Sistem Kendali 2.2. Transformasi Laplace
Summary
TLDRThe transcript covers the concept of Laplace Transform, explaining its use in transforming time-domain signals (XT) into the s-domain (XS) to simplify operations. The speaker highlights how this transformation enables the conversion of convolution operations into simple multiplication, which simplifies the calculation of output signals. Examples include the transformation of unit step functions and ramp functions, along with properties of Laplace Transforms such as handling coefficients, additions, subtractions, and the effect of exponential terms. The lecture also emphasizes the usefulness of Laplace Transform in linear systems, referring to its manual computation and use of tables.
Takeaways
- 😀 Laplace Transform is used to simplify operations on time-domain signals, turning convolutions into simple multiplications.
- 😀 The core formula of Laplace Transform is the integral of a signal multiplied by an exponential factor, e^(-st).
- 😀 Convolution in linear systems can be complex, so Laplace Transform helps to convert this to simpler algebraic operations.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform of a unit step function (U(t)) is 1/s, derived using integration techniques.
- 😀 The unit ramp function (t) has a Laplace Transform that can be found using the basic rules of the transform.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform is versatile and can handle different signal types like exponential functions (e^(-at)).
- 😀 When performing Laplace Transforms, the coefficient 'a' in an exponential term can be factored out for simplicity.
- 😀 The Laplace Transform of sinusoidal functions like sin(ωt) follows a specific pattern: ω / (s² + ω²).
- 😀 Laplace Transform has properties like linearity, where scaling a function by a constant scales its transform.
- 😀 For a function multiplied by e^(at), the Laplace Transform involves replacing s with s + a in the resulting formula.
Q & A
What is the Laplace transform?
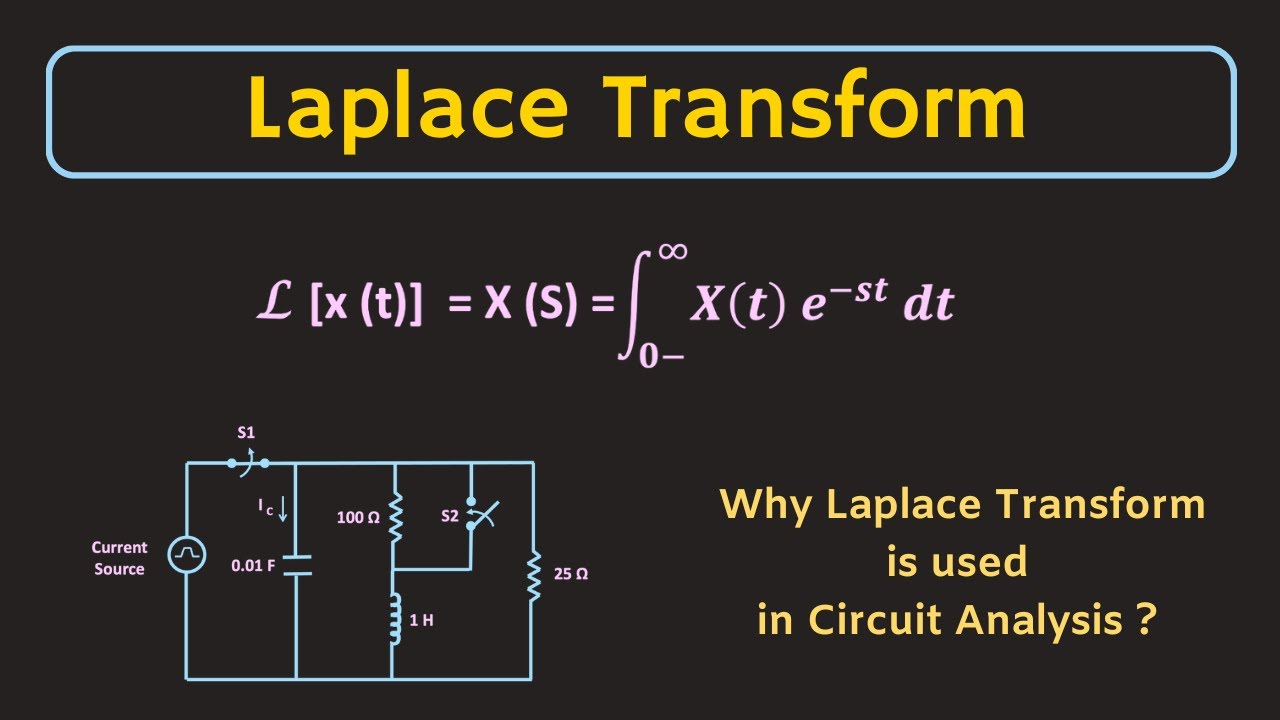
-The Laplace transform is a mathematical operation that transforms a time-domain signal, represented by X(t), into a frequency-domain signal, represented by X(s). This transformation is defined by an integral from 0 to infinity of the product of the signal X(t) and the exponential function e^(-st), where 's' is a complex variable.
Why is the Laplace transform useful in systems analysis?
-The Laplace transform simplifies the process of analyzing linear systems by converting time-domain operations, such as convolution, into simpler algebraic operations. Instead of performing complex convolution integrals to find the system output, the Laplace transform allows you to simply multiply the transformed input and system transfer function to obtain the output.
What is the convolution operation in linear systems?
-In linear systems, convolution is an operation that combines an input signal X(t) with the system's impulse response H(t) to produce the output Y(t). Mathematically, it is expressed as Y(t) = X(t) * H(t), which is a complex integral. Convolution can be avoided by using the Laplace transform, which simplifies the operation to multiplication in the s-domain.
How does the Laplace transform simplify the convolution operation?
-The Laplace transform converts the convolution operation into multiplication. Instead of performing an integral for convolution, the Laplace transform of the input signal X(t) is multiplied by the Laplace transform of the system's impulse response H(s), resulting in a simpler calculation for the output in the s-domain. The final output is then obtained by applying the inverse Laplace transform.
What is the Laplace transform of the unit step function?
-The unit step function, u(t), has a value of 0 for t < 0 and 1 for t ≥ 0. The Laplace transform of u(t) is 1/s, as shown by integrating the signal u(t) multiplied by e^(-st) from 0 to infinity. The result is 1/s because the exponential term goes to zero as t approaches infinity.
What is the Laplace transform of a ramp function?
-A ramp function is a signal of the form a * t, where 'a' is a constant. The Laplace transform of a ramp function is found by integrating t * e^(-st) from 0 to infinity. This results in the transform a / s², where 'a' is the coefficient of the ramp signal.
What is the general formula for the Laplace transform of e^(-at)?
-The Laplace transform of the exponential function e^(-at) is 1 / (s + a). This can be derived by performing the Laplace transform integration of e^(-at) * e^(-st) from 0 to infinity.
How does the Laplace transform help in analyzing sinusoidal signals?
-The Laplace transform allows for a straightforward way to analyze sinusoidal signals. For example, the Laplace transform of sin(10t) is 10 / (s² + 100), where the frequency of the sine wave is incorporated into the 's' term. This approach allows for easier manipulation and calculation in the s-domain.
What are some key properties of the Laplace transform?
-Some important properties of the Laplace transform include linearity (transforming a sum of functions corresponds to the sum of their transforms), scaling (a constant factor can be taken outside the transform), and frequency shifting (multiplying a function by e^(at) shifts its Laplace transform in the s-domain by 'a'). These properties make it easier to transform complex signals.
How is the Laplace transform used in practical system analysis?
-In practical system analysis, the Laplace transform is used to simplify the analysis of linear time-invariant systems. Engineers and analysts use it to find the system response to different input signals, such as step or sinusoidal signals, by transforming both the input and the system's transfer function into the s-domain, performing simple algebraic operations, and then applying the inverse Laplace transform to get the output in the time domain.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Materi Transformasi Fourier - MK Matematika Radiologi
What is Laplace Transform? Why Laplace Transform is used in Circuit Analysis?

Sistem Kendali 2.1. Dasar Transformasi Laplace

58. Konsep Transformasi Fourier

Control Systems Lectures - Time and Frequency Domain

Pengolahan Sinyal Digital: 08 Domain Sinyal dan Transformasinya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
