What is DCS? (Distributed Control System)
Summary
TLDRThis video explores Distributed Control Systems (DCS), highlighting their evolution from Distributed to Decentralized Control Systems. It compares DCS and PLC systems, explaining how DCS is ideal for managing large, continuous processes with integrated safety and redundancy features, while PLCs suit smaller, discrete tasks with flexible design. The video discusses DCS components like Operator Stations, servers, controllers, and field devices, emphasizing the communication protocols involved. Viewers will also learn about the future convergence of DCS and PLC technologies, with upcoming videos covering SCADA and further system contrasts.
Takeaways
- 🤖 The term DCS has evolved from 'Distributed Control System' to 'Decentralized Control System,' and both are often used interchangeably.
- ⚙️ DCS is a high-level system that supervises and coordinates an entire plant, managing many varying processes.
- 🛠️ PLCs are primarily used for repetitive, discrete control of single processes, while DCS is suited for continuous, complex operations.
- 🔄 Over time, the lines between PLCs and DCS have blurred, though they still maintain key differences in design and application.
- 🚀 PLCs are flexible, customizable, and fast, making them ideal for smaller, batch-controlled processes that require speed.
- 📊 DCS systems are slower but more integrated and are often preferred for large-scale, safety-critical operations due to their high reliability.
- 💾 DCS provides integrated control and supervisory equipment as a package, reducing integration risks and errors.
- 📉 DCS systems have an integrated control center, often compared to SCADA, and support continuous processes through various predefined functions.
- 🔧 PLC systems are best for smaller processes where redundancy can be deployed to avoid shutdowns, while DCS is suited for large processes with high I/O counts.
- 📡 Both PLCs and DCS can communicate with devices using multiple protocols, including Ethernet, Profibus, EtherCAT, and Fiber Optic.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video focuses on a deep dive into Distributed Control Systems (DCS), discussing the why’s and how’s associated with these systems.
What does DCS stand for, and how has its definition evolved?
-DCS stands for Distributed Control System, though it has also come to mean Decentralized Control System. The two terms are now somewhat interchangeable.
How does a DCS differ from a PLC in terms of application?
-A DCS is typically used for continuous, complex controls and large processes, while a PLC is used for single, discrete control tasks or high-speed control in smaller processes.
Why is a DCS considered more reliable when safety is a top priority?
-A DCS is considered more reliable for safety-critical processes because both the control and supervisory equipment are supplied as an integrated package by the manufacturer, reducing integration errors.
What are the main components of a DCS, starting from the operator’s perspective?
-The main components include Operator Stations (the control center), servers, archiving computers, engineering stations, master controllers, processors, and field devices like transmitters, switches, and valves.
How do Operator Stations function within a DCS?
-Operator Stations are the heart of the DCS, where operators observe plant operations, view alarms, monitor production, and interact with the system through a graphical display.
What is the role of the server in a DCS?
-The server collects data from the processor level and supplies it to the Operator Station for graphical interface display. It facilitates communication between the processors and the Operator Station.
How does a DCS ensure historical data storage for trends or compliance?
-A DCS uses archiving computers to store historical data, which can be used for trend analysis or to meet compliance requirements.
What type of communication protocols are typically used between various levels in a DCS?
-Industrial Ethernet is commonly used for communication between Operator Stations and processors, while Fiber Optic may be used when Ethernet cabling distances are too long. Other protocols like Profibus DP, EtherCAT, and proprietary communication methods are also used.
In what scenarios would a PLC system be more appropriate than a DCS?
-A PLC system is more suitable for smaller-sized processes with lower I/O counts, especially when budget constraints exist or if redundancy isn’t critical to prevent production halts.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
DISTRIBUTE CONTROL SYSTEM (DCS) SISTEM KONTROL TERDISTRIBUSI - DALAM OTOMASI INDUSTRI
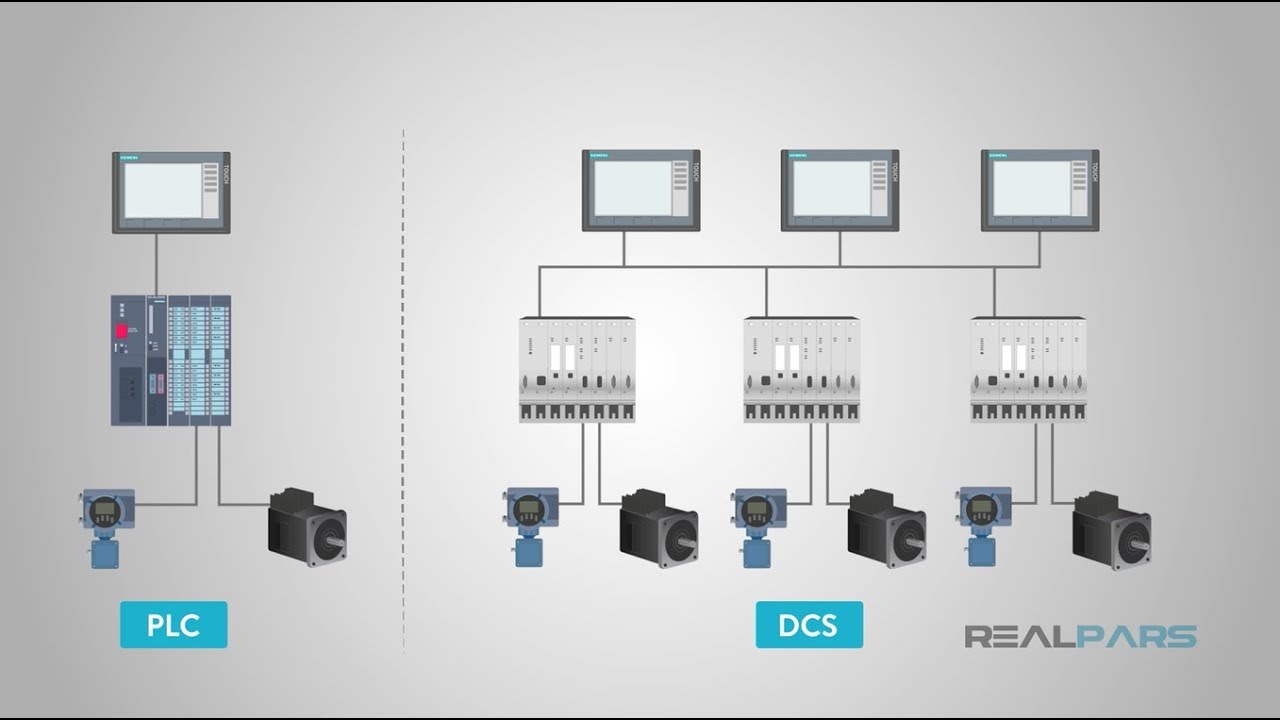
What is the Difference Between PLC and DCS?

DCS vs PLC | Understanding the Differences and Applications

#Distributed System Architecture

When to use PLC ,DCS & SCADA | PLC vs DCS vs SCADA Selection Guide
Konsep Dasar Sistem Operasi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
