How LED Works - Unravel the Mysteries of How LEDs Work!
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the workings of LEDs, explaining how these light-emitting diodes produce various colors by manipulating the semiconductor material inside. It covers the fundamental principles behind diodes and LEDs, their energy efficiency compared to incandescent lights, and the different types and applications of LEDs, including multi-color and high-powered LEDs. The script also touches on the importance of resistors in protecting LEDs from excessive current and introduces the concept of PN junctions in semiconductors, which are key to the color of light emitted. Additionally, it discusses the role of data brokers and the use of Incogni for privacy protection.
Takeaways
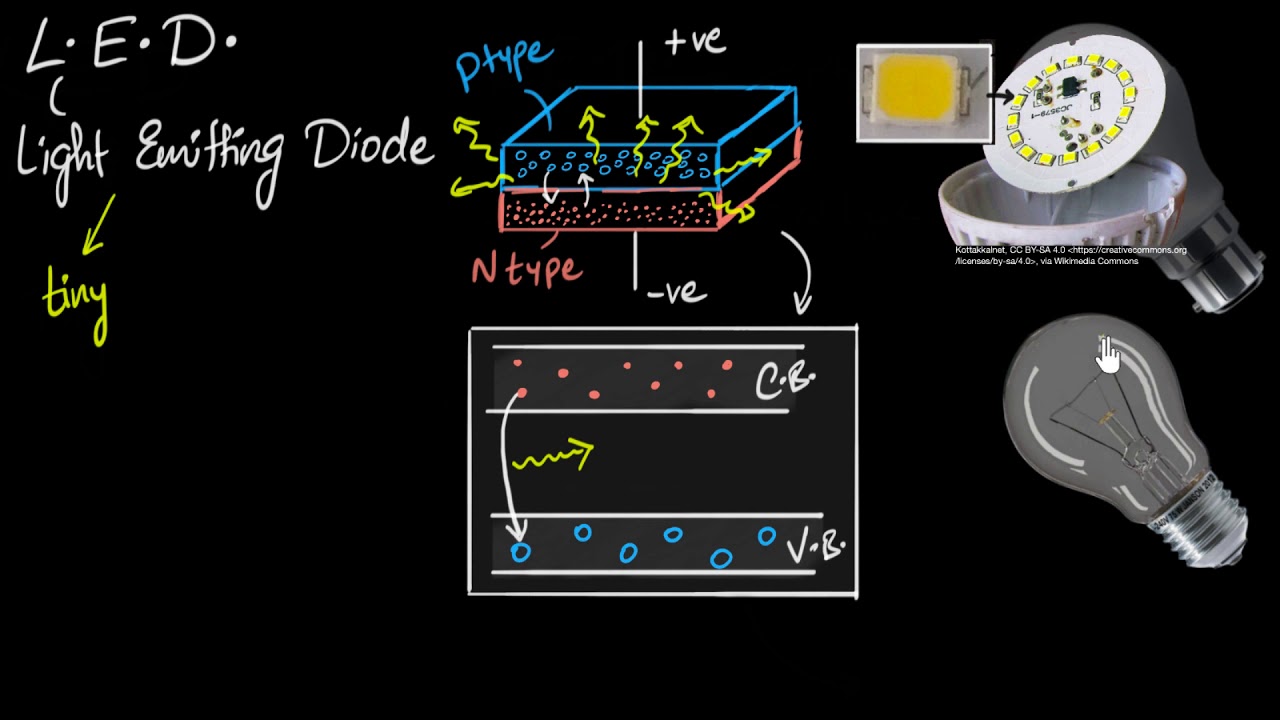
- 🚀 LEDs, or light-emitting diodes, emit light when a voltage is applied across them due to the semiconductor material inside.
- 🔍 Shining light onto an LED can reverse the process, producing a small voltage, demonstrating the dual nature of LEDs as light and electricity converters.
- 🌈 The color of the light produced by an LED is determined by the semiconductor material used, with different materials emitting different wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum.
- 🔆 LEDs are more energy-efficient than incandescent lights because they do not require heat to produce light, reducing energy consumption and heat generation.
- 🔌 The polarity of an LED is crucial; it only illuminates when the anode is connected to the positive side and the cathode to the negative.
- 🔍 The flat edge on an LED casing typically indicates the cathode side, helping to identify the correct connection polarity.
- 💡 There are various types of LEDs, including through-hole, surface-mount devices (SMD), high-powered, and multi-color LEDs, each suited for different applications.
- 🛠️ LEDs require a current-limiting resistor to prevent damage from excessive current, with the brightness controlled by varying the current or voltage.
- 🔄 Bi-directional and RGB LEDs can change colors or mix colors to produce a range of hues, including white light, by controlling the current to individual diodes within the unit.
- 🔬 The semiconductor material in LEDs is made by combining elements like gallium and arsenic, with impurities added to create n-type and p-type layers, which determine the emitted light color.
- 🌐 The development of LED technology has led to the creation of energy-efficient lighting solutions, such as LED bulbs, which are now widely used.
Q & A
What is the basic principle behind the light emission of an LED?
-An LED emits light when a voltage is applied across it, causing electrons in the semiconductor material to recombine with holes, which releases energy in the form of photons.
How does an LED symbol differ from a standard diode symbol in engineering drawings?
-An LED symbol is similar to a diode symbol but includes arrows that indicate light emission, distinguishing it from a standard diode which does not emit light.
What is the range of wavelengths for visible light to human eyes?
-Visible light to human eyes has a wavelength range of approximately 400 to 700 nanometers.
Why do standard diodes become hot, unlike LEDs?
-Standard diodes become hot because they produce photons in the near-infrared range, which are absorbed by the casing and converted to heat. LEDs, on the other hand, produce very little heat due to their different semiconductor materials and photon emission range.
What is the typical wavelength of the infrared light emitted by an LED in a TV remote?
-The typical wavelength of the infrared light emitted by an LED in a TV remote is around 940 nanometers, which is outside the visible spectrum for humans.
What is the main reason LEDs are more energy efficient compared to traditional incandescent lights?
-LEDs are more energy efficient because they do not need to produce heat to emit light, unlike incandescent lights which generate a lot of heat through the collisions of electrons with atoms in the filament.
What does the flat edge on one side of a through-hole LED indicate?
-The flat edge on one side of a through-hole LED indicates the cathode side of the LED, helping to identify the correct polarity for connection.
What is the purpose of the yellow phosphorus layer over a blue LED in some light bulbs?
-The yellow phosphorus layer over a blue LED in some light bulbs is used to combine with the blue light to produce a white light, as the mixture of yellow and blue light appears white to the human eye.
How can the color of an LED be changed by altering its semiconductor material?
-The color of an LED can be changed by altering the semiconductor material used in its construction. Different materials and their mixtures produce different band gaps, resulting in photons of different wavelengths and thus different colors of light.
What is the role of a resistor in an LED circuit?
-A resistor in an LED circuit is used to limit the current flow and protect the LED from being destroyed by an excessive amount of current. It also helps to control the brightness of the LED by varying the current.
How can the brightness of an LED be controlled?
-The brightness of an LED can be controlled by varying the current supplied to it. This can be achieved by using a resistor to set the current in the circuit or by using an LED driver that provides a constant current.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

What is LED Light Emitting Diode | How Does LED Works | Electronic Devices & Circuits | Engineering

Prinsip Kerja dan Fungsi LED
LED working & advantages | Semiconductors | Physics | Khan Academy

Types of Diodes - The Learning Circuit

Light Emitting Diode (LED) Explained (Working, Advantages and Types of LED Explained)

(Nanorush 2024) How LEDs are Made : The Journey from Start to Bright!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
