Basics of IMMUNOLOGY I Lecture 1 I Immune system I Immunity I CSIRNET I UPSC I NEET I GATE I IITJAM
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricate world of immunology, exploring the body's defense mechanisms against pathogens. It distinguishes between innate and adaptive immunity, highlighting non-specific resistance present from birth and specific responses acquired post-birth. The script discusses physical barriers, chemical components like lysozyme and lactoferrin, and the role of the complement system and cellular defense. It further explains the structure of antibodies, their function in identifying and neutralizing antigens, and the impact of enzymes like pepsin, papain, and beta-mercaptoethanol on antibody structure. The detailed explanation aims to provide viewers with a comprehensive understanding of the immune system's complex processes.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Immunology is the study of our body's response to pathogens, focusing on the body's defense mechanisms against foreign invaders.
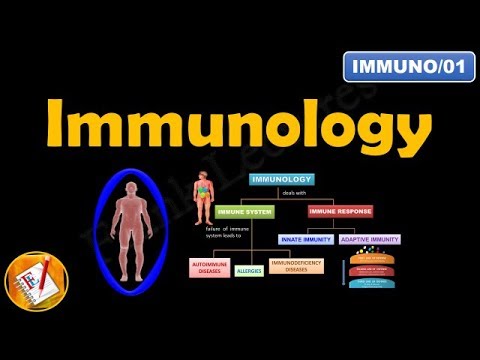
- 🛡️ Immunity can be categorized into two main types: innate immunity, which we are born with, and adaptive immunity, which we develop after birth.
- 🌱 Innate immunity is non-specific and provides a general defense against all types of pathogens, while adaptive immunity is specific and tailors the immune response to particular pathogens.
- 🔬 Physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, serve as the first line of defense by preventing pathogens from entering the body.
- 🌿 Chemical barriers, including acidic substances and enzymes, inhibit the growth of pathogens and contribute to the body's defense mechanisms.
- 🤒 The complement system, a series of over 30 proteins, plays a crucial role in identifying and eliminating pathogens by marking them for destruction.
- 💪 Cellular defense involves various cells like macrophages, monocytes, and neutrophils that actively engage in the destruction of pathogens.
- 🧬 Adaptive immunity involves the production of antibodies by B cells, which are proteins that specifically recognize and bind to antigens, facilitating their neutralization.
- 🔄 The structure of antibodies consists of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains, with specific regions for antigen binding and constant regions for effector functions.
- 🔗 Antibodies are held together by disulfide bonds, which are covalent linkages between cysteine amino acids, providing stability to the protein structure.
- 🧰 Enzymes such as pepsin, papain, and beta-mercaptoethanol can disrupt the structure of antibodies, demonstrating their flexibility and the complexity of immune responses.
Q & A
What does the term 'Immunology' refer to?
-Immunology is the study of our body's response to pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign invaders. It involves the examination of the body's defense mechanisms, including the immune system's response to antigens.
What is meant by 'Immunity'?
-Immunity refers to the body's power to resist pathogens that attempt to enter and cause disease. It is a defense mechanism that helps protect the body from infection.
What are the two main types of immunity?
-The two main types of immunity are innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity is present from birth and provides a general defense against a wide range of pathogens. Adaptive immunity develops after birth and is tailored to specific pathogens encountered throughout an individual's life.
What is the role of the physical barriers in the immune system?
-Physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, serve as the first line of defense by preventing pathogens from entering the body. They act as a physical blockade to pathogens, keeping them from reaching internal tissues.
Can you explain the function of 'Lysozyme' in the immune system?
-Lysozyme is an enzyme that breaks down the cell walls of bacteria, thereby killing them or preventing their growth. It is part of the innate immune system and can be found in various secretions, including saliva, tears, and mucus.
What is the significance of the 'Complement System' in immunity?
-The Complement System is a group of proteins that enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes from the body, promote inflammation, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane.
What is 'Cellular Defense' and how does it contribute to the immune response?
-Cellular Defense involves immune cells like macrophages, monocytes, and neutrophils that directly attack and destroy pathogens. These cells are part of the innate immune system and play a crucial role in the body's second line of defense.
What are 'Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)' and their role in the immune system?
-Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) are proteins found on immune cells that recognize and bind to conserved molecular patterns found on the surface of pathogens. This binding activates the immune response, leading to the destruction of the invading microorganisms.
How do 'Cytokines' contribute to the inflammatory response?
-Cytokines are small proteins secreted by various immune cells that have the ability to modulate the immune response. During inflammation, cytokines are released to recruit other immune cells to the site of infection or injury, enhancing the immune response.
What is the difference between 'Natural' and 'Artificial' adaptive immunity?
-Natural adaptive immunity is the immune response that naturally occurs in the body in response to a specific pathogen. Artificial adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is acquired through methods such as vaccination, where the immune system is artificially exposed to a pathogen or its components to develop immunity without causing the disease.
Can you describe the structure and function of an 'Antibody'?
-An antibody is a Y-shaped protein produced by B cells that is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody's structure includes two heavy chains and two light chains, with the variable regions determining the specificity for a particular antigen.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Human Immune System - How it works! (Animation)

Immune System, Part 2: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #46

GCSE Biology - Immune System (Defences Against Pathogens) #38

SISTEMA IMUNOLÓGICO - Imunidade Inata e Adaptativa | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
IMMUNOLOGY- Innate Immunity and Adaptive Immunity (FL-Immuno/01)

Respuesta inflamatoria | Khan Academy en Español
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
