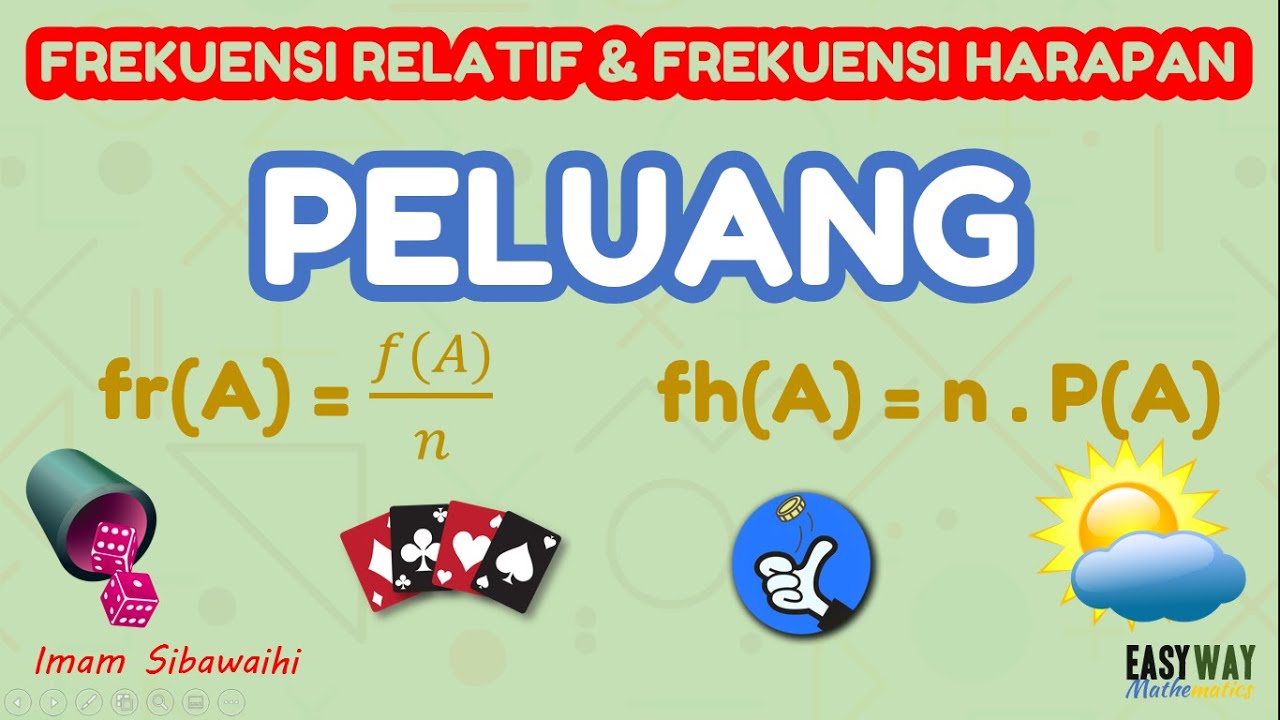
Frekuensi Harapan
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the concept of 'frekuensi harapan' (expected frequency) in probability is explained. The instructor discusses how expected frequency refers to the number of times an event is expected to occur when an experiment is repeated multiple times. The lesson uses the example of rolling a die 72 times to calculate the expected frequency of specific outcomes, such as rolling a 2 or an odd number. The formula for expected frequency is introduced, which involves multiplying the number of trials by the probability of the event. The concept is applicable to various types of probability, including independent and mutually exclusive events.
Takeaways
- 😀 The concept of expected frequency (frekuensi harapan) refers to the number of occurrences of an event when a probability experiment is repeated multiple times.
- 😀 The formula for calculating expected frequency is E = n × P, where E is the expected frequency, n is the number of trials, and P is the probability of the event happening in a single trial.
- 😀 The expected frequency applies to all types of probability, including simple probabilities, independent events, mutually exclusive events, and conditional probabilities.
- 😀 An example is given using the rolling of a die 72 times, where the goal is to calculate the expected occurrences of rolling a 2 or an odd number.
- 😀 The probability of rolling a 2 on a single die is 1/6, while the probability of rolling an odd number (1, 3, or 5) is 3/6.
- 😀 In cases of mutually exclusive events, the total probability is the sum of the individual probabilities, as demonstrated with the die example (P(2 or odd) = 1/6 + 3/6 = 4/6).
- 😀 The calculation of expected frequency involves multiplying the number of trials (n) by the total probability of the event happening.
- 😀 For the die example, the expected frequency of rolling either a 2 or an odd number over 72 rolls is 48 (72 × 2/3).
- 😀 Expected frequency is a general concept that applies to various types of probability problems and can be used to predict the number of occurrences of a specific event in repeated trials.
- 😀 The key to calculating expected frequency is first determining the correct probability of the event of interest, and then applying the formula to find the expected number of occurrences.
- 😀 The lecture emphasizes that expected frequency can be used in diverse probability contexts, so understanding how to calculate probabilities is essential before applying it to find expected frequencies.
Q & A
What is the meaning of 'frekuensi harapan' in probability?
-Frekuensi harapan, or expected frequency, refers to the number of times an event is expected to occur during a series of trials based on its probability.
How is the expected frequency calculated?
-The expected frequency is calculated by multiplying the number of trials (n) by the probability (P) of the event occurring. The formula is: Expected Frequency = n * P.
Can frekuensi harapan be applied to all types of probabilities?
-Yes, frekuensi harapan can be applied to various types of probabilities including regular probability, mutually exclusive events, independent events, and conditional probabilities.
What is an example of an event where 'frekuensi harapan' is calculated?
-An example is rolling a die 72 times and calculating how many times a 2 or an odd number would appear. The expected frequency is calculated based on the probability of these events.
What is the significance of mutually exclusive events in this context?
-Mutually exclusive events, such as rolling a 2 or an odd number, cannot happen at the same time. This allows the use of the formula for the combined probability of these events.
How do you calculate the probability of rolling a 2 on a single die?
-The probability of rolling a 2 on a single die is 1/6 because there is only one side of the die with the number 2 out of six possible outcomes.
What is the probability of rolling an odd number on a die?
-The probability of rolling an odd number on a die is 3/6, as there are three odd numbers (1, 3, 5) out of six possible outcomes.
Why do we add the probabilities of mutually exclusive events?
-We add the probabilities of mutually exclusive events because they cannot occur at the same time. Therefore, the total probability is the sum of the individual probabilities.
In the example of rolling a die 72 times, what is the combined probability for rolling a 2 or an odd number?
-The combined probability for rolling a 2 or an odd number is 4/6 or 2/3, as these events are mutually exclusive and we add their individual probabilities (1/6 + 3/6).
What is the expected frequency of rolling a 2 or an odd number if a die is rolled 72 times?
-The expected frequency is calculated by multiplying the number of trials (72) by the combined probability (2/3). Therefore, the expected frequency is 72 * 2/3 = 48.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Frekuensi Harapan dari Suatu Kejadian Matematika SMA kelas XII

Peluang (Part 1) | Definisi Peluang, Komplemen Kejadian dan Frekuensi Harapan Matematika Kelas 12

Menentukan Peluang Empirik Frekuensi Relatif dari Suatu Kejadian
Frekuensi Relatif dan Frekuensi Harapan

Peluang ~ Menentukan Nilai Peluang dan Frekuensi Harapan Suatu Kejadian (Materi PJJ Klas VIII/8 SMP)

Peluang dan Sampel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
