How to configure EBGP & IBGP connectivity along with route-reflector
Summary
TLDRThis lab demonstrates the configuration of eBGP and iBGP connectivity between routers in different autonomous systems (AS). The process involves setting up routers in AS 10 and AS 20, configuring interfaces, IP addresses, and BGP settings for both external (eBGP) and internal (iBGP) routing. Troubleshooting is covered, including fixing next-hop issues and using route reflectors for prefix advertisement. The lab highlights key BGP configurations, such as next-hop-self, and resolves network connectivity issues, providing valuable insights into BGP practices for managing inter-domain routing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the basic topology for eBGP and iBGP configuration between two autonomous systems (AS 10 and AS 20).
- 😀 eBGP establishes connectivity between routers in different autonomous systems (R1 with R2 and R1 with R4).
- 😀 iBGP is used for connectivity within the same autonomous system (AS 20), with routers R2, R3, and R4 communicating internally.
- 😀 Basic router configurations include setting up interfaces and loopback addresses on R1, R2, R3, and R4 to prepare for BGP setup.
- 😀 eBGP configuration is done by setting the neighbor IPs and remote AS numbers, ensuring routers in different ASs can communicate.
- 😀 iBGP configuration requires ensuring routers within the same AS can share routing information effectively, with SPF as the IGP.
- 😀 BGP updates and next-hop values play a critical role in determining the best path for routing, which was tested on the network.
- 😀 When R3 did not receive valid next-hop information, the 'next-hop self' command was configured on R2 to resolve the issue.
- 😀 The issue of missing network prefixes on R4 was resolved by configuring R3 as a route reflector to advertise the prefixes.
- 😀 Route maps were used on R4 to fix incorrect next-hop values for network prefixes, ensuring proper BGP functionality and updates.
- 😀 The video demonstrated troubleshooting techniques for BGP by analyzing next-hop values, route reflectors, and route maps to ensure network prefix propagation.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between EBGP and IBGP?
-EBGP (External Border Gateway Protocol) is used for routing between different Autonomous Systems (AS), while IBGP (Internal Border Gateway Protocol) is used for routing within the same AS.
What does the command 'router bgp' do in the configuration?
-'router bgp' is used to enable BGP routing on the router and define the AS number for the BGP process. For example, 'router bgp 10' configures BGP for AS 10.
Why is the 'next-hop-self' command used in the BGP configuration?
-The 'next-hop-self' command is used to ensure that the router advertises itself as the next-hop router for the routes it advertises. This is especially useful when using EBGP, as it avoids potential issues with route propagation across multiple hops.
What role do loopback interfaces play in BGP configurations?
-Loopback interfaces are used in BGP configurations as stable, virtual interfaces for BGP peering. They provide a reliable way to maintain neighbor relationships because loopback interfaces are not subject to changes in physical interface states.
What is a route reflector and why was it configured on R3?
-A route reflector is used to allow BGP routers within the same AS to exchange routing information without needing to establish full mesh connectivity. It was configured on R3 to ensure that network prefixes could be advertised to R4.
What does the command 'clear ip bgp' do in the context of troubleshooting BGP?
-'clear ip bgp' is used to reset the BGP session between routers, which can help apply new configurations or resolve issues related to stale BGP routes.
Why was the next-hop value incorrect on R3 after the route reflector configuration?
-The next-hop value was incorrect because R3, as a route reflector, did not modify the next-hop information for R4. This required further configuration to correct the next-hop value.
What is the purpose of configuring a route map on R4 in this lab?
-The route map on R4 was configured to explicitly set the correct next-hop value for the BGP routes received from R3. This ensured that the next-hop information was correct and allowed proper route advertisement.
What is the significance of the 'network' command in BGP?
-The 'network' command in BGP is used to advertise a network prefix to other BGP routers. It is necessary to specify the network that should be advertised into the BGP routing table.
What does the 'show ip bgp' command reveal during the BGP troubleshooting process?
-'show ip bgp' displays the BGP routing table, showing network prefixes, next-hop information, and route status. It is useful for verifying if prefixes are being correctly advertised and received, and helps identify issues such as incorrect next-hop values.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
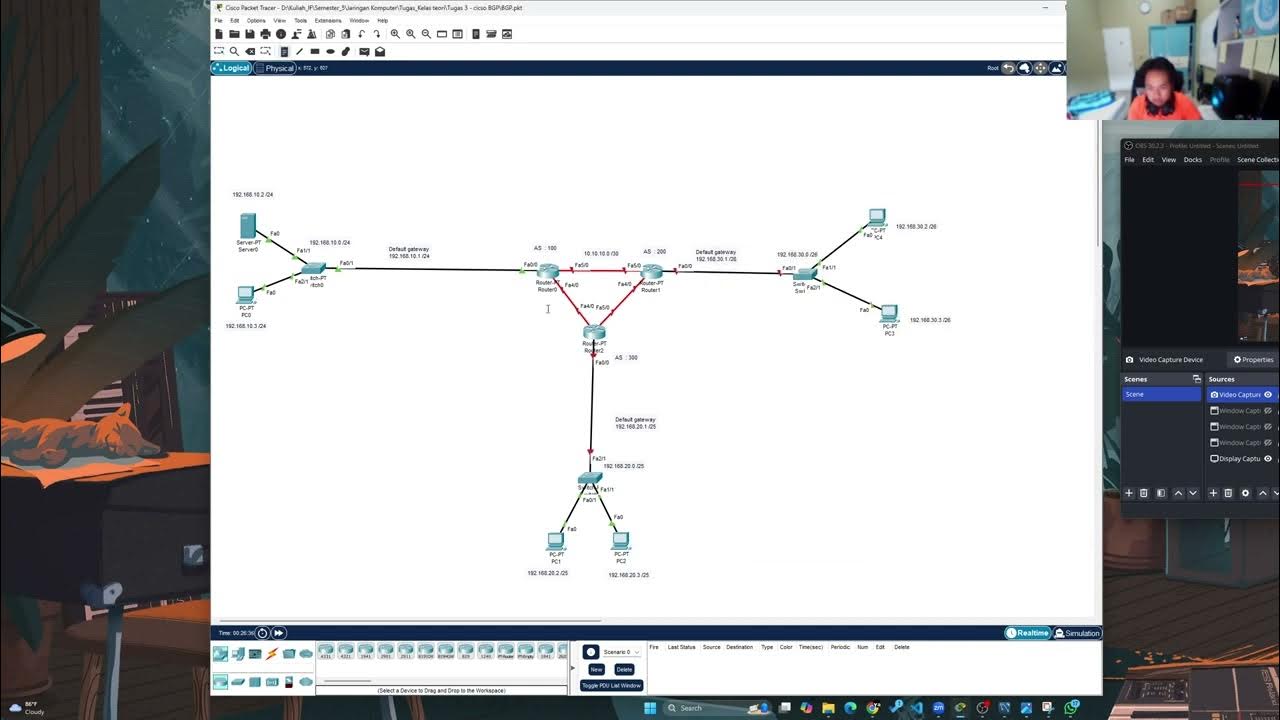
Tugas Jarkom - Konfigurasti Dynamic Routing BGP menggunakan Cisco Packet Tracer

How to configure Dynamic Routing | Dynamic Routing configuration step by step

2.How to configure EBGP? | Networkforyou | EVE ng Labs
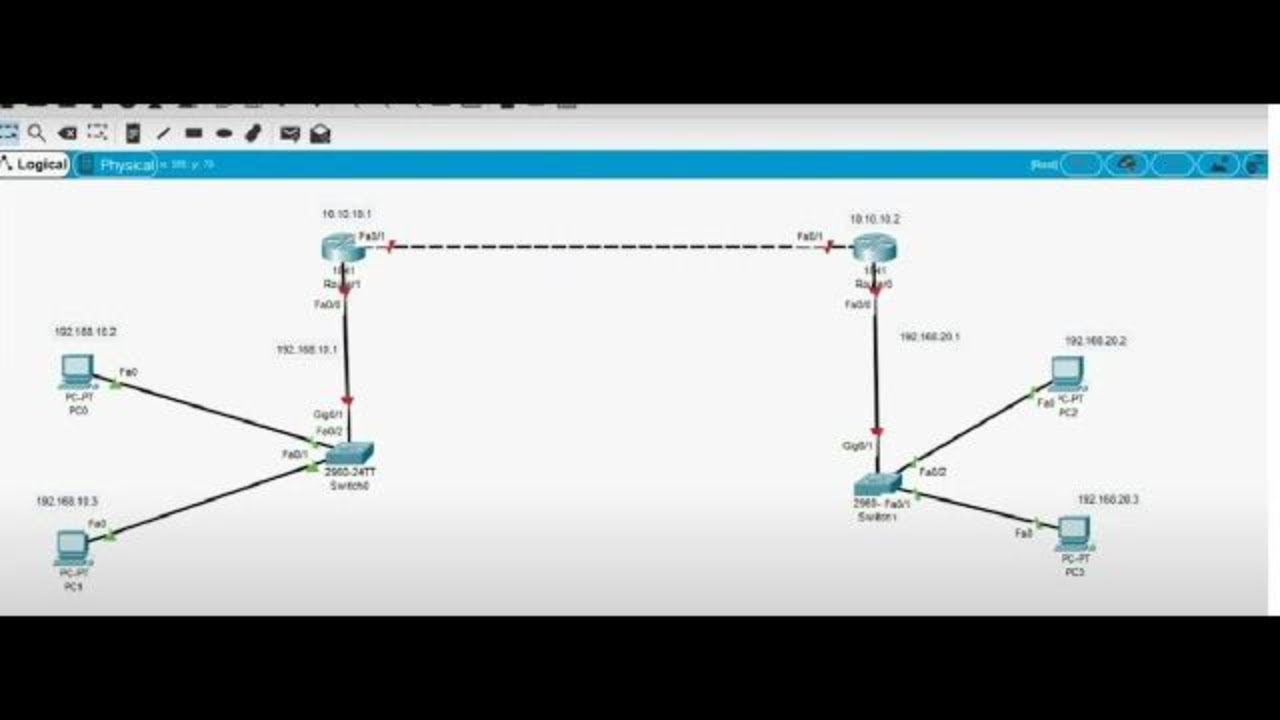
How to Configure Static Routing 2 Router Base CLI in Cisco Packet Tracer

UKK TKJ Paket 2 Tahun 2025 Full Versi Cepat
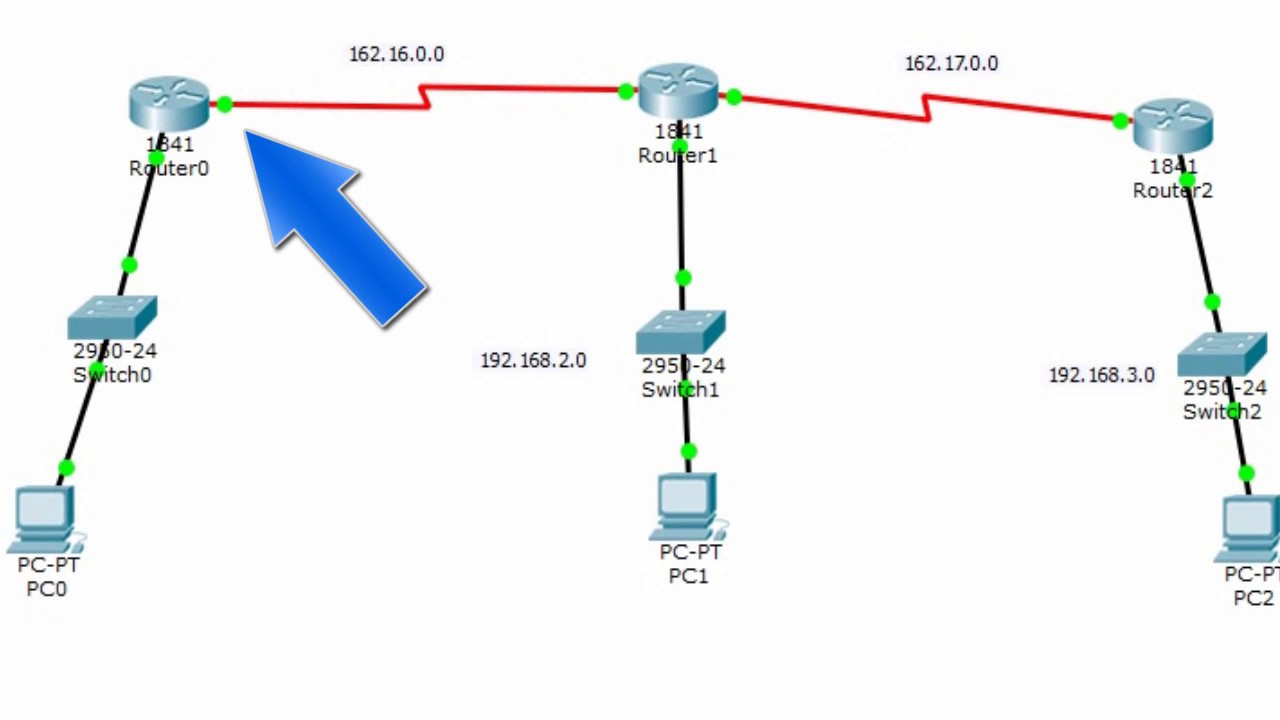
Enrutamiento estatico (3 router) Packet Tracer
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
