BAB 6 STRUKTUR BUMI DAN PERKEMBANGANNYA BAGIAN 1 - IPA Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an educational overview of Earth's structure, including its layers: the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and the tectonic processes that shape the planet. It covers the composition and characteristics of the Earth's crust, mantle, and core, as well as the dynamics of plate tectonics, including the theory of continental drift and the three types of plate movements: transform, convergent, and divergent. The script also explains the geological forces driving earthquakes and volcanic activity, and highlights the Ring of Fire in the Pacific, illustrating the active tectonic environment around Indonesia.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth’s structure consists of three main layers: the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere.
- 😀 The atmosphere is made up of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases.
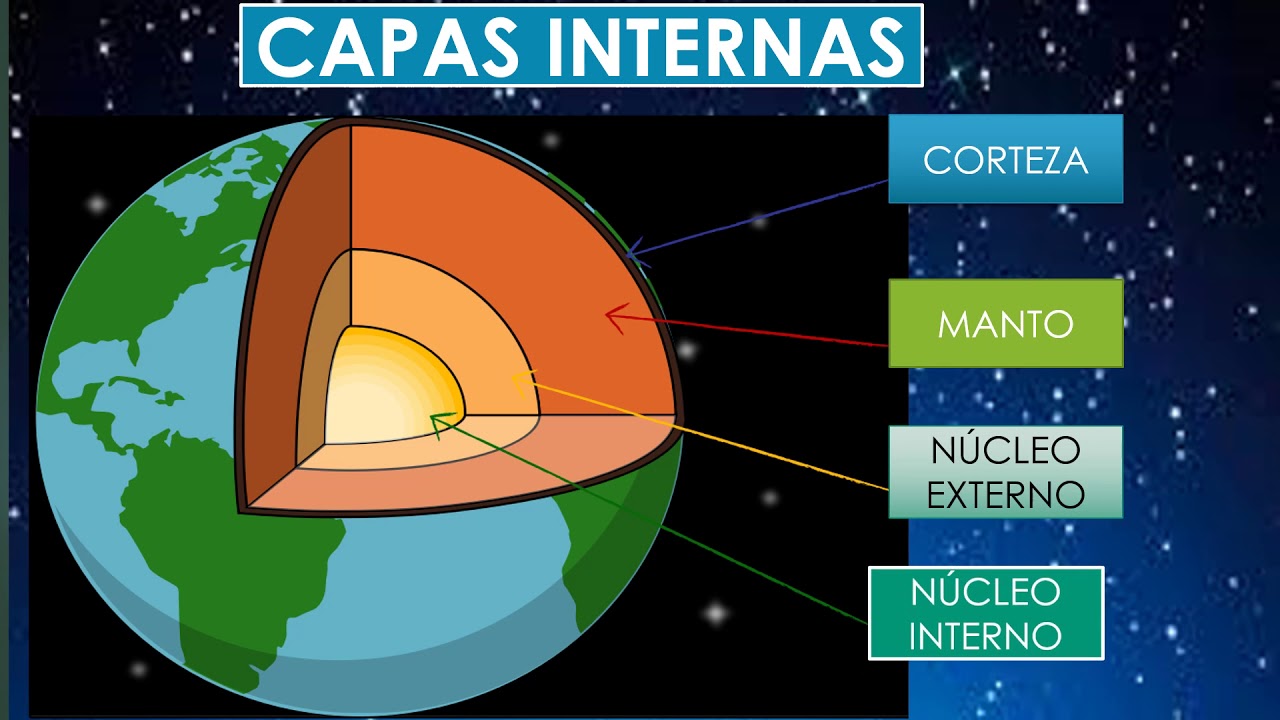
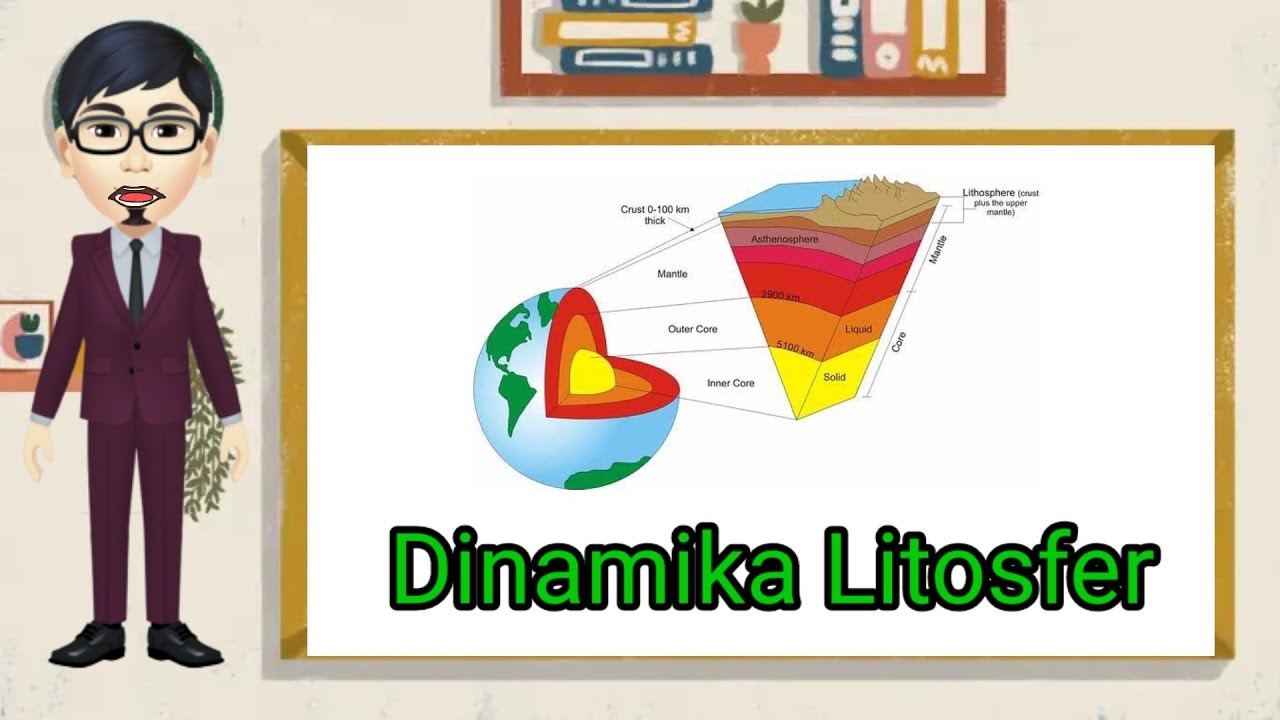
- 😀 The Earth’s lithosphere is a solid layer consisting of the crust, mantle, and core, and is crucial for supporting life.
- 😀 The crust is the thinnest layer of the Earth, ranging from 5 to 70 km thick, and supports life on the planet.
- 😀 The mantle is the thickest layer, approximately 2,900 km, and is composed of silicate rocks with iron and magnesium.
- 😀 The outer core is made of molten iron and nickel and has a thickness of 2,900 to 5,000 km, with temperatures ranging from 3,800 to 6,000°C.
- 😀 The inner core is solid due to extreme pressure, composed of iron, nickel, sulfur, silicon, and potassium, with temperatures between 5,000 and 7,000°C.
- 😀 The hydrosphere includes not only oceans and seas but also lakes, rivers, groundwater, and atmospheric water vapor.
- 😀 The theory of plate tectonics explains how Earth's crust is divided into plates that move due to geological forces, resulting in events like earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- 😀 The Earth's surface was once a single landmass called Pangaea, which split into two large continents, Gondwana and Laurasia, due to tectonic plate movements.
Q & A
What are the three main layers of Earth's structure?
-The three main layers of Earth's structure are the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere.
What gases make up the Earth's atmosphere?
-The Earth's atmosphere consists of oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases such as neon, helium, methane, krypton, xenon, hydrogen, and ozone.
What is the function of the troposphere?
-The troposphere, which is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extends from 0 to 10 km above the Earth's surface. It contains most of the Earth's weather phenomena.
What is the difference between the mantle's outer and inner layers?
-The outer mantle is relatively thinner, ranging from 35 to 400 km in thickness, while the inner mantle is much thicker, spanning from 410 to 2,900 km. The outer mantle has a lower temperature (around 250°C), and it is mostly composed of silicate rocks, whereas the inner mantle is hotter, with temperatures reaching 25,500°C, and behaves plastically due to the presence of molten metals.
What causes the Earth's tectonic plates to move?
-The movement of the Earth's tectonic plates is caused by convection currents in the asthenosphere, which transfer heat and cause molten materials to rise and move the plates.
What is the 'Ring of Fire'?
-The 'Ring of Fire' refers to a region around the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur due to the tectonic plate movements in that area.
What is the primary cause of earthquakes according to the script?
-Earthquakes are primarily caused by the movement of tectonic plates, specifically through transformations (sliding past one another), convergences (colliding), or divergences (moving apart). These movements accumulate energy that is released during seismic events.
How do divergent plate boundaries affect the Earth's surface?
-Divergent plate boundaries occur when two tectonic plates move away from each other, leading to the formation of rifts or gaps that are eventually filled with material rising from beneath the Earth's surface.
What are the two types of energy forces that shape the Earth's surface?
-The two types of energy forces that shape the Earth's surface are exogenous forces (from outside the Earth, such as erosion and weathering) and endogenous forces (from within the Earth, such as tectonism and volcanism).
What is the concept of Pangea, and how does it relate to plate tectonics?
-Pangea refers to a supercontinent that existed about 225 million years ago, where all the Earth's landmasses were joined together. Over millions of years, Pangea split into two continents, Gondwana and Laurasia, due to tectonic plate movements, which continue to shape the Earth's surface today.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)