EQUATION OF CIRCLE IN STANDARD FORM | PROF D
Summary
TLDRThis educational video tutorial teaches viewers how to derive the standard form equation of a circle. It begins by explaining the concept of a circle and its basic elements, such as the center and radius. The presenter then illustrates the process using the distance formula, providing step-by-step examples with different centers and radii. The video concludes with a practical example involving a circle with a diameter defined by two points, showcasing the calculation of the center and radius before deriving the equation. The host, Prof D, encourages viewers to ask questions in the comments for further clarification.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is an educational tutorial on finding the equation of a circle in standard form.
- 🌐 A circle is defined as the path of a point that moves at a constant distance from a fixed point, known as the center.
- 📏 The constant distance from any point on the circle to the center is called the radius.
- 📘 The standard form equation of a circle is derived from the distance formula and is given as \((x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2\).
- 📍 The variables \(h\) and \(k\) represent the coordinates of the circle's center, and \(r\) is the radius.
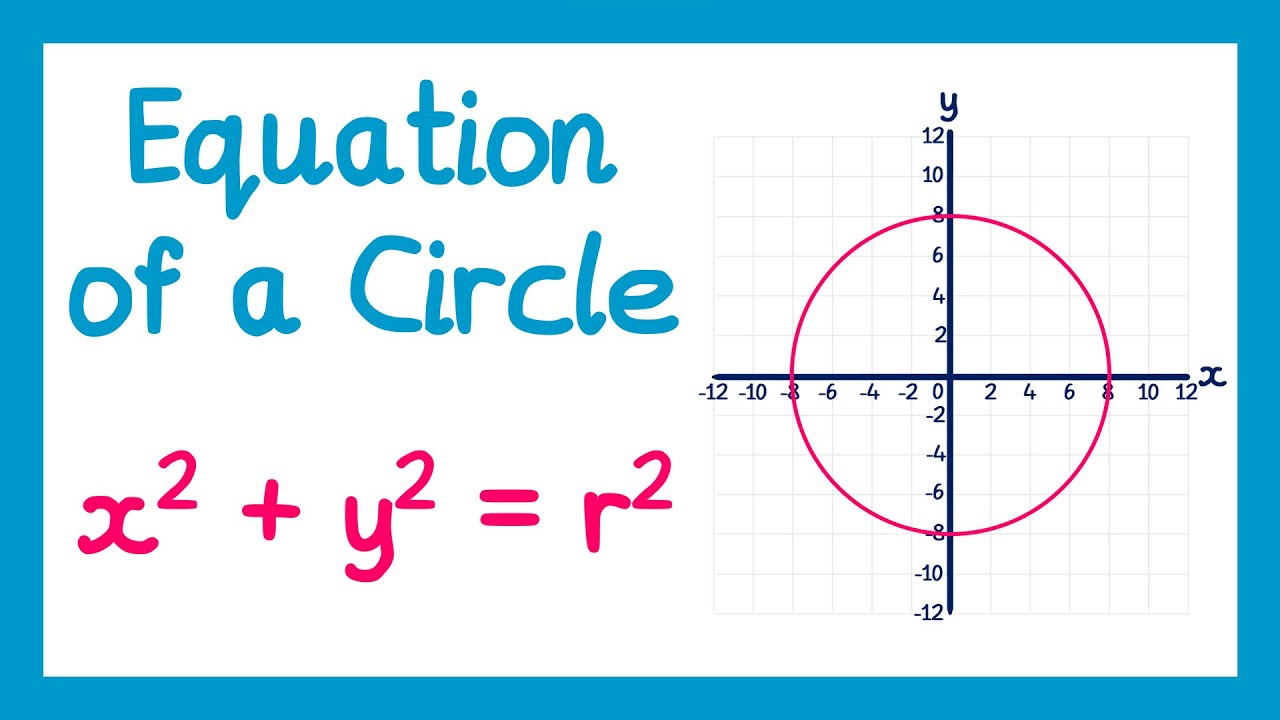
- 🔍 Example 1 demonstrates finding the equation of a circle with a center at (0,0) and a radius of 5, resulting in the equation \(x^2 + y^2 = 25\).
- 📐 Example 2 shows the process for a circle with a center at (-4,5) and a radius of 4, leading to the equation \((x + 4)^2 + (y - 5)^2 = 16\).
- 📈 Example 3 involves calculating the equation of a circle given the endpoints of its diameter, resulting in the equation \((x - 1)^2 + (y - 4)^2 = 10\).
- 🧭 The midpoint formula is used to find the center of the circle when the diameter's endpoints are known.
- 📝 The video emphasizes the importance of correctly identifying the center and radius to derive the circle's equation.
- 👋 The presenter, Prof D, encourages viewers to ask questions or seek clarifications in the comments section.
Q & A
What is the definition of a circle according to the video?
-A circle is the path or locus of a point that moves at a constant distance from a fixed point, called the center.
What is the constant distance from any point on the circle to the center called?
-The constant distance of any point from the center is called the radius.
What is the standard form of the equation of a circle?
-The standard form of the equation of a circle is (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius.
In the video, what is the first example of finding the equation of a circle?
-The first example is finding the equation of a circle with a center at (0, 0) and a radius of 5.
What is the equation of the circle in the first example after substituting the values for h, k, and r?
-The equation is x² + y² = 25 after substituting h = 0, k = 0, and r = 5.
What is the second example's circle center and radius according to the video?
-The second example has a circle with a center at (-4, 5) and a radius of 4.
How is the equation of the circle in the second example simplified?
-The equation simplifies to (x + 4)² + (y - 5)² = 16 after substituting h = -4, k = 5, and r = 4.
In the third example, how are the end points of the diameter given?
-The end points of the diameter in the third example are given as (4, 5) and (-2, 3).
What is the method used in the third example to find the center of the circle?
-The midpoint formula is used to find the center of the circle in the third example.
What is the final equation of the circle in the third example after simplification?
-The final equation is (x - 1)² + (y - 4)² = 10 after applying the midpoint formula and the distance formula to find h, k, and r.
What does the video suggest for viewers who have questions or need clarifications?
-The video suggests that viewers should put their questions or clarifications in the comment section below.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

(Part 1) Definisi Lingkaran BAB LINGKARAN DAN GARIS SINGGUNG || Matematika Tingkat Lanjut Kelas XII

Lingkaran Bagian 5 - Persamaan Garis Singgung Melalui Titik Pada Lingkaran

Lingkaran Bagian 6 - Menentukan Persamaan Garis Singgung Lingkaran Jika Diketahui Gradiennya

Conic Sections: The Circle

Standard Equation of Circle | Conic Sections | Don't Memorise
Equation of a Circle - GCSE Higher Maths
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
