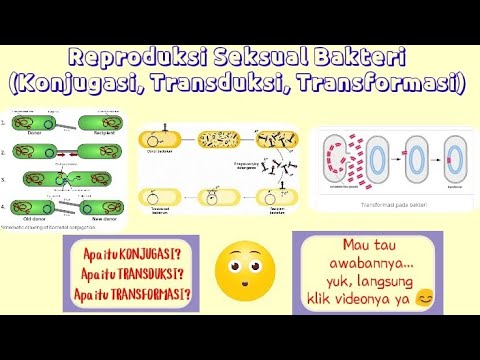
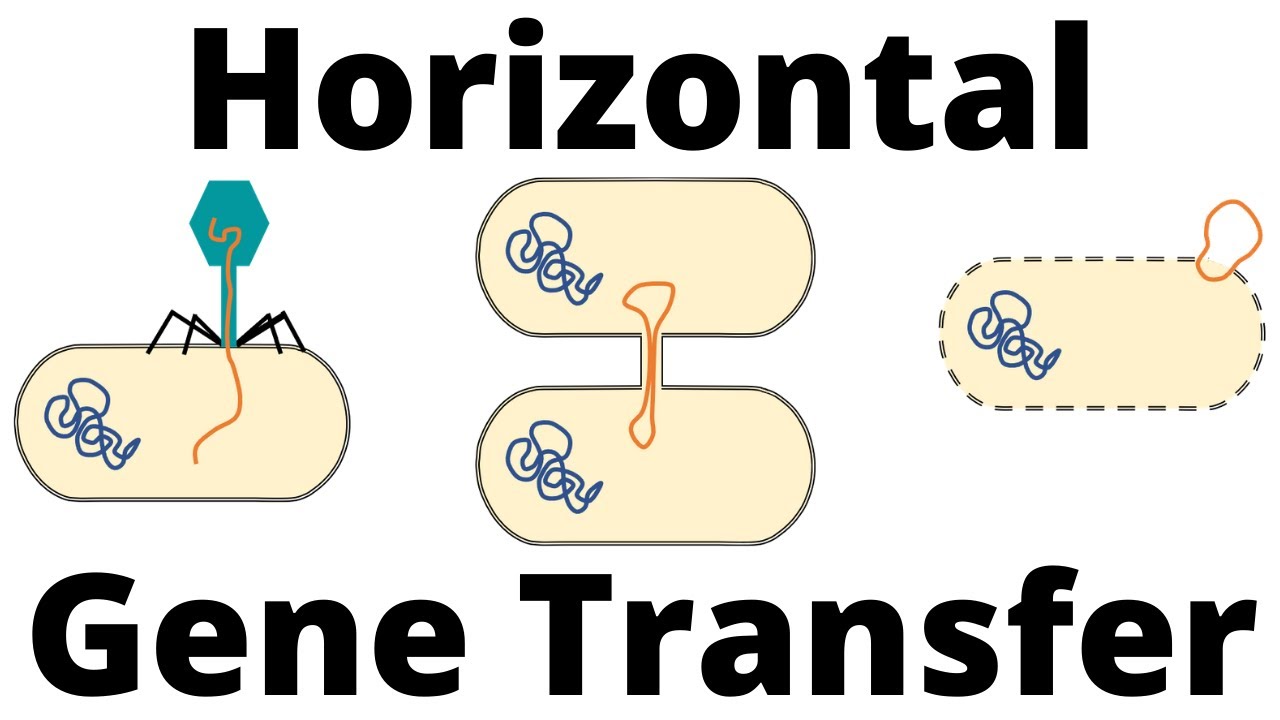
Transformasi, Transduksi, dan Konjugasi pada Bakteri
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an in-depth explanation of bacterial genetic transfer processes, focusing on transformation, transduction, and conjugation. The speaker discusses how genetic recombination occurs in bacteria, emphasizing the mapping of genes through conjugation. By monitoring gene transfer frequencies at different time intervals, the speaker illustrates how to construct genetic maps, revealing the order in which genes are transferred. The video highlights the importance of these mechanisms in bacterial evolution and genetic studies, offering insights into microbial genetics and laboratory techniques for gene mapping.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the concepts of transformation, transduction, and conjugation in bacteria, which are processes that can lead to genetic recombination.
- 😀 Transformation refers to bacteria acquiring genetic material from the environment, which can then be incorporated into their genome.
- 😀 Transduction involves the transfer of bacterial genes through viral (bacteriophage) infection.
- 😀 Conjugation is a direct transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells through physical contact, often involving plasmids.
- 😀 Gene transfer in bacteria can result in genetic diversity and the spread of beneficial traits, such as antibiotic resistance.
- 😀 The process of conjugation can be mapped by tracking the time and frequency of gene transfer using specific experimental techniques.
- 😀 During conjugation experiments, researchers can interrupt the process at different time intervals and measure the genes successfully transferred at each point.
- 😀 The frequency of gene transfer in conjugation can be measured to determine the order of gene transfer over time, creating a genetic map of bacterial genes.
- 😀 At certain time points, the gene transfer might reach 100%, indicating a successful conjugation event, while at later points, gene transfer efficiency may vary.
- 😀 The mapping of genes using conjugation can help researchers understand the sequence and spread of genetic material in bacterial populations.
- 😀 The speaker concludes by emphasizing the importance of understanding bacterial genetic transfer mechanisms, such as transformation, transduction, and conjugation, for studying bacterial evolution and genetics.
Q & A
What are the three main processes mentioned in the video that contribute to genetic recombination in bacteria?
-The three main processes mentioned are transformation, transduction, and conjugation. These processes enable genetic material exchange and lead to genetic recombination in bacteria.
How does bacterial transformation occur?
-Bacterial transformation occurs when a bacterium takes up foreign DNA from its surroundings and incorporates it into its own genome. This process is typically facilitated by environmental conditions that allow DNA uptake.
What is the role of bacteriophages in transduction?
-Bacteriophages, or phages, play a key role in transduction by carrying bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another. During infection, the phage may accidentally incorporate bacterial DNA into its own genome and transfer it to another bacterium.
What is conjugation, and how does it differ from transformation and transduction?
-Conjugation is a process where genetic material is directly transferred between two bacteria via physical contact, often through a pilus. Unlike transformation and transduction, which involve external factors like the environment or viruses, conjugation requires direct interaction between bacteria.
How can conjugation be used to map bacterial genes?
-Conjugation can be used to map bacterial genes by measuring the frequency at which different genes are transferred between bacteria at different time intervals. This helps determine the order of genes in the bacterial genome based on transfer timing.
What experimental technique is described for mapping bacterial genes using conjugation?
-The technique involves inducing conjugation between bacteria and stopping the process at various time intervals (e.g., 5, 10, 20, 30 minutes) by shaking the culture. By analyzing which genes are transferred at each time point, the sequence of gene transfer can be mapped.
What is the significance of observing gene transfer frequencies at different time intervals?
-Observing gene transfer frequencies at different time intervals helps determine the relative positions of genes in the bacterial genome. Genes that transfer earlier are closer to the origin of transfer, while those that transfer later are farther away.
Why is it important to maintain a stable environment for bacterial conjugation experiments?
-A stable environment is crucial because it ensures consistent conditions for the bacteria, allowing the conjugation process to proceed as expected. Any environmental disturbances can interfere with gene transfer, leading to unreliable results.
What happens if the conjugation process is interrupted during the experiment?
-If the conjugation process is interrupted, it prevents the full transfer of genetic material between bacteria. This interruption allows researchers to track which genes are transferred up to the point of disruption, aiding in gene mapping.
What conclusion can be drawn from the data when conjugation frequencies reach 100%?
-When conjugation frequencies reach 100%, it indicates that a particular gene or set of genes is transferred consistently across all bacterial cells, suggesting its proximity to the origin of transfer in the bacterial genome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)