Setting-Up and Commissioning a DEYE inverter - Step-by-Step Tutorial
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Norby Babos, the technical manager at Solar Kit, walks viewers through the setup of a hybrid inverter at the D Factory in Ningbo. The video covers key steps like disabling the beeping noise, configuring battery settings, ensuring no energy is fed back into the grid, and adjusting various system parameters for optimal performance. It also demonstrates how to connect the inverter to the DCloud app for remote monitoring and management. The video provides a comprehensive guide for setting up a reverse power system with a battery, ensuring proper operation and monitoring.
Takeaways
- 🔧 The video is about setting up a hybrid inverter at the Ningbo D Factory.
- 🔕 First, the beeping noise from the inverter must be disabled in the basic settings to avoid distractions.
- 🔋 The inverter connects to a lithium battery via cable, and proper settings for charging/discharging must be configured.
- 🚫 The system is set up to prevent energy from being fed back into the grid and only powers the house using solar energy.
- ⚡ Various battery parameters, such as low battery shutdown (10%) and restart (50%), are set by default to optimize power usage.
- 🔍 Zero export to the grid is enabled to avoid sending excess energy back to the grid, directing all energy to the load.
- 📅 Time of use settings allows managing battery discharge for optimal energy usage, with default discharge set at 35%.
- 🌐 The grid settings are pre-configured, and asymmetric phase feeding is enabled to balance power distribution across phases.
- 📱 The D Cloud app is used for monitoring and managing the system remotely after connecting the device to the local Wi-Fi network.
- 👤 The setup involves creating a site in the app, assigning user permissions, and granting access for monitoring the system.
Q & A
What is the purpose of disabling the beep function on the inverter?
-The beep function is disabled to avoid noise disturbance and to make the rest of the video clear to hear.
What is the significance of the electrical network being the same as home?
-It signifies that the electrical network has 230 volts between neutral and phase and 400 volts between phases, ensuring no differences in the network setup.
Why is it important to set up the inverter for a back wattage system?
-It is important for a back wattage system setup because it ensures that the battery does not feed back to the grid but instead powers the house with solar energy both day and night.
What does selecting the lithium battery option in the battery mode do?
-Selecting the lithium battery option configures the inverter to communicate with the battery via cable, managing the whole charging and discharging process.
Why is it necessary to uncheck all boxes under gen charge and grid charge?
-Unchecking these boxes ensures that the battery does not charge from the generator or the grid, which is necessary for a simple system setup.
What does the 'low battery restart' percentage value indicate?
-It indicates the point at which the inverter will charge the battery to at least 50% after it has been discharged.
Why is zero export to CT enabled in the system?
-Zero export to CT is enabled to prevent any excess power from being sent to the grid, ensuring that all energy is directed to the load port based on consumption.
What is the purpose of setting the zero export power to 500 watts?
-It ensures that the inverter always draws a minimum of 500 watts from the grid, acting as a buffer to prevent unintentional momentary feeding when consumption drops.
Why is the time of use table feature enabled?
-Enabling the time of use table feature allows the inverter to manage battery discharge in systems with reverse power, not just charge it.
What does the VDE 0410 setting in the grid settings represent?
-VDE 0410 represents the network setup, which is the same as a home electrical network, ensuring the inverter is set up correctly for the local grid.
Why is asymmetric phase feeding enabled in the advanced functions?
-Asymmetric phase feeding is enabled to allow the system to feed power back asymmetrically based on consumption demand across the three phases, rather than symmetrically.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
Time Charging via Soliscloud (Phone Version)

Solar Wind Hybrid System can generate more energy for you | ECO-WORTHY
GivEnergy vs SunSynk : Which Hybrid Solar Inverter?!
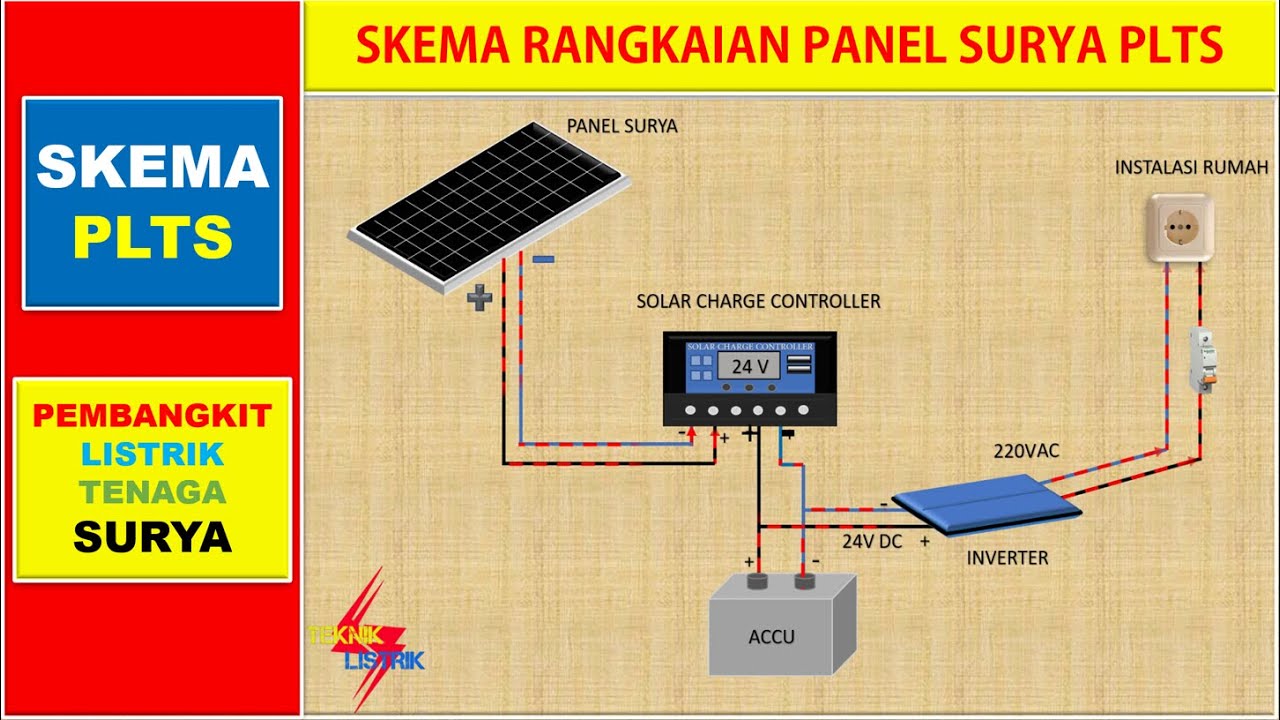
Skema Rangkaian Panel Surya PLTS (Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya/Matahari)

Solar Wind Hybrid Energy System using MATLAB Simulink | IEEE Project | Solar PV Wind Hybrid System

78000/- மானியத்துடன் தடையில்லா மின்சாரம் 365 நாட்களுக்கும் இலவசம்! PM Surya Ghar Scheme Solar Plant
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
