E-FUNLEARNING HMAK: PERPAJAKAN PPH PASAL 28 DAN 29
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging video, Edo and Maya from the Divisi Edukasi Mahasiswa break down essential concepts of Indonesian income tax, focusing on PPh Pasal 28 (overpayment) and PPh Pasal 29 (underpayment). Using clear examples, they explain how these two sections of the tax code apply to both individuals and businesses. Viewers will learn about tax refunds for overpayments and the process of settling underpaid taxes. Whether you're a student or a taxpayer, this video provides valuable insights into calculating and understanding your tax obligations.
Takeaways
- 😀 **Introduction to PPh Pasal 28 and Pasal 29**: PPh Pasal 28 deals with overpayment (lebih bayar), while PPh Pasal 29 is about underpayment (kurang bayar) in tax calculations.
- 😀 **PPh Pasal 28**: If the calculated tax is less than the tax credits, the excess payment can either be refunded or carried forward to the next tax year.
- 😀 **PPh Pasal 29**: If the calculated tax exceeds the payments made, the taxpayer must pay the remaining balance after the tax year ends.
- 😀 **Key Similarity**: Both PPh Pasal 28 and Pasal 29 are used for year-end tax calculations (annual tax report).
- 😀 **Difference in Payments**: PPh Pasal 28 results in a refund or carryover, while PPh Pasal 29 requires additional payments for the remaining balance.
- 😀 **Example of PPh Pasal 28**: If the taxable income for 2016 is 200 million, and there are tax credits from various sources (e.g., PPh Pasal 22, 23), the excess payment (6.5 million) is refunded.
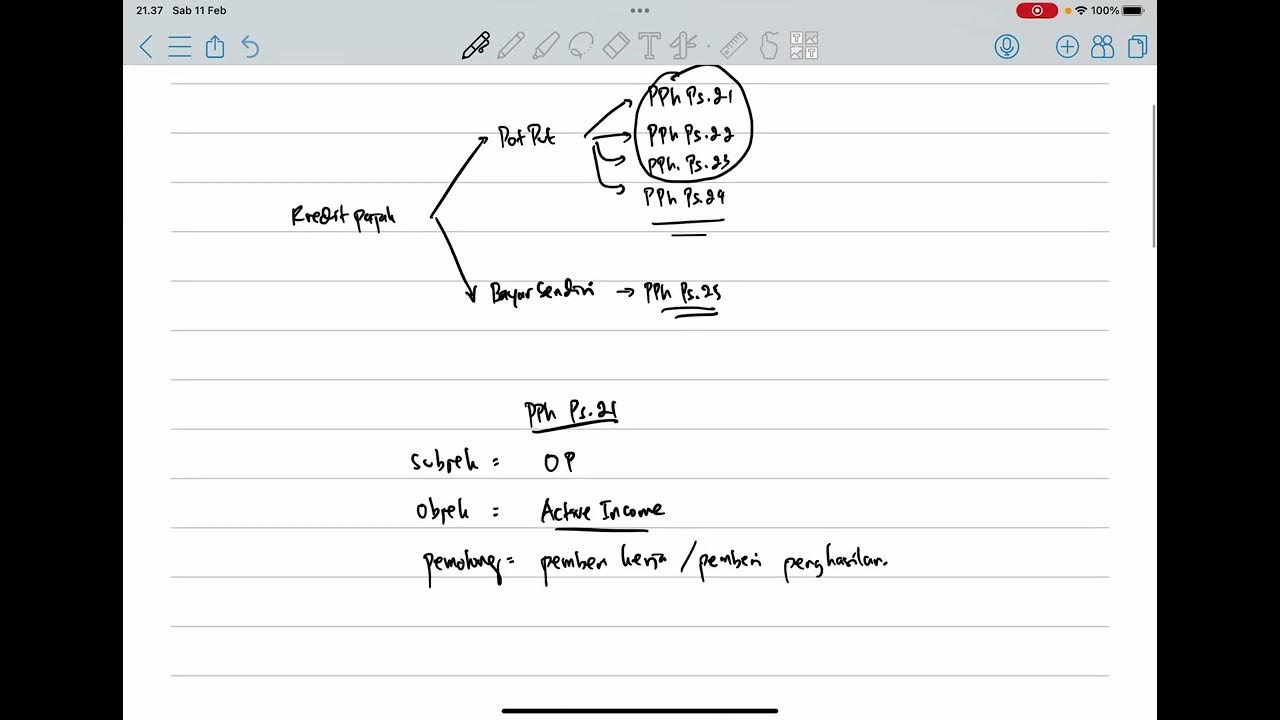
- 😀 **Tax Credit Types for PPh Pasal 28**: Includes credits from PPh Pasal 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, and 26, all related to different sources of income and tax payments.
- 😀 **Due Date for Payments**: PPh Pasal 28 (excess payment) must be processed after the tax report submission, and the refund or carryover happens within the tax period.
- 😀 **PPh Pasal 29 Example for Individuals**: A businesswoman (Ibu Nur) with a taxable income of 2 billion had a tax shortfall of 500,000 after payments, showing how underpayment works.
- 😀 **PPh Pasal 29 for Companies**: For businesses, if tax due in 2020 is 500 million, but it rises to 700 million in 2021, the company must pay the difference of 200 million as underpaid tax.
Q & A
What is the main difference between PPh Pasal 28 and PPh Pasal 29?
-PPh Pasal 28 deals with overpayment of taxes (lebih bayar), where the taxpayer has paid more than required, and the excess is refunded or carried forward. PPh Pasal 29, on the other hand, deals with underpayment of taxes (kurang bayar), where the taxpayer owes additional taxes after the year-end calculation.
How does PPh Pasal 28 benefit taxpayers who overpay their taxes?
-Taxpayers who overpay their taxes under PPh Pasal 28 can receive a refund for the excess payment or apply it to the next tax year.
What are the conditions that must be checked before the refund of overpaid taxes under PPh Pasal 28?
-Before the refund is made, the following conditions must be checked: the accuracy of the taxable income, the validity of tax payment proofs, and the correctness of tax deductions and withholdings.
What happens if there is underpayment of taxes at the end of the tax year under PPh Pasal 29?
-If there is underpayment of taxes under PPh Pasal 29, the taxpayer must pay the remaining amount before submitting the annual tax return (SPT) or by the specified deadline.
When is the deadline for paying the underpaid taxes for individuals under PPh Pasal 29?
-For individuals, underpaid taxes must be paid no later than April 30th of the following year, unless their fiscal year differs from the calendar year.
How does PPh Pasal 29 apply to businesses (WP badan)?
-For businesses, PPh Pasal 29 involves paying the difference between the tax owed in the current year and the installments already paid through PPh Pasal 25. The tax owed is determined based on their annual taxable income.
Can you explain the concept of PPh Pasal 22 credit mentioned in the script?
-PPh Pasal 22 refers to the tax collected on imports or certain business activities. This tax can be credited toward the taxpayer's annual tax obligations, as shown in the example with the total PPh Pasal 22 credit of 7 million.
What was the total tax credit in the example from the script, and how was it calculated?
-In the example, the total tax credit was calculated as follows: PPh Pasal 22 (7 million), PPh Pasal 23 (9.5 million), and PPh Pasal 22 additional credit of 15 million. This gave a total of 31.5 million in credits.
How does the installment payment work for PPh Pasal 25?
-PPh Pasal 25 involves monthly installment payments made by taxpayers throughout the year. These payments are credited against the total tax owed at year-end. For instance, the monthly installment is calculated as 0.75% of the total income, and the sum is applied to the tax return.
What are the different tax rates for businesses based on their revenue under PPh Pasal 29?
-For businesses, the tax rate varies based on their gross revenue: 0.5% for businesses with gross revenue up to 4.8 billion, 11% for revenue between 4.8 billion and 50 billion, and 22% for revenue over 50 billion.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
PPh Orang Pribadi (Update 2023) - 5. Kredit Pajak

Tips memahami apa saja jenis pajak perusahaan yang harus Anda laporkan

Perbedaan Pemotongan & Pemungutan Pajak || Withholding Tax #tutorialpajak

Menghitung Pajak Penghasilan Pasal 21 || Materi Ekonomi Kelas XI

MENGENAL PPH 21 LEBIH DEKAT AGAR TIDAK SALAH PAHAM DENGAN PERUSAHAAN ANDA

Konsep dan Penghitungan PPh Pasal 23
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
