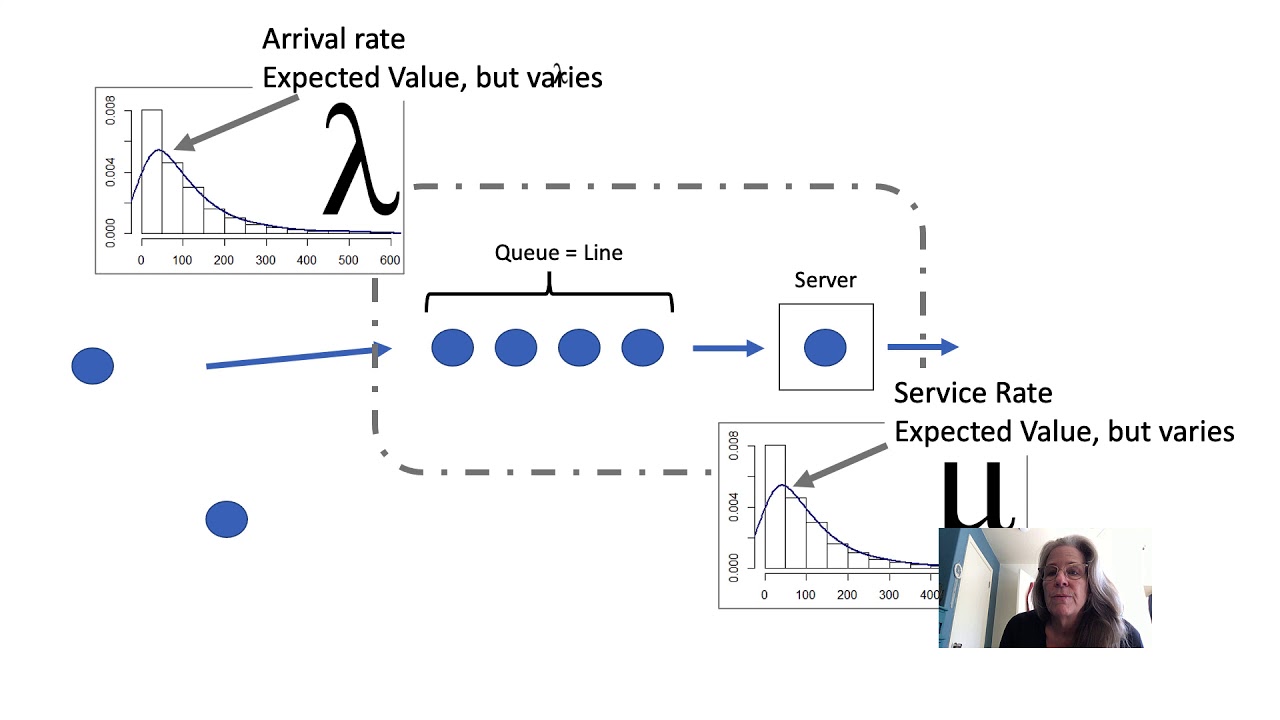
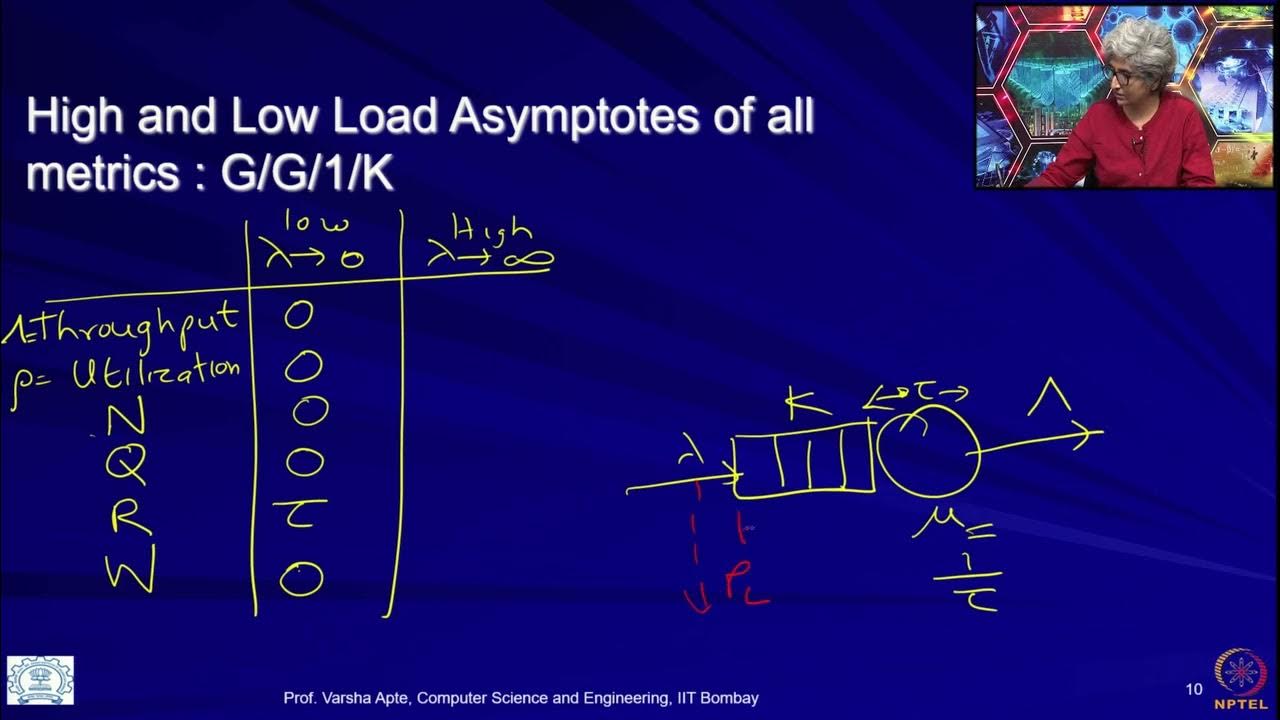
The Kingman Law - Capacity Utilization vs Queue Time
Summary
TLDRThe Kingman formula from queuing theory illustrates the exponential relationship between capacity utilization and queue time. As utilization increases beyond 80%, queue times soar, leading to increased inventory, working capital, and customer wait times. This can result in a vicious cycle of disruption and potential business failure. The formula highlights the importance of balancing capacity utilization to avoid operational pitfalls and maintain customer satisfaction.
Takeaways
- 📐 The Kingman formula is a mathematical model from queuing theory that illustrates the relationship between queue time and capacity utilization.
- 📈 As capacity utilization increases, the queue time grows exponentially, not linearly.
- 🚨 When capacity utilization exceeds 80%, there is a significant and sudden increase in queue time.
- 🔄 Higher capacity utilization leads to increased work in progress, inventory, working capital, and customer wait times.
- 🆘 Urgent tasks arriving at high capacity utilization can cause disruption, either by long waits or by expediting and causing further delays.
- 🔄 A vicious cycle of increased workload and customer dissatisfaction can lead to business failure if not managed properly.
- 💡 The choice of capacity utilization is a critical decision that can impact the success or failure of an organization.
- 🚫 The temptation to maximize capacity utilization can be detrimental, as it can lead to system overload and inefficiency.
- 🔄 Reducing variation in demand and capacity can lower the queue time and allow for higher capacity utilization.
- 🔄 Operations that can manage variation effectively can achieve higher efficiency and better performance.
Q & A
What is the Kingman formula?
-The Kingman formula is a mathematical formula from queuing theory that illustrates the relationship between queue time and capacity utilization in systems with varying levels of demand and supply.
How does the Kingman formula apply to real-world scenarios?
-In real-world scenarios, the Kingman formula helps to understand the impact of capacity utilization on wait times. It shows that as utilization increases, wait times increase exponentially, not linearly.
What happens when capacity utilization is low?
-When capacity utilization is low, the queue or wait time is also low, indicating that there is less demand and more capacity to handle it.
Why does queue time increase exponentially with higher capacity utilization?
-Queue time increases exponentially with higher capacity utilization because each additional percentage point of utilization has a greater impact on wait times than the previous one, due to the diminishing returns on capacity.
At what point does capacity utilization start to cause a dramatic increase in queue time?
-Capacity utilization starts to cause a dramatic increase in queue time when it climbs past about 80 percent.
What are the consequences of high capacity utilization on a business?
-High capacity utilization can lead to increased work in progress inventory, higher working capital, longer customer wait times, and potential disruption from urgent tasks, which can disrupt the overall output and lead to a vicious cycle.
How does the Kingman formula relate to customer satisfaction?
-The Kingman formula implies that high capacity utilization can lead to long wait times, which can frustrate customers and cause them to seek alternatives, thus affecting customer satisfaction negatively.
What is the 'vicious downward cycle' mentioned in the script?
-The 'vicious downward cycle' refers to the situation where increased capacity utilization leads to longer wait times, which in turn causes customer dissatisfaction, loss of demand, and potential financial failure for the business.
What is the significance of the 'perfect efficiency' of 100% capacity utilization mentioned in the script?
-The 'perfect efficiency' of 100% capacity utilization is a theoretical point where the system is operating at maximum capacity without any idle time. However, striving for this level can be risky as it may lead to excessive wait times and system breakdown.
How can an organization reduce the level of variation in demand and capacity?
-An organization can reduce the level of variation by implementing strategies such as better demand forecasting, inventory management, flexible workforce, and efficient scheduling to achieve higher capacity utilization without increasing queue times.
What insights does the Kingman formula offer for improving operations?
-The Kingman formula offers insights into the importance of balancing capacity utilization with queue times to maintain efficient operations. It suggests that reducing variation in demand and capacity can lead to higher utilization without increasing wait times.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)