PV Diagrams, How To Calculate The Work Done By a Gas, Thermodynamics & Physics
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains various thermodynamic processes and the calculations involved in determining the work done by a gas. It covers isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, and adiabatic processes, highlighting key formulas for each type. The script demonstrates the calculation of work in practical examples, such as calculating work during constant pressure expansion, zero work in constant volume, and work done in isothermal and adiabatic processes. It also delves into cyclic processes, emphasizing the importance of direction and calculating enclosed areas in PV diagrams. The video provides comprehensive insights into how work is calculated in different thermodynamic scenarios.
Takeaways
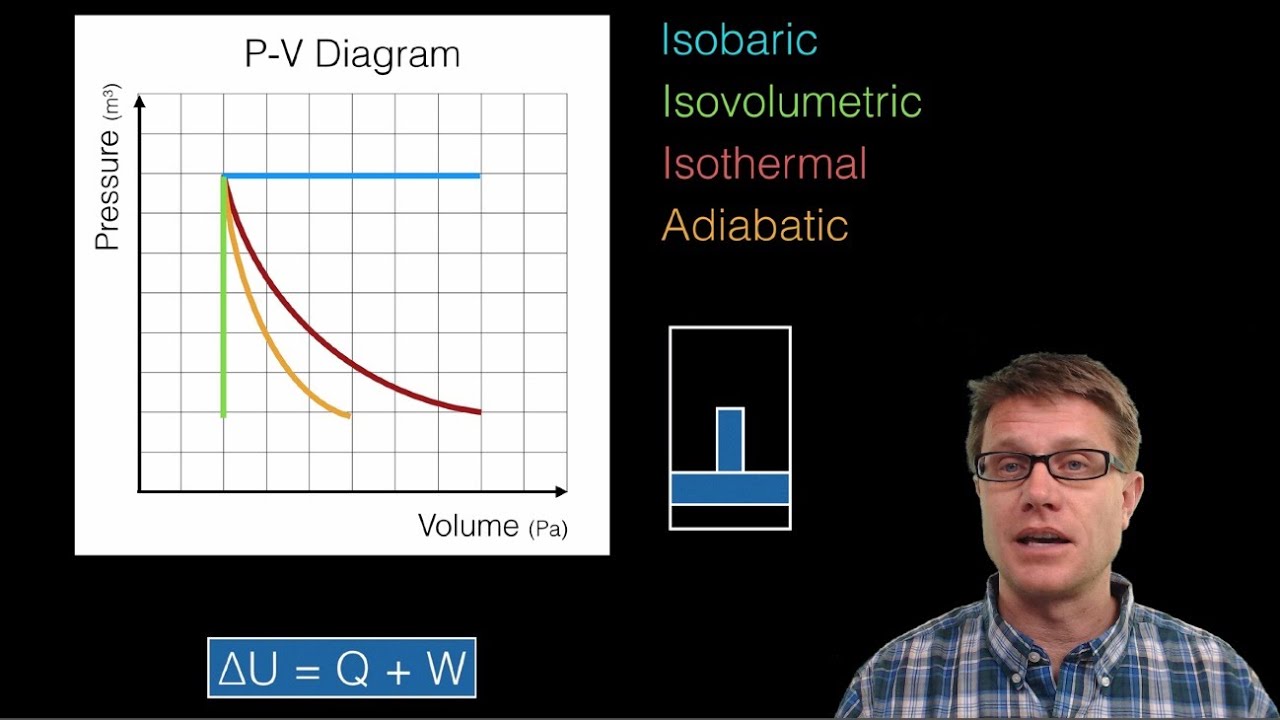
- 😀 Isobaric processes occur at constant pressure, and work is calculated as the pressure times the change in volume.
- 😀 In an isochoric process, the volume remains constant, meaning no work is done by the gas (work = 0).
- 😀 For isothermal processes (constant temperature), work is calculated using the formula W = nRT ln(V_f / V_i).
- 😀 Adiabatic processes involve no heat exchange, and work is calculated using a specific formula involving pressure and volume changes.
- 😀 The area under the curve on a P-V diagram represents the work done by the gas during a thermodynamic process.
- 😀 For cyclic processes, the total work done is the area enclosed by the P-V diagram, and the direction of rotation determines whether work is positive or negative.
- 😀 In a cyclic process moving clockwise, the work done is positive; in a counterclockwise cycle, the work is negative.
- 😀 In an isobaric process, the pressure remains constant, and work is the product of pressure and the change in volume.
- 😀 The work done during an isothermal expansion can be calculated using the ideal gas law and logarithmic functions.
- 😀 For a monoatomic gas in an adiabatic expansion, the work done is calculated using the formula involving the specific heat and pressure-volume products.
Q & A
What is the primary formula used to calculate work done in an isobaric process?
-The formula used to calculate work in an isobaric process is W = P * ΔV, where P is the pressure and ΔV is the change in volume.
Why is the work done in an isochoric process always zero?
-In an isochoric process, the volume of the gas remains constant, meaning there is no change in volume (ΔV = 0). Since work is the product of pressure and change in volume, the work done is zero.
How do you calculate the work done in an isothermal process?
-In an isothermal process, the work done can be calculated using the formula W = nRT * ln(Vf / Vi), where n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature, and Vf and Vi are the final and initial volumes, respectively.
What is the work calculation for an adiabatic process?
-In an adiabatic process, the work done can be calculated using the formula W = - (3/2) * R * (P_f * V_f - P_i * V_i), where P_f, V_f, P_i, and V_i are the final and initial pressures and volumes, respectively.
What is the significance of the area under the curve in a PV diagram?
-The area under the curve in a PV diagram represents the work done by or on the gas. The shape of the area depends on the type of process (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic, etc.).
In a cyclic process, how is the work done calculated?
-In a cyclic process, the work done is the area enclosed by the PV diagram. If the cycle follows a clockwise direction, the work is positive; if it follows a counterclockwise direction, the work is negative.
How does the direction of rotation in a cyclic process affect the work done?
-The direction of rotation in a cyclic process affects the sign of the work done. A clockwise rotation results in positive work, while a counterclockwise rotation results in negative work.
How can you calculate the work done for each segment in a cyclic process?
-The work done for each segment in a cyclic process is calculated by applying the appropriate formula for each type of process (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) and then summing the individual work values for all segments.
What is the formula for calculating work in an isobaric process when pressure is constant?
-In an isobaric process, the work done is calculated by the formula W = P * (V_f - V_i), where P is the constant pressure, V_f is the final volume, and V_i is the initial volume.
What do you need to know in order to calculate work in an isothermal process?
-To calculate work in an isothermal process, you need to know the number of moles of gas (n), the gas constant (R), the temperature (T), and the initial and final volumes (V_i and V_f).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
Thermodynamics and P-V Diagrams

Pembahasan Soal LKS Fisika Intan Pariwara Kelas 11 : Termodinamika_Part 1

F197 - Proses proses termodinamika ( isobaris,isokoris,isotermis,adiabatis) : Teori + Contoh soal

BTEC Applied Science: Unit 5 Physics The First Law of Thermodynamics

Thermodynamics - A-level Physics

AARAMBH 2.0 - CHEMISTRY | CHAPTER - 4 | CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS | LEC -4 | CLASS XII
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
