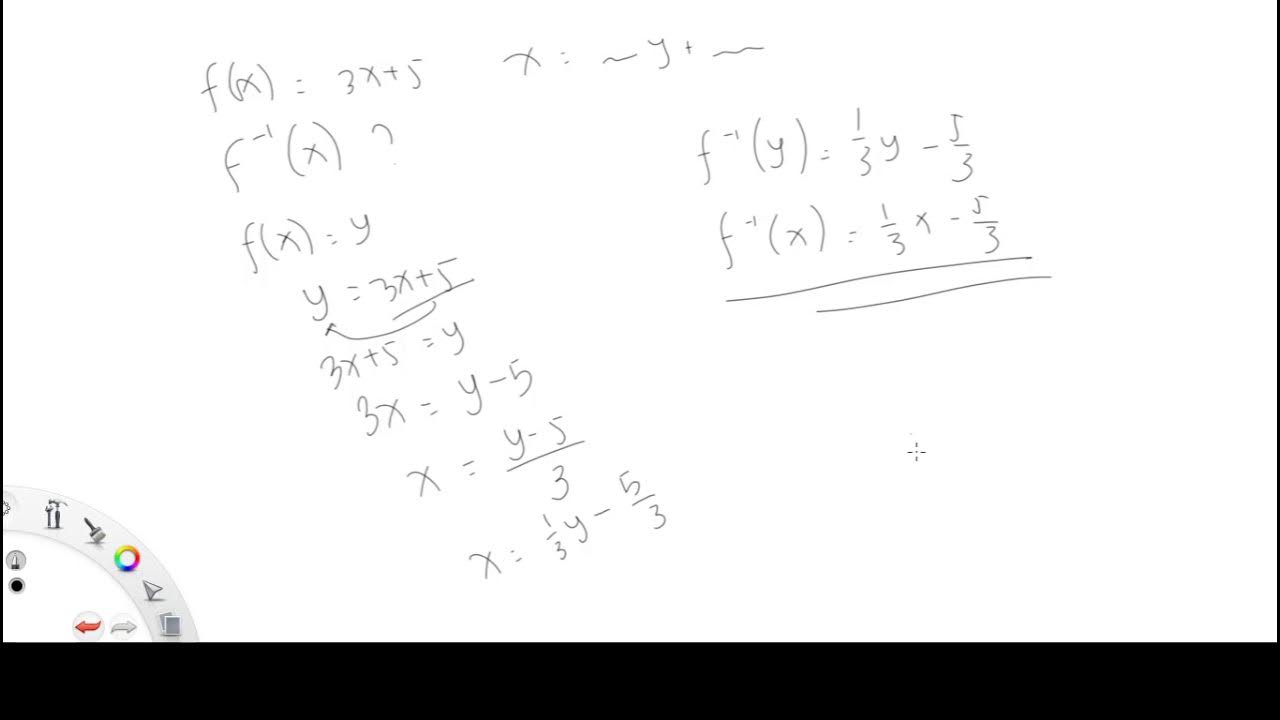INVERSE FUNCTION // GENERAL MATHEMATICS // TAGALOG
Summary
TLDRThe video explains how to find the inverse of various mathematical functions step by step. It begins by substituting 'y' for 'f(x)' and then interchanging 'x' and 'y' in the equation. The video demonstrates solving for 'y' through examples involving linear, rational, and cubic functions, and touches on more complex cases like quadratic functions. For each example, the instructor walks through the process of solving the equation, cross-multiplying, simplifying, and factoring to isolate 'y', ultimately determining the inverse function.
Takeaways
- 🔄 The first step in finding an inverse function is to change f(x) to y.
- ↔️ After that, swap x and y in the equation to find the inverse function.
- ➗ Solve for y by isolating it on one side of the equation and simplifying.
- ➕ Example 1: The inverse of f(x) = 3x + 6 is (x - 6) / 3.
- ➕ Example 2: The inverse of f(x) = 2x + 3 is (x - 3) / 2.
- ➕ Example 3: For a more complex function like f(x) = (3x - 7) / (4x + 3), you use cross-multiplication to solve.
- 💡 Use cross-multiplication when the function is a fraction to eliminate denominators.
- 🧮 Factor out common terms when simplifying expressions to find the inverse.
- 🔎 Always check for steps like removing fractions by multiplying both sides by the denominator.
- 🧩 Cube root functions require applying the cube root to both sides to isolate y.
Q & A
What is the first step in finding the inverse function?
-The first step is to change f(x) into y, so the equation becomes y = f(x).
After changing f(x) to y, what is the next step?
-The next step is to switch the roles of x and y, so x = f(y), and then solve for y.
How do you isolate y in the equation x = 3y + 6?
-To isolate y, first subtract 6 from both sides to get x - 6 = 3y. Then, divide both sides by 3 to get y = (x - 6)/3.
What does the inverse function represent in this context?
-The inverse function represents the function that 'undoes' the original function, mapping outputs back to inputs.
How do you find the inverse of a function when fractions are involved, such as f(x) = (3x - 7)/(4x + 3)?
-Start by switching x and y, then cross-multiply to eliminate the fraction, and solve for y using algebraic methods.
Why is cross-multiplication necessary when solving for the inverse of a rational function?
-Cross-multiplication helps eliminate the denominator, simplifying the equation so that you can isolate y and solve for the inverse.
How do you deal with cube roots when finding the inverse of functions like f(x) = x^3 + 5?
-To find the inverse, switch x and y to get x = y^3 + 5, then subtract 5 from both sides, and take the cube root of both sides to isolate y.
When dealing with quadratic functions, such as f(x) = x^2 - 2x + 3, what special technique is often used?
-Completing the square is a common technique used to simplify quadratic equations when finding their inverses.
What does it mean to 'complete the square' when finding the inverse of a quadratic function?
-Completing the square involves rewriting the quadratic equation in the form of (x + a)^2 to simplify solving for y.
Why might some inverse functions include both positive and negative solutions?
-Some inverse functions, especially those involving squares or cube roots, can have both positive and negative solutions due to the nature of the operations involved.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)