Finding Angles - Trigonometry in Right-angled Triangles - Tutorial / Revision (4/5)
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial introduces the use of inverse trigonometric functions to find missing angles in right-angled triangles. It guides viewers through labeling sides, identifying active sides, and applying formulas like tan and cos with their inverses to solve for angles. The instructor demonstrates using a calculator to find angles, rounding the results to 41.0 and 72.2 degrees, respectively. The video concludes with an invitation for questions and a comparison of Pythagoras and trigonometry for future lessons.
Takeaways
- 📚 This tutorial is part of a series on trigonometry, focusing on using inverse trigonometric functions to find missing angles in right-angled triangles.
- 🔍 The presenter suggests reviewing previous tutorials if one is not familiar with trigonometric formulas, indicating the importance of foundational knowledge.
- 🧭 The tutorial introduces inverse trigonometric functions: sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹, tan⁻¹, and how they are accessed on calculators, which is crucial for solving the problems.
- 📐 The first step in solving the problem is labeling the sides of the triangle, which helps in identifying the 'active' sides needed for the calculations.
- 🔢 The tutorial demonstrates using the tangent function (tan) to find an angle when given the lengths of the opposite and adjacent sides.
- ✅ The use of the inverse tangent function (tan⁻¹) is shown to isolate and find the value of the angle, with an example calculation provided.
- 📉 The process of substituting values into the trigonometric formula and solving for the angle is explained step by step, emphasizing precision.
- 📈 Another example is given using the cosine function (cos) to find an angle when given the lengths of the adjacent side and the hypotenuse.
- 🔄 The inverse cosine function (cos⁻¹) is used similarly to tan⁻¹ to find the angle, with an example calculation shown.
- 📝 The importance of writing out the formulas in full is highlighted to ensure correct substitution and avoid errors.
- 🤔 The tutorial ends with an invitation for questions and a reminder of the availability of further resources for understanding trigonometry and its applications.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this tutorial?
-The main topic of this tutorial is using trigonometry to find missing angles in right-angled triangles.
What is the series number of this tutorial in the trigonometry series?
-This is tutorial number 4 in the trigonometry series.
What are the inverse trigonometric functions mentioned in the script?
-The inverse trigonometric functions mentioned are sin^(-1), cos^(-1), and tan^(-1).
How can you access the inverse trigonometric functions on a calculator?
-On a calculator, these functions are usually accessed by pressing shift or sometimes 2nd F and then the sin, cos, or tan buttons.
What are the active sides in a triangle when using trigonometric ratios?
-The active sides are the two sides given in the problem statement, which are used in the trigonometric formula to find the missing angle.
What trigonometric ratio uses the opposite and adjacent sides of a right-angled triangle?
-The tangent ratio (tan) uses the opposite and adjacent sides of a right-angled triangle.
How do you find the angle X using the tangent ratio?
-To find the angle X, you use the inverse tangent function, tan^(-1), on the calculator with the opposite side divided by the adjacent side.
What is the result of the first example calculation in the script?
-The result of the first example calculation is 41.0 degrees for the angle X.
What trigonometric ratio uses the adjacent side and the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle?
-The cosine ratio (cos) uses the adjacent side and the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle.
How do you find the angle Y using the cosine ratio?
-To find the angle Y, you use the inverse cosine function, cos^(-1), on the calculator with the adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse.
What is the result of the second example calculation in the script?
-The result of the second example calculation is 72.2 degrees for the angle Y.
What is the purpose of the tutorial mentioned at the end of the script?
-The purpose of the mentioned tutorial is to compare Pythagoras' theorem with trigonometry and to determine when to use each.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

TRIGONOMETRI - Ukuran Sudut dan Perbandingan Trigonometri

Contoh Soal Perbandingan Trigonometri pada segitiga siku siku
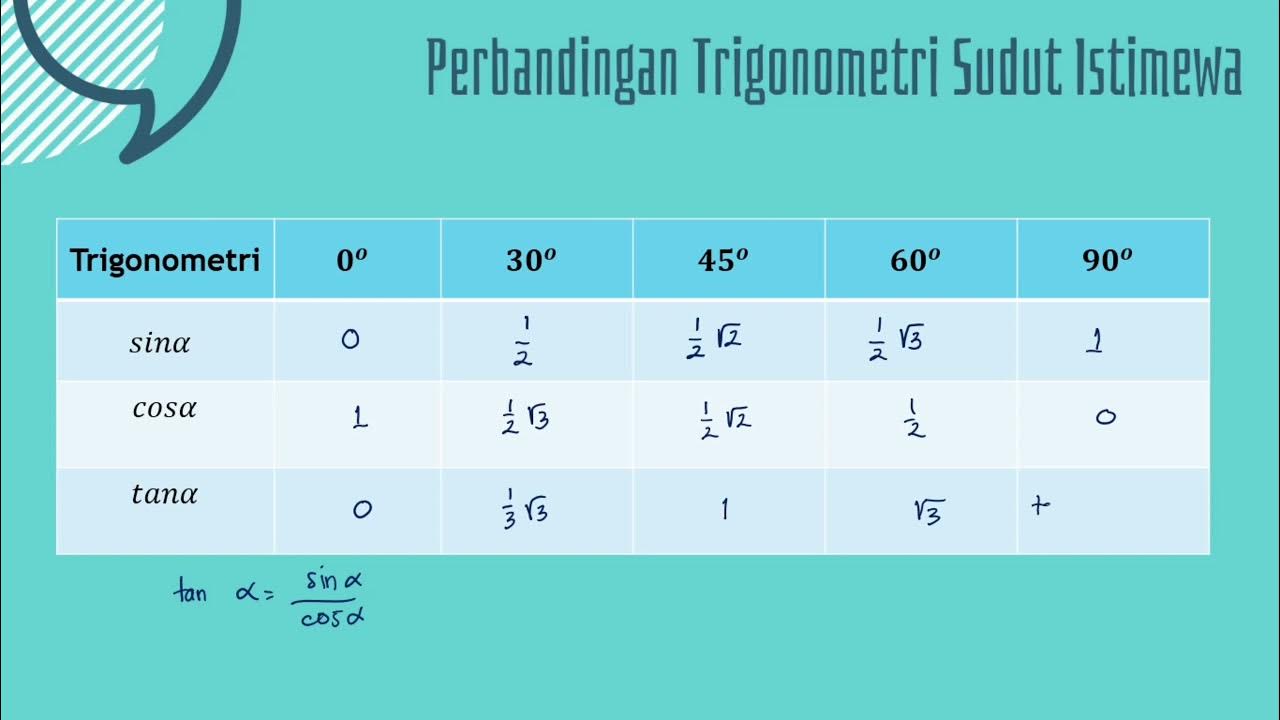
Perbandingan Trigonometri Sudut Istimewa
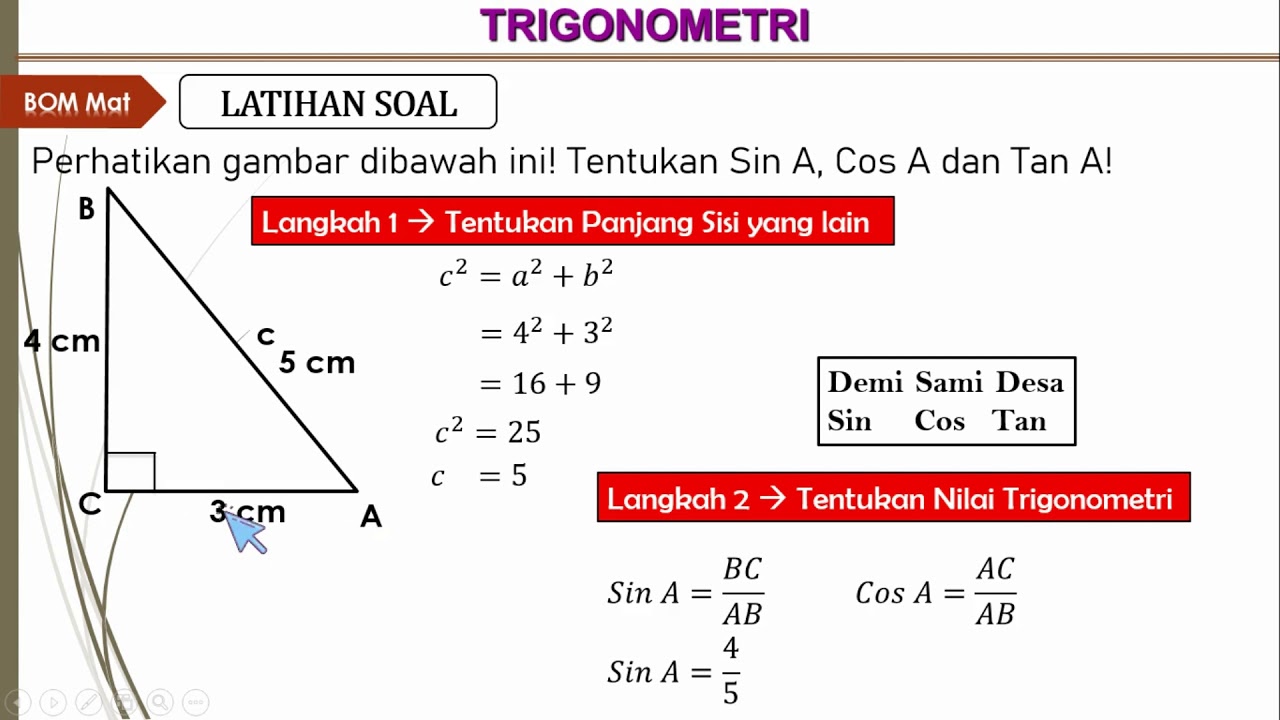
Perbandingan trigonometri pada segitiga siku siku, Menjelaskan rasio trigonometri

Trigonometry made easy
¿Qué son las razones trigonométricas? @MatematicasprofeAlex
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
