when rocks bend or fold under continuous stress over time.
- 😀 Brittle deformation leads to rocks breaking when stress is applied too quickly or when rocks exceed their elastic limit.
- 😀 Faults are fractures where rocks break and move, classified as strike-slip, dip-slip, or oblique-slip based on their movement.
- 😀 Normal faults occur due to tension stress, where the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
- 😀 Reverse faults, caused by compression stress, involve the hanging wall moving upward relative to the footwall.
- 😀 Strike-slip faults can be classified as right-lateral or left-lateral based on the relative motion of the fault's sides.
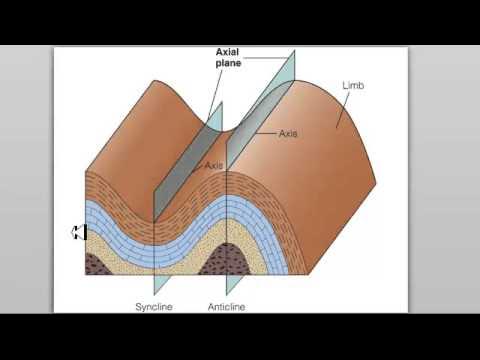
- 😀 Folds form when rocks bend under stress, with anticlines and synclines being the most common types of folds.
- 😀 A plunge in folds occurs when the fold’s hinge axis dips into the ground, which changes the fold’s appearance in map view.
- 😀 Domes and basins are special folds formed by vertical pressure, with domes pushing rocks up and basins pushing them down.
- 😀 Understanding the direction of rock layers and fold shapes is crucial in resource exploration and construction planning.
Q & A
What are the three types of stress that can be applied to rocks?
-The three types of stress applied to rocks are compression, tension, and shear. Compression squeezes rocks together, tension pulls them apart, and shear causes rocks to slide past each other.
What happens to rocks when they experience compression?
-When rocks experience compression, they are squeezed together, typically occurring at convergent plate boundaries, causing the crust to thicken.
How does tension stress affect rocks?
-Tension stress pulls rocks apart, which happens at divergent plate boundaries, leading to the crust becoming thinner.
What is shear stress and where does it occur?
-Shear stress occurs when rocks slide past each other, typically at transform plate boundaries. It happens when one side moves in one direction while the other side moves in the opposite direction.
What is the difference between elastic and plastic deformation?
-Elastic deformation occurs when rocks return to their original shape after the stress is released. Plastic deformation happens when rocks bend or fold without returning to their original shape.
What is brittle deformation and what causes it?
-Brittle deformation occurs when rocks break due to rapid stress application. It happens when stress is applied too quickly for the rock to bend, causing it to fracture.
Why are colder rocks more likely to undergo brittle deformation?
-Colder rocks are more brittle and less likely to bend, making them more prone to breaking under stress compared to warmer rocks, which are more likely to bend or fold.
Where do we typically see brittle deformation and plastic deformation on Earth?
-Brittle deformation is usually observed at the surface of the Earth, while plastic deformation occurs at greater depths where rocks are warmer.
What are the different types of faults and how are they classified?
-Faults are classified by the type of stress and the movement of rocks along the fault plane. The main types are normal faults (due to tension), reverse faults (due to compression), and strike-slip faults (due to shear).
What is the difference between a normal fault and a reverse fault?
-A normal fault occurs due to tension, where the hanging wall moves downward. A reverse fault occurs due to compression, where the hanging wall moves upward.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Types of stress in the crust

TYPES OF STRESS THAT INFLUENCE ROCK BEHAVIOR

TYPES OF ROCK STRESS

FOLDING AND FAULTING OF ROCKS / EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE / SCIENCE 11 - MELC 10

Rheology Part 2 - Deformation Forces - A Video Tutorial by samMorell.com

Materials Science Mechanical Engineering - Part 1 Stress and Strain Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)