3. Movement into and out of cells (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023,2024 and 2025)
Summary
TLDRThis IGCSE study video delves into the essential topic of cellular movement, exploring the three primary methods: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It explains how substances and water molecules move across the cell membrane, highlighting factors affecting these processes. The video also contrasts passive and active transport, emphasizing the role of energy in moving molecules against concentration gradients, crucial for understanding cellular function.
Takeaways
- 🚀 The video discusses three main methods of substance movement in and out of cells: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport.
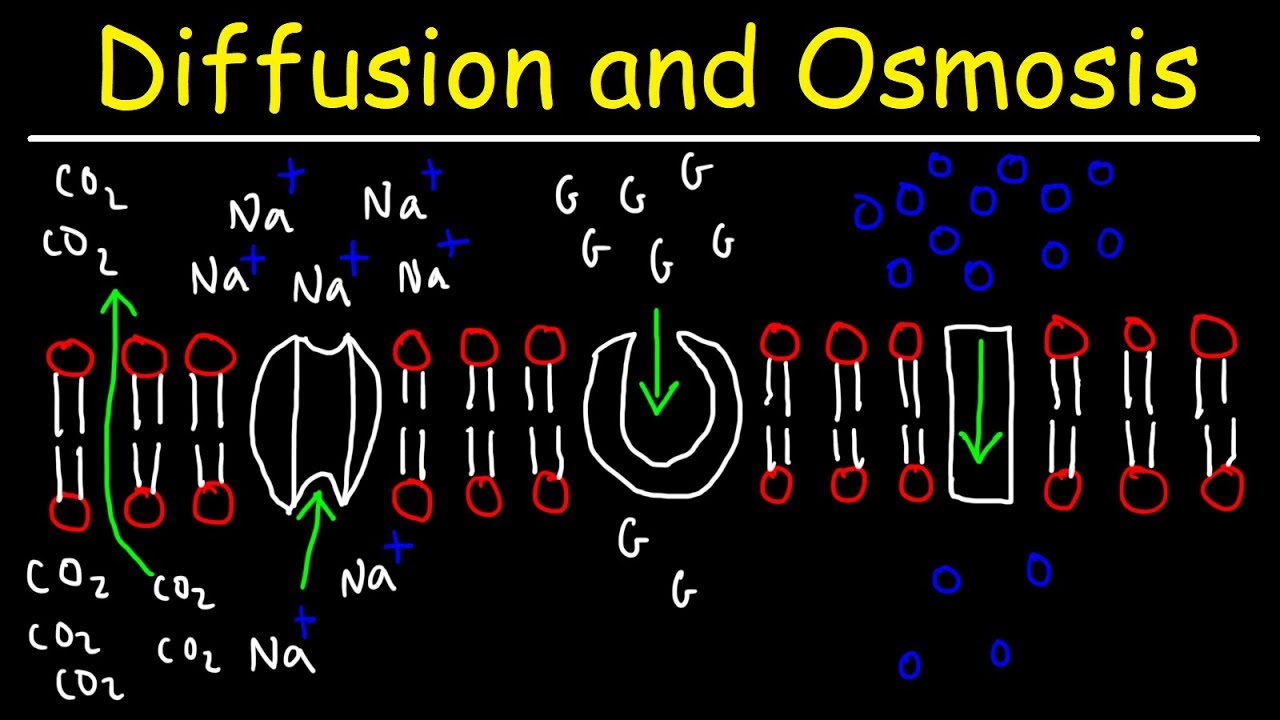
- 🔍 Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, driven by random movement and influenced by factors like surface area, temperature, concentration gradient, and distance.
- 🌡️ Temperature affects the rate of diffusion, with higher temperatures increasing the kinetic energy of molecules, thus speeding up the process.
- 🌊 Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential, essential for the transport of dissolved substances in organisms.
- 💧 Water potential is a key concept in osmosis, distinguishing between dilute and concentrated solutions based on the amount of water available.
- 🌿 Plant cells differ from animal cells in their response to osmotic changes due to the support provided by the cell wall, preventing them from bursting when water enters.
- 💥 Active transport moves particles against the concentration gradient, requiring energy from respiration, and is essential for cells to absorb nutrients against concentration differences.
- 🔄 Protein carriers in the cell membrane facilitate active transport by capturing and transporting molecules from one side of the cell to the other, using energy to change shape.
- 🌱 Plants obtain water and nutrients through osmosis, which is crucial for maintaining turgor pressure and supporting the plant structure.
- 🌳 Water loss in plants can lead to wilting if the rate of water loss exceeds the rate of water gain, highlighting the importance of osmotic balance.
- 🔬 The video provides a comprehensive overview of cellular movement processes, emphasizing the importance of understanding these mechanisms for IGCSE biology students.
Q & A
What are the three main ways substances move into and out of cells?
-The three main ways substances move into and out of cells are diffusion, osmosis, and active transport.
How does the cell membrane control the movement of substances?
-The cell membrane controls the movement of substances by selectively allowing necessary molecules like glucose and proteins to enter the cell and waste products like carbon dioxide and lactic acid to exit.
What is diffusion and how does it occur in cells?
-Diffusion is the process where molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through the cell membrane until equilibrium is reached. It occurs due to the random movement of particles.
What factors influence the rate of diffusion?
-Factors that influence the rate of diffusion include surface area, temperature, concentration gradient, and distance. Larger surface area, higher temperature, greater concentration gradient, and shorter distance all increase the rate of diffusion.
What is the role of water as a solvent in organisms?
-Water acts as a medium for the transport of dissolved substances around the body, aids in digestion by moving nutrients to cells, and is necessary for excretion by dissolving waste substances for easy removal from the body.
Define osmosis and explain its significance in biological systems.
-Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (more dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (more concentrated solution) through a partially permeable membrane. It is significant for the uptake and loss of water by organisms, maintaining cell turgor, and transporting nutrients and minerals.
What is meant by 'water potential' and why is it important in osmosis?
-Water potential refers to the potential energy of water in a solution, with higher water potential in more dilute solutions and lower in more concentrated solutions. It is important in osmosis because water moves from areas of high water potential to areas of low water potential.
How does a plant cell respond to being placed in a concentrated solution?
-When a plant cell is placed in a concentrated solution, water moves out of the cell due to a higher water potential inside the cell compared to the outside. This can cause the cell to become flaccid or shrink, and in extreme cases, the cell may plasmolyze, where the cytoplasm detaches from the cell wall.
What is active transport and why is it necessary?
-Active transport is the movement of particles against a concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, using energy from respiration. It is necessary when cells need to absorb nutrients against the concentration gradient, such as in the case of certain plant roots and villi epithelial cells.
How do protein carriers in the cell membrane facilitate active transport?
-Protein carriers in the cell membrane capture molecules from one side of the cell, change shape to transport the molecules to the other side, and require energy from respiration to do so, thus facilitating active transport against the concentration gradient.
What is the main difference between the processes of diffusion and active transport?
-The main difference between diffusion and active transport is the direction of particle movement in relation to the concentration gradient. In diffusion, particles move down the concentration gradient, while in active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient, requiring energy.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Transport in Cells: Diffusion and Osmosis | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool

Mekanisme Transpor Pada Membran Sel || BIOLOGI SMA
Diffusion and Osmosis - Passive and Active Transport With Facilitated Diffusion

General Biology I - Transport Mechanisms - Part I

Transpor membran lengkap- difusi sederhana, osmosis, difusi terfasilitasi, pompa NA+/K+, biologi sel

Cell Membrane Transport - Transport Across A Membrane - How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
