A Brief History of The Scramble For Africa
Summary
TLDRThe script explores Africa's rich cultural history and its colonization by European powers during the Scramble for Africa. It discusses the Sahara's impact on trade, early Arab and Portuguese trade with African empires, the transatlantic slave trade, and European settlements like the Cape of Good Hope. The script also covers the establishment of Liberia, the Suez Canal's significance, and the Berlin Conference's colonial carve-up. It highlights key explorers like Livingstone and Stanley, the exploitation of the Congo, and resistance movements, particularly Abyssinia's victory over Italy, culminating in the continent's division among European powers by 1914.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, with 54 countries and a rich diversity in ethnicity and language.
- 🏖 The continent is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Atlantic Ocean, which have historically influenced its trade and cultural interactions.
- 🗺️ The borders of African countries were largely determined by European powers during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly during the Scramble for Africa.
- 🏜️ The Sahara Desert is a significant geographical feature of Africa, acting as a barrier to communication and trade but also a route for historical expeditions.
- 🛶 Historical trade routes were established by Arabs and later the Portuguese, facilitating the exchange of goods like gold, ivory, and slaves with West African empires.
- 👑 The Kongo Kingdom's interaction with the Portuguese in the 15th century led to the introduction of Catholicism and trade of European goods for slaves.
- 🚢 The transatlantic slave trade, starting in the 16th century, involved over 12 million Africans being transported to the Americas under harsh conditions.
- 🏰 The Dutch East India Company established a settlement at the Cape of Good Hope, leading to conflicts with the indigenous Khoikhoi population and the importation of slaves.
- 🇺🇸 The American Colonisation Society transported free blacks and freed slaves to Africa, leading to the establishment of the independent republic of Liberia in 1847.
- 🛠 The industrial revolution in Europe led to a search for new markets and resources, prompting European exploration and colonization of Africa's interior.
- 🏛️ The Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 formalized European claims to African territories and aimed to avoid conflicts between colonial powers.
- 📊 The exploitation of Africa's natural resources like rubber, palm oil, gold, copper, and diamonds was a driving force behind European colonization.
- 🔫 Technological advantages, such as the machine gun, allowed small European forces to overpower larger African populations and establish control.
- 🛡️ Notable African resistance to European colonization included Abyssinia (modern-day Ethiopia) and the Boers in South Africa.
- 🏴 By 1914, most of Africa was under European control, with only Ethiopia and Liberia maintaining their independence.
Q & A
What is the geographical location of Africa?
-Africa is located to the south of Europe, bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
How many countries does Africa have?
-Africa contains 54 countries, making it an extremely diverse continent in terms of ethnicity and language.
What historical event led to the borders of African countries being largely decided by European nations?
-The borders of African countries were largely decided during the late 19th and early 20th century in what is known as the Scramble for Africa.
What is the significance of the Sahara in Africa's history?
-The Sahara, being the largest desert in the world, has been a major obstacle for communication, trade, and exchange of ideas in Africa.
Who were the first Europeans to establish contact with the Kongo Kingdom?
-Explorer Diogo Cao was the first to establish contact with the Kongo Kingdom in the 1480s.
What was the purpose of the Portuguese trading with the Kongo Kingdom?
-The Portuguese traded guns, cloth, and other European luxuries for slaves who were captured by the Kongo in wars against rival kingdoms.
What was the first European settlement in the south of Africa?
-The first European settlement in the south of Africa was established by the Dutch East India Company, known as the Cape of Good Hope.
What led to the Great Trek by the Dutch citizens known as Boers?
-The abolition of slavery in 1834 and the subsequent financial catastrophe led the Boers to move further inland into Africa during the Great Trek.
What was the purpose of the American Colonisation Society's transportation of Freeborn blacks and freed slaves to Africa?
-The American Colonisation Society aimed to establish a colony in Africa, believing that blacks would be better off there, leading to the establishment of the independent republic of Liberia in 1847.
What was the main goal of the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885?
-The Berlin Conference aimed to discuss how European countries would claim colonies in Africa and avoid war between them.
How did the technological advantage of Europeans, particularly the machine gun, impact the colonization of Africa?
-The technological advantage, especially the machine gun, allowed small bands of Europeans to overpower much larger African forces, facilitating the colonization of the continent.
Which African country remained independent during the European colonization of Africa?
-Abyssinia, now known as Ethiopia, managed to remain independent by exploiting European rivalries and securing modern weapons.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Scramble for Africa | World History | Lecture - 7 | UPSC | GS History by Aadesh Singh
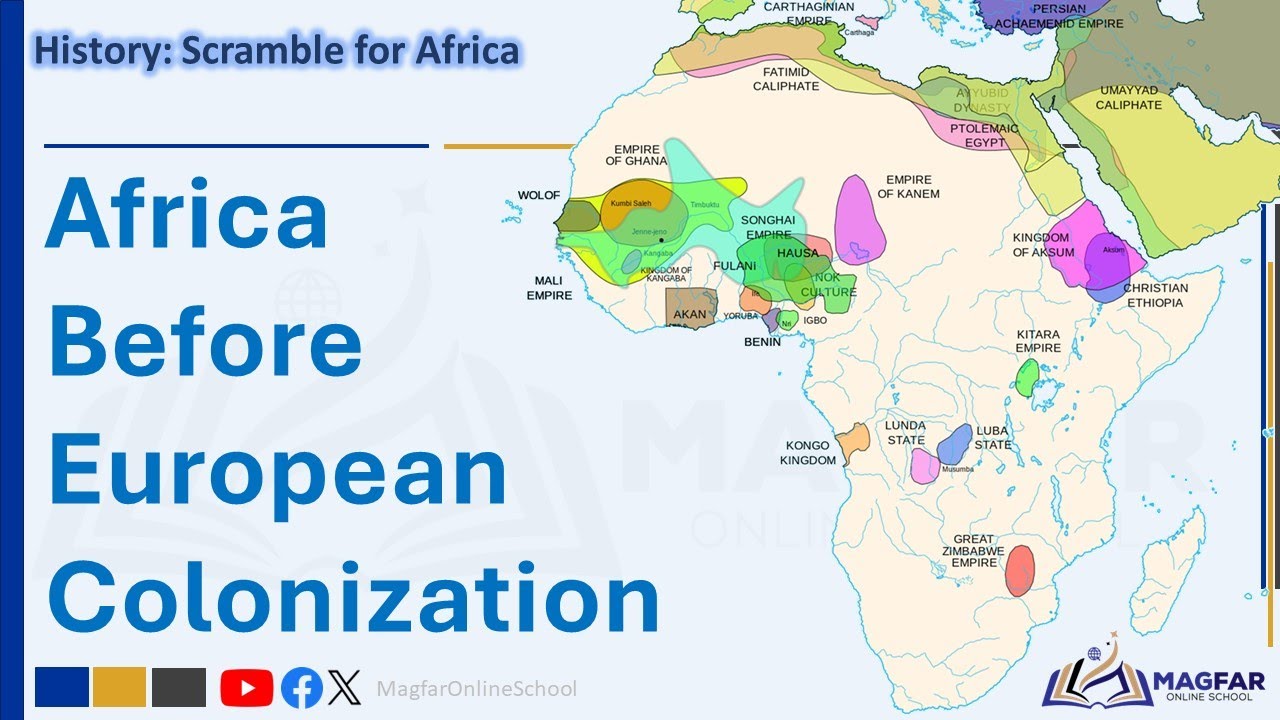
Scramble for Africa: Africa before European Colonization. Grade 8 Term 3 History.

SERAKAHNYA BANGSA EROPA Yang Menjajah Hampir Seluruh Benua Afrika!

Causes of Colonization in Africa | Industrial Revolution, Imperialism, and Racism.

Imperialismo na África

ASSIM era a ÁFRICA antes da chegada dos EUROPEUS | IMPÉRIOS AFRICANOS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
