GCSE Biology - Active Transport #9
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores active transport, contrasting it with diffusion. It explains that active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy from the cell, unlike passive diffusion. The script uses root hair cells in plants as an example, detailing how these cells absorb mineral ions against their concentration gradient using energy from cellular respiration. Highlighting the role of ATP, the script emphasizes the adaptations of root hair cells, such as a large surface area and abundant mitochondria, which facilitate this essential process for plant survival.
Takeaways
- 🚰 Active transport is the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy from the cell.
- 🌊 Diffusion is a passive process where substances move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration without energy input.
- 🔁 Active transport requires special proteins in the cell membrane to facilitate the transfer of molecules from one side to the other.
- 🌱 The energy for active transport comes from cellular respiration, which is mainly carried out in the mitochondria.
- 💡 ATP molecules act as energy carriers, transferring energy from mitochondria to parts of the cell that require it.
- 🌳 Plants use active transport in root hair cells to absorb water and mineral ions from the soil.
- 🌿 Root hair cells have a large surface area due to their hair-like protrusions, which aids in absorption.
- 🌟 Mineral ions needed by plants, such as magnesium and nitrates, are at a higher concentration inside the cell than in the soil.
- 🔋 Root hair cells contain many mitochondria to provide the necessary energy for active transport.
- 🌱 Plants cannot absorb needed minerals by diffusion alone due to the concentration gradient.
- 📚 The script mentions a learning platform offering free resources for science and math, with the option to track progress.
Q & A
What is the main difference between active transport and diffusion?
-Active transport involves the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, and requires energy from the cell. Diffusion, on the other hand, is a passive process where substances move down their concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without requiring any energy.
Why is energy required for active transport?
-Energy is required for active transport because it involves moving molecules against their natural concentration gradient, which is an uphill process that cannot occur spontaneously. This energy is provided by the cell, specifically from cellular respiration.
What role do special proteins play in active transport?
-Special proteins embedded in the cell membrane are required for active transport. They facilitate the transfer of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other, against the concentration gradient.
Where does the energy for active transport come from in cells?
-The energy for active transport comes from cellular respiration, a process that occurs mainly in the mitochondria where glucose is broken down to release energy.
What is ATP and how does it relate to active transport?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that stores energy in the cell. It acts like a 'little battery,' transferring energy from the mitochondria to different parts of the cell that require it, including the process of active transport.
Why are root hair cells important for plants?
-Root hair cells are important for plants because they are responsible for absorbing water and mineral ions from the soil. They have a large surface area for absorption due to their hair-like protrusions, which helps in efficiently taking in necessary substances.
How do root hair cells adapt to absorb mineral ions?
-Root hair cells adapt to absorb mineral ions through active transport by having a large surface area for absorption and a high number of mitochondria to provide the necessary energy for this process.
What concentration gradient issue do plants face when trying to absorb certain minerals from the soil?
-Plants face the issue of certain minerals, like magnesium and nitrates, being at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside in the soil. This prevents the use of passive diffusion and requires active transport to absorb these minerals.
What is the role of mitochondria in root hair cells during active transport?
-Mitochondria in root hair cells play a crucial role in providing the energy needed for active transport. They perform cellular respiration, breaking down glucose to release energy, which is then stored in ATP molecules for use in active transport.
How does the learning platform mentioned in the script support the understanding of active transport and other scientific concepts?
-The learning platform offers a space where users can watch all related videos, practice what they've learned with questions, and track their progress in both sciences and maths. It is a free resource that enhances understanding through interactive learning.
What is the main purpose of the video script provided?
-The main purpose of the video script is to explain the concept of active transport, compare it with diffusion, and illustrate how active transport works in the root hair cells of plants, particularly focusing on the absorption of water and mineral ions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

AP Biology Unit 2 Review: Cell Structure and Function
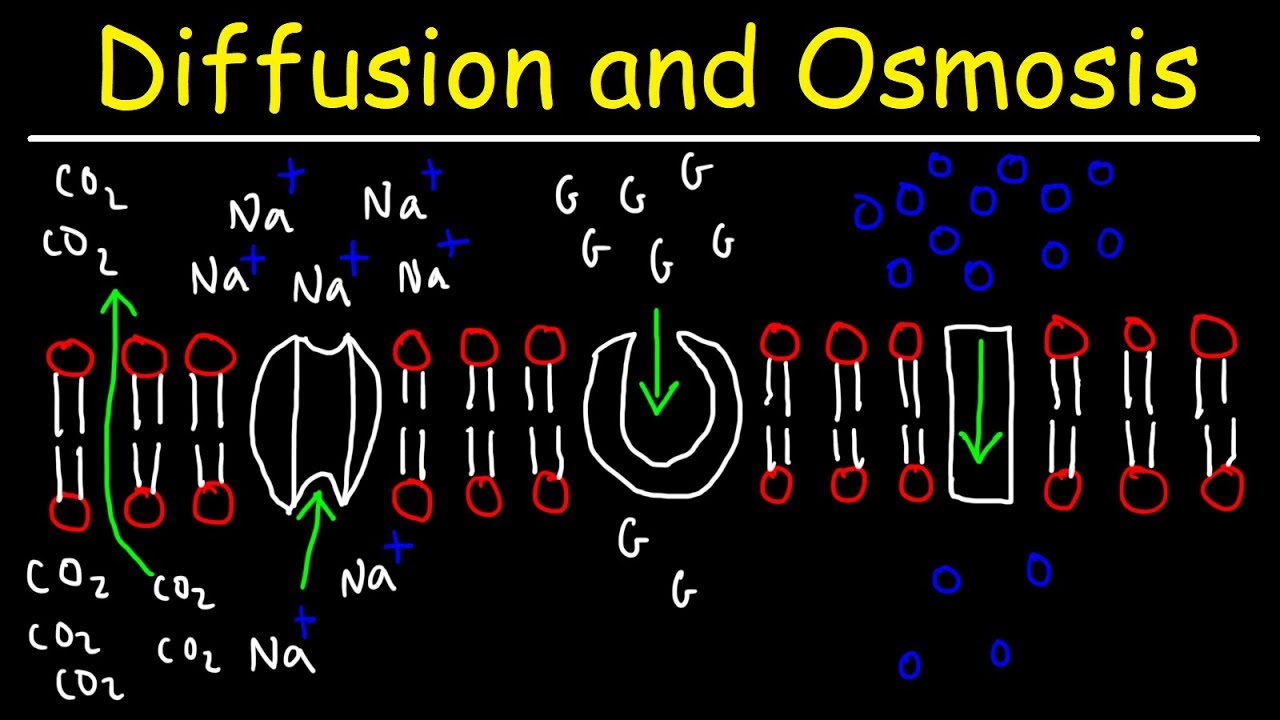
Diffusion and Osmosis - Passive and Active Transport With Facilitated Diffusion

Transpor membran lengkap- difusi sederhana, osmosis, difusi terfasilitasi, pompa NA+/K+, biologi sel

Active vs. Passive Transport: Compare and Contrast
BIOLOGI KELAS 11 MATERI SEL : Tipe Sel, Organel Sel dan Transportasi Zat Antar Membran

Mekanisme Transpor Pada Membran Sel || BIOLOGI SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
