Statistika Deskriptif Ukuran Pemusatan dan Penyebaran Data | Zulfanita Dien Rizqiana, S.Stat., M.Si.
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the essential concepts of central tendency and dispersion in data analysis. The speaker, Sulfani Bujana, a lecturer at FEBI UIN Raden Mas Said Surakarta, introduces various measures such as mean, median, mode, and quartiles for summarizing and analyzing data. The video also explores how to calculate these measures for both individual and grouped data, and discusses how they reflect the distribution and spread of data. Key techniques such as frequency distribution, interpolation, and standard deviation are explained to better understand statistical variability, providing a comprehensive guide for students of statistics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mean (average) is a measure of central tendency, representing the center of mass of a data set.
- 😀 Median is the middle value in a sorted data set, dividing the data into two equal parts.
- 😀 Mode refers to the most frequent value in a data set and can have multiple values (bimodal).
- 😀 Quartiles (Q1, Q2, Q3) divide data into four equal parts and are resistant to outliers.
- 😀 The mean is calculated by summing all values in a population or sample and dividing by the number of observations.
- 😀 For grouped data, the mean is calculated using the weighted average of class midpoints multiplied by their frequencies.
- 😀 Mode for grouped data is found by determining the class with the highest frequency and applying a specific formula.
- 😀 Median for grouped data is calculated by finding the class that contains the middle observation and using interpolation.
- 😀 Range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set and shows the spread of the data.
- 😀 Standard deviation measures how spread out the data points are from the mean, providing insight into variability in the data.
Q & A
What is the concept of central tendency in statistics?
-Central tendency refers to the central or typical value around which a set of data points tend to cluster. It includes measures such as mean, median, and mode, which summarize data and help in comparing populations or samples.
What is the mean or average in statistics, and how is it calculated?
-The mean (or average) is the sum of all data points divided by the number of data points. For a population, the formula is: Mean = Σx / N, where Σx is the sum of all data points, and N is the total number of data points. For a sample, the formula is: Mean = Σx / n, where n is the number of data points in the sample.
How is the median defined, and how is it calculated?
-The median is the middle value of a data set when arranged in ascending or descending order. For an odd number of data points, the median is the middle value. For an even number of data points, it is the average of the two middle values.
What is the mode in a data set, and when can a data set have more than one mode?
-The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. A data set can have more than one mode if multiple values appear with the same highest frequency, which is known as a bimodal or multimodal distribution.
What are quartiles, and how do they divide a data set?
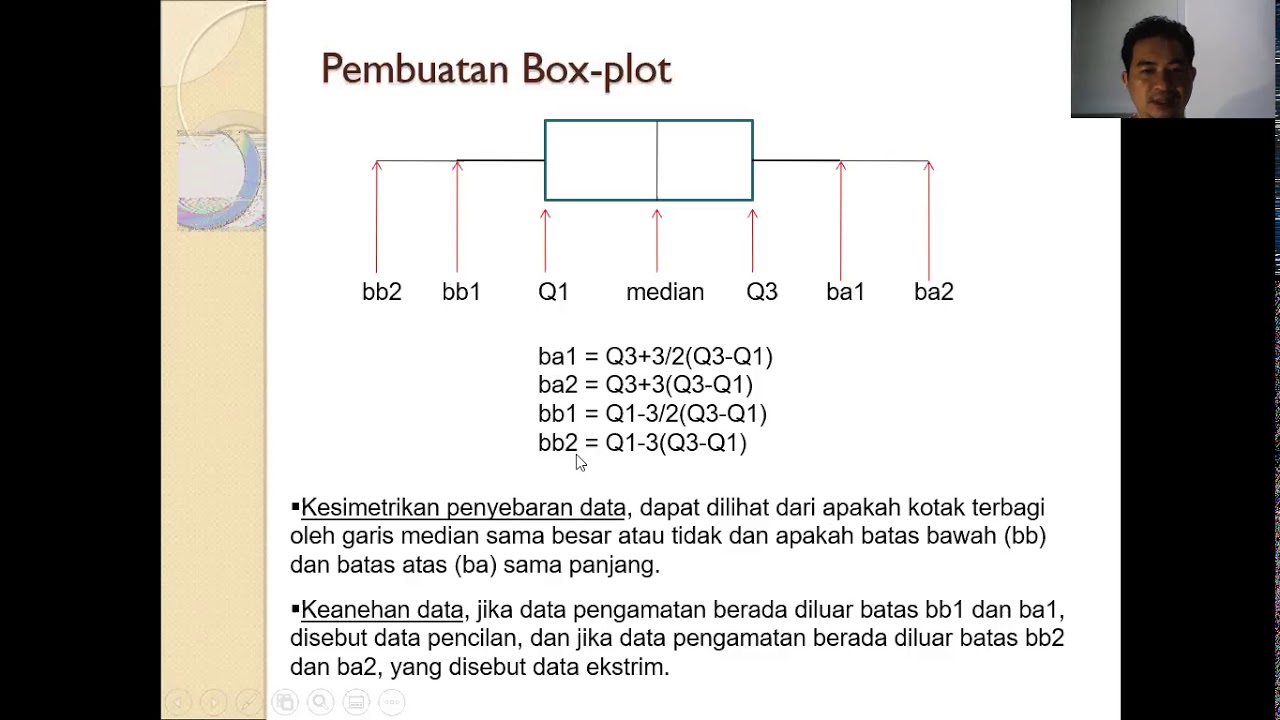
-Quartiles are values that divide a data set into four equal parts. The first quartile (Q1) marks the 25th percentile, the second quartile (Q2) is the median or 50th percentile, and the third quartile (Q3) is the 75th percentile. The fourth quartile (Q4) is the maximum value in the data set.
How is the range of a data set calculated?
-The range is calculated by subtracting the smallest value from the largest value in the data set. It provides a measure of the spread of the data.
What is the interquartile range (IQR), and how is it calculated?
-The interquartile range (IQR) is the difference between the third quartile (Q3) and the first quartile (Q1). It is used to measure the spread of the middle 50% of the data and is resistant to outliers.
How is variance different from standard deviation?
-Variance is the average of the squared differences from the mean, and it represents the spread of data points in a data set. Standard deviation is the square root of variance and provides a measure of spread in the original units of the data.
What are the steps involved in calculating the variance for a sample?
-To calculate the variance for a sample, first find the mean of the sample. Then, subtract the mean from each data point, square the result, and sum these squared deviations. Finally, divide by the sample size minus one (n-1) to obtain the sample variance.
What factors influence the shape of a data distribution, and how do mean, median, and mode relate to it?
-The shape of a data distribution can be influenced by the symmetry or skewness of the data. If the mean, median, and mode are the same, the distribution is symmetric. If the mean is greater than the median, the distribution is skewed to the right. If the mean is less than the median, the distribution is skewed to the left.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)