Node Voltage Analysis (Circuits for Beginners #15)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of Node Voltage Analysis in electrical circuits. It emphasizes the importance of voltage differences, the need for a reference point (like ground), and how current is different from voltage. By defining a common ground, voltages at different nodes can be calculated easily without confusion. The tutorial also demonstrates solving a circuit using node voltage analysis, applying Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Current Law to find unknowns. It highlights how node voltage analysis simplifies circuit analysis compared to Kirchhoff's Voltage Law while still yielding the same results.
Takeaways
- 😀 Voltage is always a difference between two points; you need a reference point to define it.
- 😀 Unlike voltage, current only requires one wire for measurement because it represents flow through a wire.
- 😀 In Node Voltage Analysis (NVA), you can define a reference point (e.g., ground) to simplify voltage measurements.
- 😀 A voltage source defines the difference in voltage between two points, but it’s meaningless unless referenced.
- 😀 Node Voltage Analysis helps avoid writing voltage differences all over the circuit by defining a common ground point.
- 😀 By defining a zero or reference voltage point (ground), you can easily label other nodes with their respective voltages.
- 😀 If you change the reference (e.g., to 10 volts), all voltage values in the circuit adjust accordingly, but the relative differences remain the same.
- 😀 Node Voltage Analysis simplifies circuit analysis by reducing the need for Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law and focuses on node voltages.
- 😀 In Node Voltage Analysis, you use Ohm's Law and current relationships to write equations for voltage and current at nodes.
- 😀 While NVA primarily uses Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) is also necessary to solve for all unknowns in the circuit.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is Node Voltage Analysis, a method for analyzing electrical circuits by determining the voltages at different nodes relative to a common reference point.
Why can't you just define voltage as a single number in a circuit?
-Voltage is always a difference between two points. Without defining a reference point, it’s impossible to give a meaningful value to the voltage at any given point in the circuit.
How does current differ from voltage in circuit analysis?
-Current can be measured with respect to a single wire, as it is a flow of charge through the wire. In contrast, voltage always requires two points for its measurement, as it represents a difference between those points.
What is the significance of defining a ground in node voltage analysis?
-By defining a ground (common reference point) in node voltage analysis, you can simplify voltage measurements in the circuit, allowing for the labeling of node voltages relative to that ground, thus avoiding ambiguity.
What happens when you add more voltage sources in series in a circuit?
-When voltage sources are added in series, their voltages sum up, but the voltage at each node in the circuit depends on the reference point (ground) chosen.
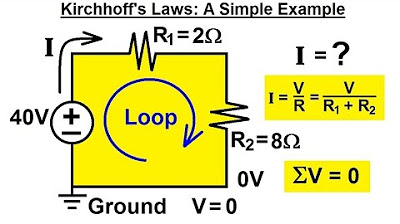
Why is it incorrect to simply write 25 volts at a point in a circuit?
-Writing 25 volts at a point without specifying a reference is incorrect because voltage is a relative measure and must always be defined with respect to a reference point (usually ground).
How does node voltage analysis relate to Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)?
-Node voltage analysis can be seen as a different approach to solving circuits that is mathematically connected to Kirchhoff's Voltage Law. Both methods ultimately provide the same results, but node voltage analysis focuses on defining voltages at each node relative to a ground point.
What role does Ohm’s Law play in node voltage analysis?
-Ohm’s Law is used in node voltage analysis to relate voltages to currents through resistors. By applying Ohm's Law at each node, you can set up equations that allow you to solve for the unknown voltages and currents in the circuit.
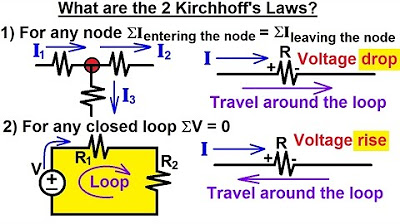
Why is it necessary to use Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) in addition to Ohm’s Law in node voltage analysis?
-Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) is necessary in node voltage analysis to account for the currents flowing into and out of a node. It provides the third equation needed to solve for the unknowns when there are multiple nodes and currents.
How can you define the voltage at a node in node voltage analysis?
-In node voltage analysis, the voltage at a node is defined relative to the ground node. Once the ground is set, the voltages at other nodes can be determined based on their voltage differences relative to the ground.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)