Scramble for Africa | World History | Lecture - 7 | UPSC | GS History by Aadesh Singh
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the colonization of Africa by European powers during the New Imperialism era, spanning from 1881 to 1914. It explains the economic, political, and religious motives behind colonization, including the exploitation of Africa's abundant resources like ivory, rubber, and palm oil. The script also discusses the scramble for Africa, detailing how European nations carved up the continent without the consent of its people, leading to significant socio-political and economic impacts. It highlights the strategies employed by colonizers, such as exploiting existing rivalries among African leaders and tribes, and the use of superior weaponry and technology. The summary also touches on the profound effects of colonization on African societies, including the imposition of European political systems, the disruption of traditional practices, and the transformation of family structures and education.
Takeaways
- 😐 The colonization of Africa by European nations took place between 1881 and 1914, known as the 'Scramble for Africa'.
- 🏰 Initially, European interest in Africa was limited to the Slave Coast, with only a few regions such as Algeria and the Cape Colony under direct European control.
- 🌍 The colonization was driven by economic, political, and religious factors, including the need for resources and a response to economic depression in Europe.
- 📈 The Industrial Revolution increased the demand for African products like rubber, palm oil, and cotton, leading to intensified European interest in Africa.
- 💡 European explorers and missionaries played a significant role in sparking interest in Africa, with missionaries indirectly aiding imperial ambitions through their work.
- 🔫 European powers had a significant military advantage over African nations, with advanced weaponry and technology like the Maxim gun.
- 🤝 European nations exploited existing rivalries among African leaders and tribes to establish control over different territories.
- 💎 The discovery of valuable resources like gold, diamonds, and ivory in Africa further fueled the rush for colonization.
- 🗺️ The entire African continent was divided among European powers without the consent of the African people, creating artificial boundaries.
- 🏛️ Colonial policies disrupted traditional African practices and beliefs, leading to significant cultural and social changes.
- 📚 The establishment of the public education system in Africa was largely neglected by colonial governments, with missionaries taking the lead in educational efforts.
Q & A
What does the term 'Scramble for Africa' refer to?
-The 'Scramble for Africa' refers to the period of intense colonial rivalry among European powers for the conquest and division of African territories between 1881 and 1914.
Why were European nations interested in colonizing Africa during the late 19th century?
-European nations were interested in colonizing Africa due to economic depression in Europe, the need for new markets and resources, and the abundance of raw materials like ivory, rubber, palm oil, wood, and cotton that could be exploited for industrial production.
What role did the Industrial Revolution play in the colonization of Africa?
-The Industrial Revolution increased the demand for raw materials, which led European powers to seek out new sources in Africa, thus accelerating the colonization process.
How did European explorers and missionaries contribute to the colonization of Africa?
-European explorers and missionaries played a significant role by awakening European interest in Africa, providing valuable information about the continent, and indirectly aiding European governments in gaining control over African regions.
What was the impact of diseases like smallpox on the African population during the colonization period?
-Diseases like smallpox had a devastating impact on the African population, as indigenous Africans had no immunity or resistance to these diseases, making them particularly vulnerable and weakening their ability to resist European powers.
How did European powers use technological advantages to establish control over African territories?
-European powers used technological advantages such as powerful weapons, including the Maxim gun which could fire multiple rounds per second, to easily overpower and establish control over African territories.
What was the significance of the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 in the colonization of Africa?
-The Berlin Conference established the rules and conditions under which European powers could claim territories in Africa, effectively legitimizing the 'Scramble for Africa' and leading to the rapid colonization of the continent.
How did the division of Africa among European powers affect the local African populations?
-The division of Africa among European powers led to the disruption of traditional practices, forced migration, and the establishment of colonial rule that often disregarded the rights and well-being of local African populations.
What were some of the long-term effects of colonization on Africa's political landscape?
-Colonization led to the artificial division of Africa into territories that often ignored ethnic and cultural boundaries, established undemocratic political systems, and left a legacy of underdevelopment and political instability in many regions.
How did colonization impact the economic development of Africa?
-Colonization resulted in the exploitation of Africa's natural resources for the benefit of European powers, often at the expense of local economies, and contributed to the underdevelopment of Africa's economic infrastructure.
What role did religion play in the colonization of Africa?
-Religion played a significant role as Christian missionaries accompanied explorers, aiming to convert the African population to Christianity. This religious aspect was often intertwined with the imperial ambitions of European powers.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Imperialismo na África
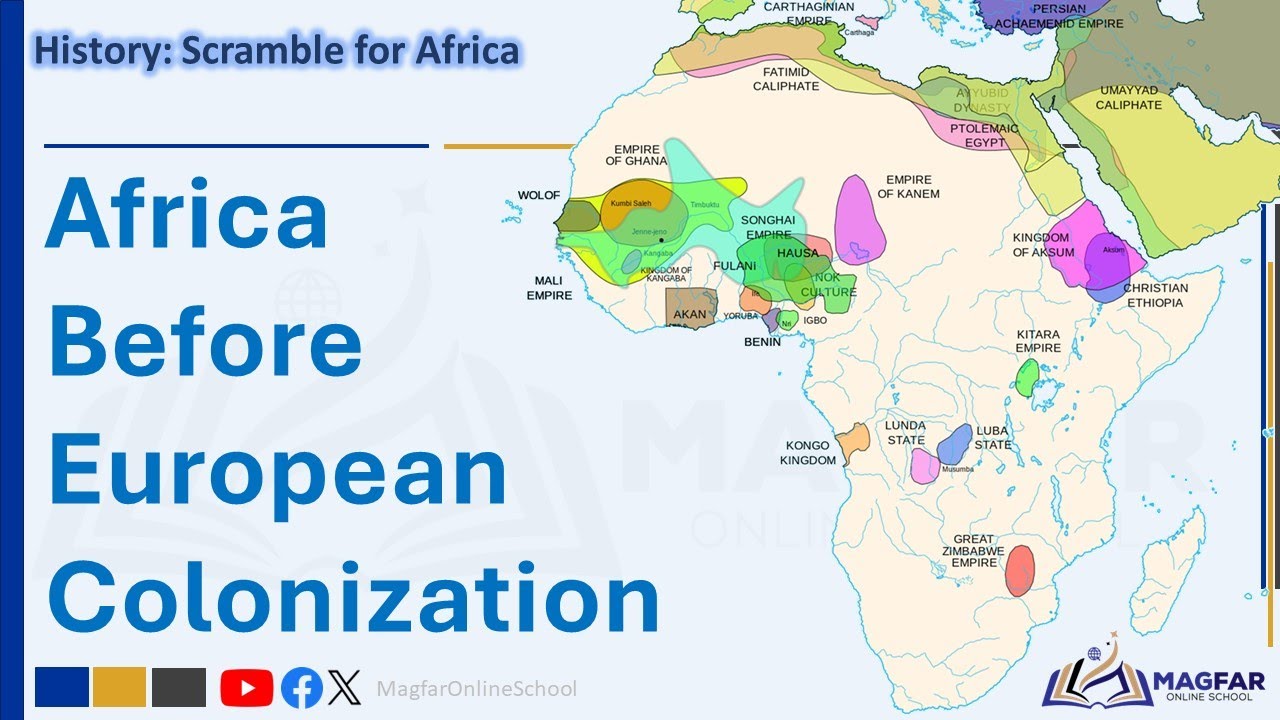
Scramble for Africa: Africa before European Colonization. Grade 8 Term 3 History.

How Europe Stole Africa (so quickly)

Causes of Colonization in Africa | Industrial Revolution, Imperialism, and Racism.

O IMPERIALISMO EUROPEU E O NEOCOLONIALISMO | Resumo de História Enem. Professor Dudu Volpato

State EXPANSION [AP World History] Unit 6 Topic 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)