Biomechanical properties of skeletal muscle | Biomechanics of skeletal muscle
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the biomechanics of human skeletal and non-striated muscles, explaining their structure, functions, and key properties like extensibility, elasticity, and contractility. It focuses on how muscles develop tension to generate force, maintain posture, and facilitate movement. The script covers essential concepts such as the structural organization of muscles, the relationship between muscle fibers and proteins, and the impact of external and internal stimuli on muscle responses. The video aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of muscle behavior and the factors affecting their performance, including recovery and injury prevention.
Takeaways
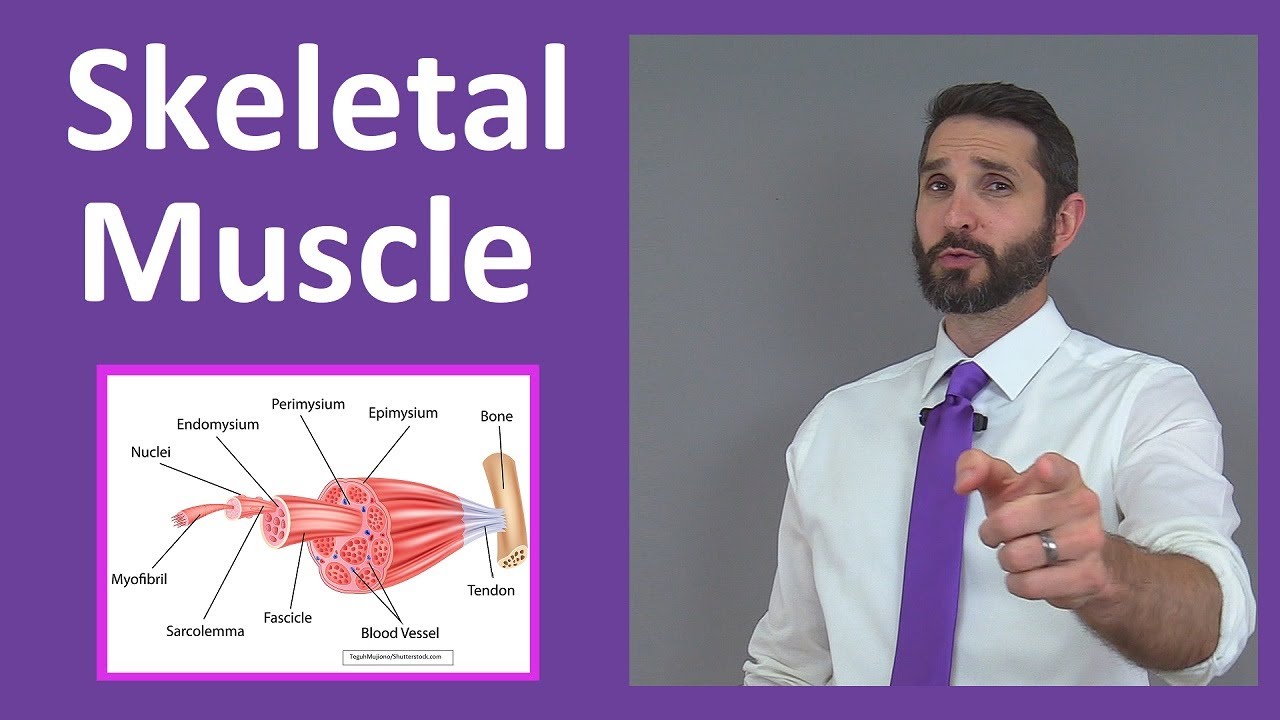
- 😀 Human skeletal muscles are also called striated muscles due to the arrangement of muscle fibers that contain protein filaments.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles generate force and develop tension to perform body functions and maintain posture.
- 😀 Muscle fibers are composed of myofibrils, which consist of protein filaments that enable muscle contraction.
- 😀 Skeletal muscles are essential for body movement, such as the movement of lips, limbs, and other bodily functions.
- 😀 The primary function of muscles is to maintain posture, generate movement, and absorb forces acting on the body.
- 😀 The behavior properties of muscles include extensibility, elasticity, and the ability to develop tension, which are important for muscle function.
- 😀 Extensibility refers to the ability of muscles to stretch or lengthen when subjected to force or stimulus.
- 😀 Elasticity is the muscle's ability to return to its normal length after being stretched or deformed.
- 😀 The muscle's ability to generate force (tension) is crucial for contraction, which leads to movement.
- 😀 Tendons, which are series elastic components, store energy during muscle contraction and release it during rapid, jerky movements.
- 😀 Muscle response to stimuli involves neuro-muscular coordination, where the nervous system triggers muscle contraction by generating action potentials.
Q & A
What are the two types of muscles discussed in the script?
-The two types of muscles discussed are skeletal muscles (striated muscles) and non-striated muscles.
Why are skeletal muscles referred to as 'striated' muscles?
-Skeletal muscles are called 'striated' because their fibers contain protein filaments arranged in a striped or striated pattern.
What is the primary function of skeletal muscles in the body?
-Skeletal muscles are primarily responsible for generating force, maintaining posture, enabling body movement, and absorbing forces during physical activity.
What are muscle fibers made of?
-Muscle fibers are composed of myofibers, which contain protein filaments that contribute to the muscle's contraction ability.
What does 'extensibility' refer to in the context of muscles?
-'Extensibility' refers to the ability of muscles to stretch or elongate when a force is applied, increasing their length temporarily.
How is 'elasticity' different from 'extensibility' in muscles?
-Elasticity is the ability of a muscle to return to its original length after being stretched, whereas extensibility is the ability to stretch and increase in length.
What role does elasticity play in muscle behavior?
-Elasticity allows muscles to resume their normal length after being stretched, which is essential for maintaining the muscle's function during repeated movements and contraction cycles.
What is the significance of the ability of muscles to develop tension?
-The ability of muscles to develop tension, also known as contractility, is crucial for generating force that enables muscle contraction, movement, and the execution of various physical tasks.
What factors affect the ability of muscles to generate force?
-The ability of muscles to generate force is affected by internal stimuli (like signals from the nervous system) and external stimuli (such as physical force applied to the muscle).
How do tendons contribute to the muscle's function?
-Tendons play a role in connecting muscles to bones and are involved in storing energy during muscle contraction. They also contribute to the muscle's overall mechanical behavior by participating in elastic components.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)