Bacterial Conjugation
Summary
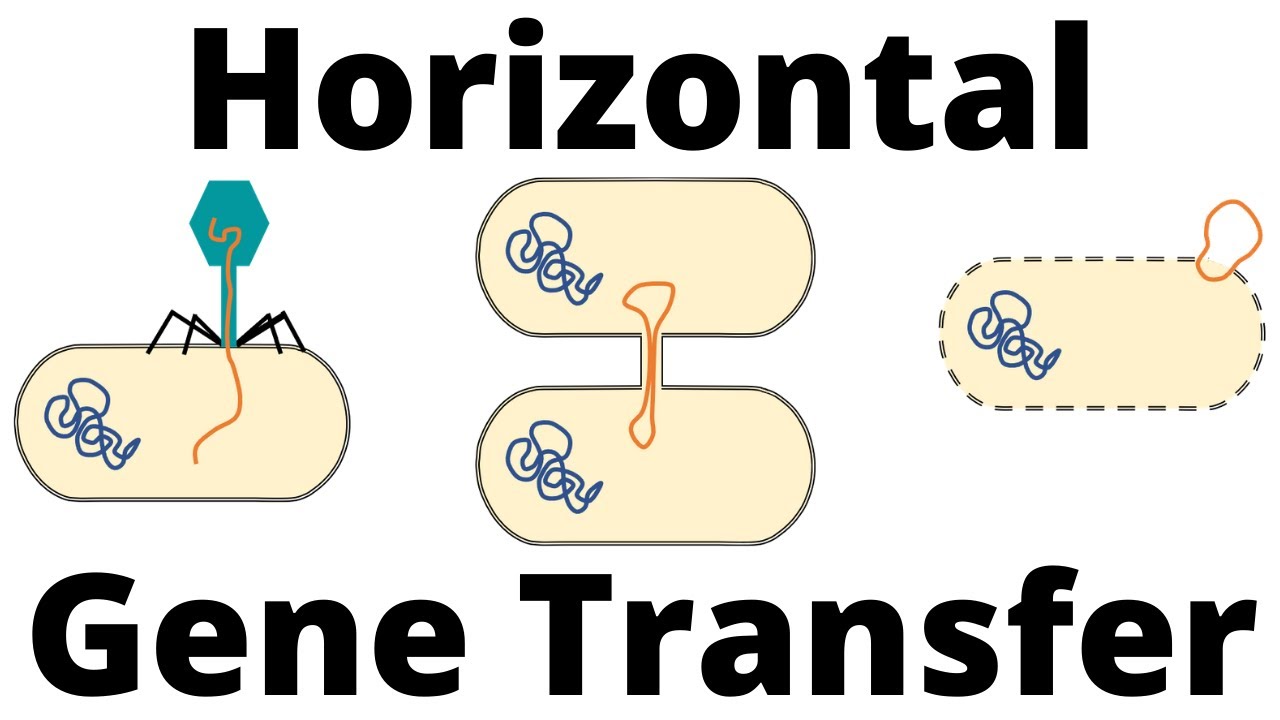
TLDRBacterial conjugation is a direct cell-to-cell genetic transfer process requiring contact, facilitated by the F factor, a fertility factor in bacteria. F+ cells, containing the F factor, form a pilus to connect with F- recipient cells. The F factor is cut at the origin of transfer, and the T DNA strand is transferred via a pilus-linked exporter. Once in the recipient, the T DNA replicates, and both cells become F+, capable of further conjugation.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Bacterial conjugation is a genetic transfer process between bacterial cells that requires direct cell-to-cell contact.
- 🔁 Conjugation can occur between cells of the same species or between different species.
- 🔵 The F factor, a small DNA circle or plasmid, is essential for bacterial conjugation and is referred to as the fertility factor.
- 📌 Bacteria containing the F factor are designated as F+ (donor cells), while those without it are F- (recipient cells).
- 🔗 The F+ cell produces a pilus, a structure that connects with a recipient cell to initiate conjugation.
- ✂️ The F factor is cut at the origin of transfer by a relaxer protein assembly, which associates with the T (transferred) DNA strand.
- 🔄 The relaxer protein complex, along with the T DNA strand, is recognized and transferred to the exporter complex in the F+ cell.
- 🚀 The exporter complex pumps the T DNA-relaxer complex into the recipient cell through the pilus.
- 🔁 During transfer, the T DNA is replicated in the donor cell, ensuring that both donor and recipient cells end up with a double-stranded copy of the F factor.
- 🔄 After the transfer, both the original and recipient cells become F+, capable of conjugating with other cells.
Q & A
What is bacterial conjugation?
-Bacterial conjugation is a process of genetic transfer between bacterial cells that requires direct contact between the cells.
Can conjugation occur between different species of bacteria?
-Yes, conjugation can occur between cells of the same species or even between cells of two different species.
What is the role of the F factor in bacterial conjugation?
-The F factor, or fertility factor, is a small DNA circle or plasmid required for conjugation.
How are bacteria with and without the F factor distinguished?
-Strain of bacteria containing the F factor are called F+, while those without it are called F-.
What structure does an F+ cell produce to initiate conjugation?
-An F+ cell produces a structure called a pilus to connect with another recipient cell to begin conjugation.
What is the origin of transfer and its role in conjugation?
-The origin of transfer is a specific region on the F factor where it is cut to initiate the transfer of genetic material.
What is the function of the relaxer protein complex in conjugation?
-The relaxer protein complex cuts the F factor at the origin of transfer and associates with the T DNA strand to be transferred.
How is the T DNA relaxase complex transferred to the recipient cell?
-The T DNA relaxase complex is recognized by a coupling factor and transferred to the exporter complex in the F+ cell, which pumps it into the recipient cell.
What happens to the T DNA once it is transferred to the recipient cell?
-Once the entire T DNA molecule is transferred to the recipient cell, the relaxase joins the ends to make a circular DNA molecule.
How does the F factor DNA become double-stranded in the donor and recipient cells?
-The F factor DNA is replicated to become double-stranded in the donor cell as the T DNA is being transferred to the recipient cell.
What is the outcome for the cells after the conjugation process?
-After the connection through the pilus is released, each cell, now containing a double-stranded copy of the F factor, becomes an F+ cell capable of conjugating with other cells.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)