NÍVEL DE ORGANIZAÇÃO CELULAR DOS SERES VIVOS: CÉLULA, TECIDO, ÓRGÃO, SISTEMA E ORGANISMO! #fyp
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful review of the level of cellular organization in living beings. It explains the basic unit of life, the cell, its types (prokaryotic and eukaryotic), and their structures such as the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material. The video covers how cells form tissues, organs, and systems, with each level increasing in complexity. It emphasizes how these systems work in harmony to maintain life, drawing examples from humans, animals, and plants. The video underscores the importance of understanding cellular organization for comprehending the functions of living beings.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cell is the basic unit of life, capable of existing independently or as part of a multicellular organism.
- 😀 Cells perform vital functions like nutrition, reproduction, and excretion, ensuring the continuation of life.
- 😀 Cells have specific characteristics, including autonomy (performing all vital functions) and organization (diversity in cell types).
- 😀 Cells can be divided into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic, each with different levels of complexity.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells are simpler, lack a nucleus, and their genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm, found in bacteria and archaea.
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and membranous organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
- 😀 Multicellular organisms are formed by various cells working together, and these cells are organized in a hierarchical manner.
- 😀 The cell level is the foundation of cellular organization, with tissues, organs, systems, and the complete organism forming a complex structure.
- 😀 Tissues are groups of similar cells working together for a specific function, and they include epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
- 😀 Organs are formed by different tissues and work together to perform specialized functions, such as digestion, blood circulation, or respiration.
- 😀 Organ systems are composed of organs that cooperate to perform complex functions, and these systems must work in harmony to maintain the life of the organism.
Q & A
What is the basic unit of life, and why is it so important?
-The basic unit of life is the cell. It is important because it is responsible for all vital functions such as nutrition, reproduction, and excretion, which ensure the existence and perpetuation of life.
What are the two main types of cells, and what differentiates them?
-The two main types of cells are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a defined nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and more complex structures, including membranous organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What is the significance of the plasma membrane in a cell?
-The plasma membrane, also known as the lipid bilayer, is crucial because it controls the entry and exit of substances, maintaining the internal environment of the cell.
How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in terms of genetic material?
-In prokaryotic cells, genetic material is not enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus and is dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. In contrast, eukaryotic cells have their genetic material contained within a well-defined nucleus.
What role do organelles play within a cell?
-Organelles are specialized structures within the cytoplasm that perform specific functions, such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste processing, contributing to the cell's overall function.
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms?
-Unicellular organisms are made up of a single cell, whereas multicellular organisms consist of many cells that work together, allowing for greater complexity and specialization.
How does cellular organization progress from the cell to the organism?
-Cellular organization begins with the cell, which groups together to form tissues, which combine to form organs. Organs then join to create systems, and systems work together to form the complete organism.
What are the four basic tissue types in multicellular organisms?
-The four basic tissue types are epithelial tissue (covers and protects organs), connective tissue (supports and connects tissues), muscular tissue (enables movement), and nervous tissue (coordinates and communicates body functions).
How do organs and systems work together in multicellular organisms?
-Organs work together within systems, where each organ performs a specific function. Systems integrate multiple organs to carry out complex functions that sustain the organism's life.
Can you give an example of how cellular organization results in specific characteristics of an organism?
-The cellular organization in a lion allows it to have great strength and agility, which are characteristics essential for a top predator. Similarly, the structure of a redwood tree's cells contributes to its size and longevity.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

12. Biology | Cell Structure and Function | Basic Concepts of Cell Biology | MDCAT 2025

Biology EOC Review - Part 1
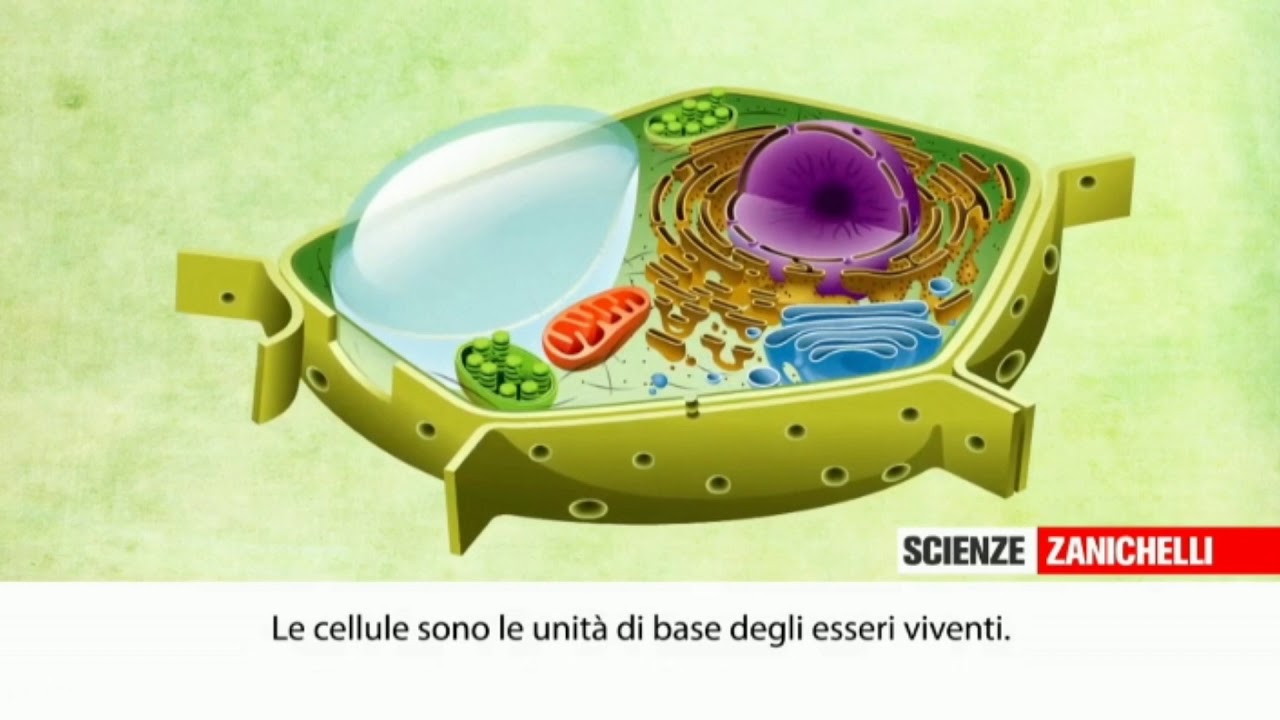
La cellula animale e vegetale

CARACTERÍSTICAS GERAIS DOS SERES VIVOS | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

AP Biology Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function Summary

VIDA E CARACTERÍSTICAS GERAIS DOS SERES VIVOS (PROVA, VESTIBULAR, ENEM) - OLHAR QUÍMICO |PROF. ROMEU
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
